Android自定義View-Layout原理篇
阿新 • • 發佈:2018-12-11
Android自定義View通常需要經過measure、layout和draw過程,如果你沒有了解過measure過程,可以先看看這篇文章。
一、Layout的作用:計算檢視的位置,即Left、Top、Right、Bottom四點的位置
二、layout過程:跟measure類似,layout也會根據View的型別分成兩種情況進行處理。
| View型別 | layout過程 |
| 單一View | 只計算View本身的位置 |
| ViewGroup | 確定View本身及子View在父容器中的位置 |
接下來我們對這兩種情況分別進行分析。
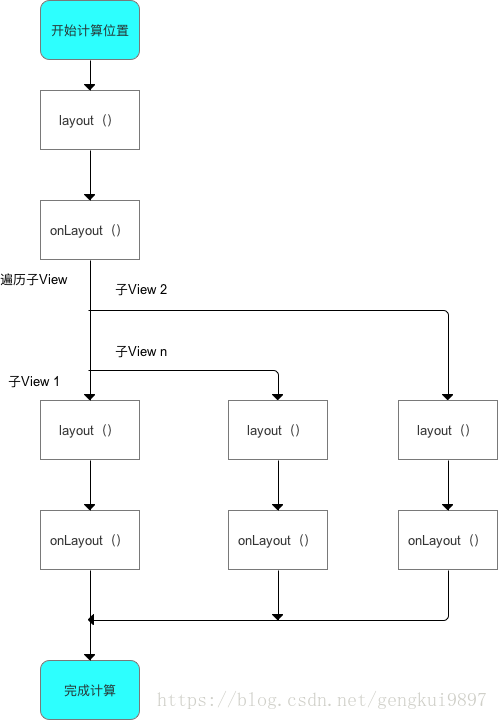
(1)單一View的layout過程
具體流程:layout()→onLayout()
相關原始碼分析如下:
/** * 原始碼分析:layout() * 作用:確定View本身的位置,即設定View本身的四個頂點位置 */ public void layout(int l, int t, int r, int b) { // 當前檢視的四個頂點 int oldL = mLeft; int oldT = mTop; int oldB = mBottom; int oldR = mRight; // 1. 確定View的位置:setFrame() / setOpticalFrame() // 即初始化四個頂點的值、判斷當前View大小和位置是否發生了變化 & 返回 // ->>分析1、分析2 boolean changed = isLayoutModeOptical(mParent) ? setOpticalFrame(l, t, r, b) : setFrame(l, t, r, b); // 2. 若檢視的大小 & 位置發生變化 // 會重新確定該View所有的子View在父容器的位置:onLayout() if (changed || (mPrivateFlags & PFLAG_LAYOUT_REQUIRED) == PFLAG_LAYOUT_REQUIRED) { onLayout(changed, l, t, r, b); // 對於單一View的laytou過程:由於單一View是沒有子View的,故onLayout()是一個空實現->>分析3 // 對於ViewGroup的laytou過程:由於確定位置與具體佈局有關,所以onLayout()在ViewGroup為1個抽象方法,需重寫實現(後面會詳細說) ... } /** * 分析1:setFrame() * 作用:根據傳入的4個位置值,設定View本身的四個頂點位置 * 即:最終確定View本身的位置 */ protected boolean setFrame(int left, int top, int right, int bottom) { ... // 通過以下賦值語句記錄下了檢視的位置資訊,即確定View的四個頂點 // 從而確定了檢視的位置 mLeft = left; mTop = top; mRight = right; mBottom = bottom; mRenderNode.setLeftTopRightBottom(mLeft, mTop, mRight, mBottom); } /** * 分析2:setOpticalFrame() * 作用:根據傳入的4個位置值,設定View本身的四個頂點位置 * 即:最終確定View本身的位置 */ private boolean setOpticalFrame(int left, int top, int right, int bottom) { Insets parentInsets = mParent instanceof View ? ((View) mParent).getOpticalInsets() : Insets.NONE; Insets childInsets = getOpticalInsets(); // 內部實際上是呼叫setFrame() return setFrame( left + parentInsets.left - childInsets.left, top + parentInsets.top - childInsets.top, right + parentInsets.left + childInsets.right, bottom + parentInsets.top + childInsets.bottom); } // 回到呼叫原處 /** * 分析3:onLayout() * 注:對於單一View的laytou過程 * a. 由於單一View是沒有子View的,故onLayout()是一個空實現 * b. 由於在layout()中已經對自身View進行了位置計算,所以單一View的layout過程在layout()後就已完成了 */ protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int left, int top, int right, int bottom) { // 引數說明 // changed 當前View的大小和位置改變了 // left 左部位置 // top 頂部位置 // right 右部位置 // bottom 底部位置 }
我們對單一View的layout過程總結一下:
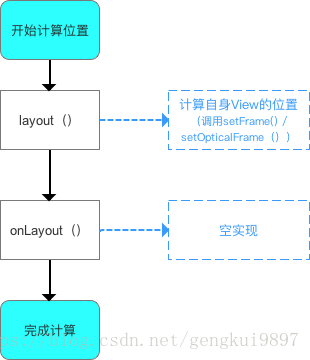
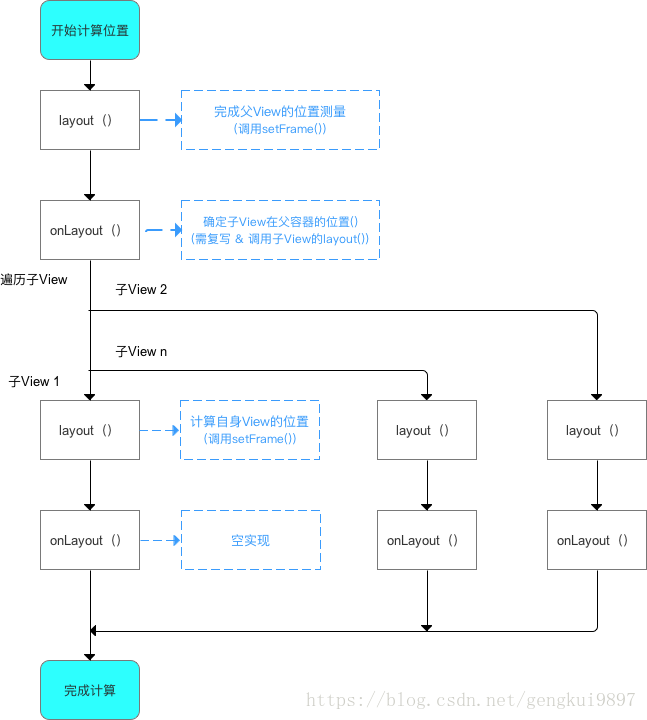
(2)ViewGroup的layout分析
流程:
相關原始碼分析如下:
/** * 原始碼分析:layout() * 作用:確定View本身的位置,即設定View本身的四個頂點位置 * 注:與單一View的layout()原始碼一致 */ public void layout(int l, int t, int r, int b) { // 當前檢視的四個頂點 int oldL = mLeft; int oldT = mTop; int oldB = mBottom; int oldR = mRight; // 1. 確定View的位置:setFrame() / setOpticalFrame() // 即初始化四個頂點的值、判斷當前View大小和位置是否發生了變化 & 返回 // ->>分析1、分析2 boolean changed = isLayoutModeOptical(mParent) ? setOpticalFrame(l, t, r, b) : setFrame(l, t, r, b); // 2. 若檢視的大小 & 位置發生變化 // 會重新確定該View所有的子View在父容器的位置:onLayout() if (changed || (mPrivateFlags & PFLAG_LAYOUT_REQUIRED) == PFLAG_LAYOUT_REQUIRED) { onLayout(changed, l, t, r, b); // 對於單一View的laytou過程:由於單一View是沒有子View的,故onLayout()是一個空實現(上面已分析完畢) // 對於ViewGroup的laytou過程:由於確定位置與具體佈局有關,所以onLayout()在ViewGroup為1個抽象方法,需重寫實現 ->>分析3 ... } /** * 分析1:setFrame() * 作用:確定View本身的位置,即設定View本身的四個頂點位置 */ protected boolean setFrame(int left, int top, int right, int bottom) { ... // 通過以下賦值語句記錄下了檢視的位置資訊,即確定View的四個頂點 // 從而確定了檢視的位置 mLeft = left; mTop = top; mRight = right; mBottom = bottom; mRenderNode.setLeftTopRightBottom(mLeft, mTop, mRight, mBottom); } /** * 分析2:setOpticalFrame() * 作用:確定View本身的位置,即設定View本身的四個頂點位置 */ private boolean setOpticalFrame(int left, int top, int right, int bottom) { Insets parentInsets = mParent instanceof View ? ((View) mParent).getOpticalInsets() : Insets.NONE; Insets childInsets = getOpticalInsets(); // 內部實際上是呼叫setFrame() return setFrame( left + parentInsets.left - childInsets.left, top + parentInsets.top - childInsets.top, right + parentInsets.left + childInsets.right, bottom + parentInsets.top + childInsets.bottom); } // 回到呼叫原處 /** * 分析3:onLayout() * 作用:計算該ViewGroup包含所有的子View在父容器的位置() * 注: * a. 定義為抽象方法,需重寫,因:子View的確定位置與具體佈局有關,所以onLayout()在ViewGroup沒有實現 * b. 在自定義ViewGroup時必須複寫onLayout()!!!!! * c. 複寫原理:遍歷子View 、計算當前子View的四個位置值 & 確定自身子View的位置(呼叫子View layout()) */ protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int left, int top, int right, int bottom) { // 引數說明 // changed 當前View的大小和位置改變了 // left 左部位置 // top 頂部位置 // right 右部位置 // bottom 底部位置 // 1. 遍歷子View:迴圈所有子View for (int i=0; i<getChildCount(); i++) { View child = getChildAt(i); // 2. 計算當前子View的四個位置值 // 2.1 位置的計算邏輯 ...// 需自己實現,也是自定義View的關鍵 // 2.2 對計算後的位置值進行賦值 int mLeft = Left int mTop = Top int mRight = Right int mBottom = Bottom // 3. 根據上述4個位置的計算值,設定子View的4個頂點:呼叫子view的layout() & 傳遞計算過的引數 // 即確定了子View在父容器的位置 child.layout(mLeft, mTop, mRight, mBottom); // 該過程類似於單一View的layout過程中的layout()和onLayout(),此處不作過多描述 } } }
對於ViewGroup的layout過程總結如下:
最後,說一個比較重要的問題:getWidth()、getHeight()與getMeasureWidth()、getMeasureHeight()獲取的寬高的區別是什麼?
首先,我們先看下兩者的定義,
getWidth()/getHeight():獲取View最終的寬高
getMeasureWidth()/getMeasureHeight():獲取View測量的寬高
然後,再看一下二者的原始碼:
// 獲得View測量的寬 / 高
public final int getMeasuredWidth() {
return mMeasuredWidth & MEASURED_SIZE_MASK;
// measure過程中返回的mMeasuredWidth
}
public final int getMeasuredHeight() {
return mMeasuredHeight & MEASURED_SIZE_MASK;
// measure過程中返回的mMeasuredHeight
}
// 獲得View最終的寬 / 高
public final int getWidth() {
return mRight - mLeft;
// View最終的寬 = 子View的右邊界 - 子view的左邊界。
}
public final int getHeight() {
return mBottom - mTop;
// View最終的高 = 子View的下邊界 - 子view的上邊界。
}
最後,我們看看它們的區別:
這裡需要注意一下,在非一般情況下,也就是通過人為設定,重寫View的layout()強行設定,這種情況下,測量的值與最終的值是不一樣的。