python 程式設計語言 筆記(三)
第三週 分支與迴圈
3.1 程式基本結構
1. 程式流程圖 — 用規定的一系列圖形、流程線和文字說明演算法中的基本操作和控制流程。
流程圖的基本元素包括:
(1)表示相應操作的框
(2)帶箭頭的流程線
(3)框內外必要的文字說明
2. 設計程式框圖的步驟:
(1)用自然語言表述演算法步驟
(2)確定步驟邏輯結構,用相應框圖表示
(3)流程線連線框圖,加上終端框,得到整個演算法的程式框圖
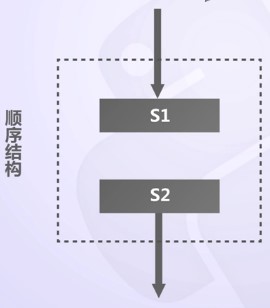
3. 任何演算法都可以由順序、選擇、迴圈三種基本結構組合實現:
(1)順序結構:按邏輯順序自上而下依次執行的結構,如:溫度轉換程式;
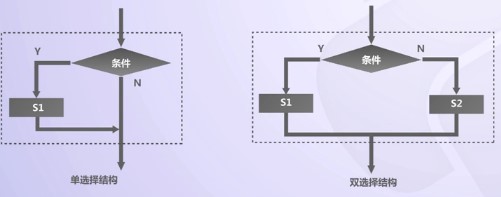
(2)選擇結構(分支結構):在演算法中通過對條件的判斷,根據條件是否成立而選擇不同流向的演算法結構;
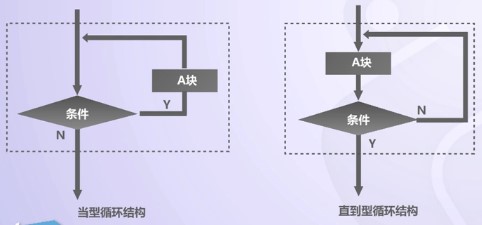
(3)迴圈結構:指在一定條件下反覆執行某部分程式碼的操作;
3.2 簡單分支
例:
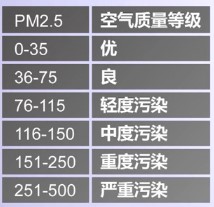
PM2.5指數分級程式功能IPO模式描述:
輸入:接受外部輸入PM2.5值
處理:空氣質量分級演算法
輸出:列印空氣質量提醒
PM2.5指數分級虛擬碼
If PM2.5值> 75
列印空氣汙染警告
If PM2.5值< 35
列印空氣質量優,建議戶外運動
流程圖如圖所示:
程式5:
- #pm25.py
- #空氣質量提醒
- def main():
- PM = eval(input("What is today'sPM2.5? "))
- # 列印相應提醒
- if PM > 75:
- print("Unhealthy. Becareful!")
- if PM < 35:
- print("Good. Go running!")
- main()
【執行結果】
輸出: 輸入:
What is today'sPM2.5? 90
Unhealthy. Becareful!
(1)If語句格式:
If <condition>:
<body>
【注】<condition>是條件表示式,<body>是一個或多個語句序列
先判斷<condition>條件,若true,則執行<body>,再轉向下一條語句;
若false,則直接跳過<body>,轉向下一條語句
(2)簡單條件構造
① 簡單條件基本形式 <expr><relop> <expr>
② <relop>是關係操作符<, <=, ==, >=, >, !=
③ 使用“=”表示賦值語句,使用“==”表示等於
④ 除數字外,字元或字串也可以按照字典順序用於條件比較
⑤ <condition>是布林表示式,為bool型別
布林值的真假以True和False表示
(3)二分支語法結構
If <condition>:
<statements>
else:
<statements>
程式6:
- # quadratic.py
- # 計算二次方程的實數根程式
- import math
- def main():
- print("Thisprogram finds the real solutions to a quadratic\n")
- a,b,c =eval(input("Please enter the coefficients(a,b,c): "))
- delta = b*b -4*a*c
- if delta >= 0:
- discRoot =math.sqrt(delta)
- root1 = (-b +discRoot) / (2*a)
- root2 = (-b -discRoot) / (2*a)
- print("\nThe solutions are:", root1, root2)
- else:
- print("Theequation has no real roots!")
- main()
輸出:
This program finds the real solutions to a quadratic
輸入:
Please enter the coefficients(a,b,c): 1,2,3
The equation has no real roots!
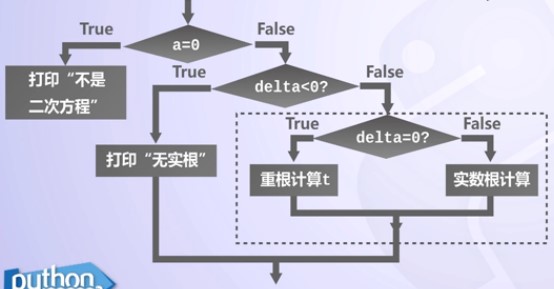
3.3 多分支
(1)多分支決策
要解決雙根問題,就需要對delta等於0的情況進行處理。
語句的結構上要引入巢狀結構:
① 當delta < 0,處理無實根情況
② 當delta = 0,處理實根情況
③ 當delta > 0,處理雙根情況
一種方案是在程式中使用兩個if-else語句。
把一個複合語句放到另一個語句的結構之中稱為巢狀。
1. 多分支決策是解決複雜問題的重要手段之一
2. 一個三分之決策可以由兩個二分支結構巢狀實現
3. 使用if-else描述多分支決策時,
實現更多分支需要更多巢狀,影響程式易讀性
Python使用if-elif-else描述多分支決策,簡化分支結構的巢狀問題。
格式如下:
If <condition1>:
<case1 statements>
elif<condition2>:
<case2 statements>
elif<condition3>:
<case3 statements>
…
else:
<default statements>
例:程式7:
- # quadratic.py
- import math
- def main():
- print("This program finds the realsolutions to a quadratic\n")
- a,b,c =eval(input("Please enter the coefficients(a,b,c): "))
- delta = b*b - 4*a*c
- if a == 0:
- x = -b/c
- print("\nThere is ansolution", x)
- elif delta < 0:
- print("\nThe equation has no real roots!")
- elif dalta == 0:
- x = -b/(2*a)
- print("\nTheere is a double rootat", x)
- else:
- discRoot = math.sqrt(delta)
- root1 = (-b +discRoot) / (2*a)
- root2 = (-b -discRoot) / (2*a)
- print("\nThesolutions are:", root1, root2)
- main()
 3.4 異常處理
3.4 異常處理
異常處理語句
Python使用try…except…,可使程式不因執行錯誤而崩潰
Python的異常處理語句還可以使用else和finally關鍵字
(可選項,若使用則else必須在finally之前)
格式如下:
try:
<body>
except<ErrorType1>:
<handler1>
except<ErrorType2>:
<handler2>
except:
<handler0>
else:
<process_else>
finally:
<process_finally>
try…except可以捕捉任何型別的錯誤
對於二次方程,還會有其他可能的錯誤
如:輸入非數值型別(NameError)
輸入無效的表示式(SyntaxError)等
此時可以用一個try語句配多個except來實現
程式8:
- # 異常處理測試
- def main():
- try:
- number1,number2 = eval(input("Enter two numbers,
- separated by a comma:"))
- result = number1/number2
- exceptZeroDivisionError:
- print("Division by zero!")
- exceptSyntaxError:
- print("Acomma may be missing in the input")
- else:
- print("Noexceptions, the result is", result)
- finally:
- print("executing the final clause")
- main()
【執行結果】
輸出: 輸入:
Enter two numbers, separated by a comma: 1 2
A comma may be missing in the input
executing the final clause
Enter two numbers, separated by a comma: 3,2
No exceptions, the result is 1.5
executing the final clause
Enter two numbers, separated by a comma: 3,0
Division by zero!
executing the final clause