SpringMVC Interceptor 解析,載入原始碼流程
阿新 • • 發佈:2018-12-11
SpringMVC Interceptor 解析,載入原始碼流程
本文說什麼
interceptor從哪裡來,怎麼建立,怎麼載入,在哪裡被使用,以xml的配置形式為例
xml配置解析階段
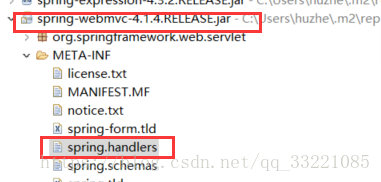
直接開啟spring-webmvc的原始碼包找到spring.handlers,這個是spring對於元件xml解析模組。
開啟後一看說明,mvc這個標籤是,是通過這個 org.springframework.web.servlet.config.MvcNamespaceHandler,解析的直接找到看一下
http\://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc=org.springframework.web.servlet.config.MvcNamespaceHandler
發現是
public class MvcNamespaceHandler extends NamespaceHandlerSupport {
@Override
public void init() {
registerBeanDefinitionParser("annotation-driven", new AnnotationDrivenBeanDefinitionParser 這個就直接找到<mvc:*> 的所有表現對應的解析類了,直接找到
registerBeanDefinitionParser("interceptors", new InterceptorsBeanDefinitionParser());
開啟看一下,
@Override
public BeanDefinition parse(Element element, ParserContext parserContext) {
CompositeComponentDefinition compDefinition = new CompositeComponentDefinition(element.getTagName(), parserContext.extractSource(element));
parserContext.pushContainingComponent(compDefinition);
RuntimeBeanReference pathMatcherRef = null;
if (element.hasAttribute("path-matcher")) {
pathMatcherRef = new RuntimeBeanReference(element.getAttribute("path-matcher"));
}
List<Element> interceptors = DomUtils.getChildElementsByTagName(element, "bean", "ref", "interceptor");
for (Element interceptor : interceptors) {
RootBeanDefinition mappedInterceptorDef = new RootBeanDefinition(MappedInterceptor.class);
mappedInterceptorDef.setSource(parserContext.extractSource(interceptor));
mappedInterceptorDef.setRole(BeanDefinition.ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE);
ManagedList<String> includePatterns = null;
ManagedList<String> excludePatterns = null;
Object interceptorBean;
if ("interceptor".equals(interceptor.getLocalName())) {
includePatterns = getIncludePatterns(interceptor, "mapping");
excludePatterns = getIncludePatterns(interceptor, "exclude-mapping");
Element beanElem = DomUtils.getChildElementsByTagName(interceptor, "bean", "ref").get(0);
interceptorBean = parserContext.getDelegate().parsePropertySubElement(beanElem, null);
}
else {
interceptorBean = parserContext.getDelegate().parsePropertySubElement(interceptor, null);
}
mappedInterceptorDef.getConstructorArgumentValues().addIndexedArgumentValue(0, includePatterns);
mappedInterceptorDef.getConstructorArgumentValues().addIndexedArgumentValue(1, excludePatterns);
mappedInterceptorDef.getConstructorArgumentValues().addIndexedArgumentValue(2, interceptorBean);
if (pathMatcherRef != null) {
mappedInterceptorDef.getPropertyValues().add("pathMatcher", pathMatcherRef);
}
String beanName = parserContext.getReaderContext().registerWithGeneratedName(mappedInterceptorDef);
parserContext.registerComponent(new BeanComponentDefinition(mappedInterceptorDef, beanName));
}
parserContext.popAndRegisterContainingComponent();
return null;
}
就找到了對於這些標籤的解析,然後把 interceptors 節點全部生成對應的RootBeanDefinition放入到spring容器中,對於xml的解析都結束了容器中已經都全部的interceptor了
載入interceptor
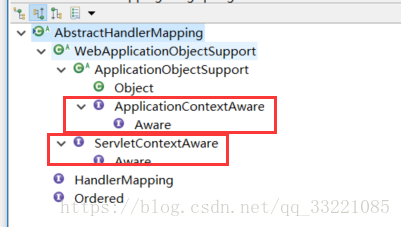
直接找 AbstractHandlerMapping 這個類,handlerMapping的基礎實現類,裡面把interceptor 初始化,分類。因為他繼承實現了webapplicationObjectSupport。有幾個初始化方法,這就是初始化把interceptor的入口
org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.AbstractHandlerMapping
sping注入applicationContext,就是呼叫 初始化的時候呼叫 initApplicationContext 中開始填充handlerMapping中的intercetor 集合
入口程式碼展示
pjavaublic abstract class ApplicationObjectSupport implements ApplicationContextAware {
.........
@Override
public final void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext context) throws BeansException {
if (context == null && !isContextRequired()) {
// Reset internal context state.
this.applicationContext = null;
this.messageSourceAccessor = null;
}
else if (this.applicationContext == null) {
// Initialize with passed-in context.
if (!requiredContextClass().isInstance(context)) {
throw new ApplicationContextException(
"Invalid application context: needs to be of type [" + requiredContextClass().getName() + "]");
}
this.applicationContext = context;
this.messageSourceAccessor = new MessageSourceAccessor(context);
initApplicationContext(context); // 入口 入口 入口 入口 入口 入口
}
else {
// Ignore reinitialization if same context passed in.
if (this.applicationContext != context) {
throw new ApplicationContextException(
"Cannot reinitialize with different application context: current one is [" +
this.applicationContext + "], passed-in one is [" + context + "]");
}
}
}
protected void initApplicationContext(ApplicationContext context) throws BeansException {
initApplicationContext();
}
protected void initApplicationContext() throws BeansException {
//子類實現
}
.........
}
public abstract class AbstractHandlerMapping extends WebApplicationObjectSupport
implements HandlerMapping, Ordered {
.......
@Override
protected void initApplicationContext() throws BeansException {
extendInterceptors(this.interceptors);
detectMappedInterceptors(this.mappedInterceptors);//從spring中找到interceptor
initInterceptors();
}
/**
* 在容器中找到所有的interceptor,一個個放入 AbstractHandlerMapping,然後在對其初始化分類,後面就可以用了
**/
protected void detectMappedInterceptors(List<MappedInterceptor> mappedInterceptors) {
mappedInterceptors.addAll(
BeanFactoryUtils.beansOfTypeIncludingAncestors(
getApplicationContext(), MappedInterceptor.class, true, false).values());
}
/**
* 分類
**/
protected void initInterceptors() {
if (!this.interceptors.isEmpty()) {
for (int i = 0; i < this.interceptors.size(); i++) {
Object interceptor = this.interceptors.get(i);
if (interceptor == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Entry number " + i + " in interceptors array is null");
}
if (interceptor instanceof MappedInterceptor) {
this.mappedInterceptors.add((MappedInterceptor) interceptor);
}
else {
this.adaptedInterceptors.add(adaptInterceptor(interceptor));
}
}
}
}
......
}
這樣整個流程就搞一段落
總結
mvc自己的包,自己定義標籤,解析xml把所有的interceptor放入spring中,在初始化handlerMapping 中在一個個找出來,放到 handlermapping 中,在初始化分類準備後面使用
ps:
MappedInterceptor 包換 MappedInterceptor
public final class MappedInterceptor {
// 需要攔截的url
private final String[] includePatterns;
// 排除的url
private final String[] excludePatterns;
private final HandlerInterceptor interceptor;
// 判斷是否符合
private PathMatcher pathMatcher;