Fiber Optic Cable or Wireless Network, Which Is Better for Your Network?
Fiber optic cables convert packets of data into a stream of light. The light travels through the cables from sender to the receiver, which converts it back into its original form. While wireless communication converts the data by transmitting into electromagnetic waves for broadcasting. Both alternatives have advocates who regard them as the superior communication medium. So on earth which of these is the best choice? This article will give you the answer.
Fiber optic cables are made up of bundles of very thin glass or plastic strands that transmit data in the form of modulated light. Each strand is slightly thicker than a human hair. The center of each strand is called the core, which provides the pathway for light to travel. The core is surrounded by a layer of glass called cladding, which reflects light inward to avoid signal loss and allow the light to pass through bends in the cable.
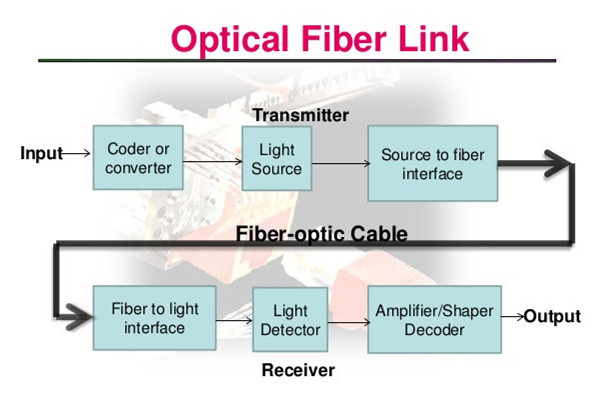
Figure1: Optical Fiber Link Principle
The Properties of Wireless Wi-Fi TechnologyWi-Fi is a technology for wireless local area networking with devices based on the IEEE 802.11 standards. A Wi-Fi network makes use of radio waves to transmit information across a network. The connection is established using a wireless adapter to create a hotspot (a wireless access point). A wireless adapter will translate data into a radio signal. This same signal will be transmitted via an antenna to a decoder known as the router. Once decoded, the data will be sent to the Internet through a wired Ethernet connection.
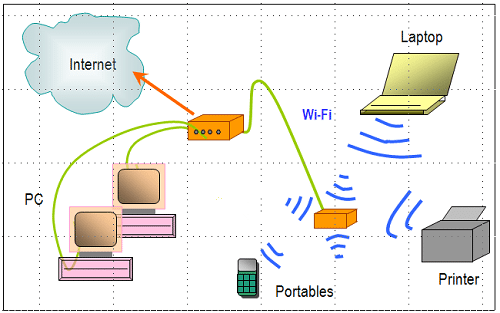
Figure 2: Wi-Fi Network to Internet
Pros and Cons of Wireless Network Advantages of Wireless Network- Flexibility: Because there is no wires to manage your network, wireless network avoids a time-consuming and tedious process to connect your devices. It also makes it easier to add extra devices to the network.
- Mobility: As the radio waves can go through walls, users can move around freely and connect the internet within the limited area.
- Convenience: Users are able to share files and resources with other devices that are connected to the network without having to be cabled to a port. So instant transfer of information to social media is made much easier.
- Work With Multiple Devices: Wireless networks can sometimes handle a larger amount of users because they are not limited by a specific number of connection ports.
- Interference: Wireless networks have an increased chance of jamming and interference due to external factors. When many people use wireless networks in the same area, the signal transmission will be affected.
- Limited range: The speeds can also vary considerably according to your location in relation to the network.
- Security: Wireless networks are generally less secure. There can also be problems with neighbors stealing bandwidth, if the network hasn’t been set up to be password protected. Information is also less secure too and can be easier to hack into.
In theory, a wireless network can transmit data at the same speed as optical fiber. In practice, fiber optic cables attain higher maximum speeds. This is particularly true when networks become congested, as all users of wireless networks share the same bandwidth. The more users at any one time, the more congested and slower the wireless network becomes. Optical fiber is capable of much faster speeds than current networks provide. At this time, fiber optic cables can send faster messages.
ReliabilityWi-Fi signals are easily attenuated by physical objects, such as walls, trees or buildings. In addition, the wireless links are low availability in aggressive atmospheric and weather conditions. If it’s raining very heavily, Wi-Fi can be interrupted. However, these scenarios have no concern with fiber optic cable, which can be guaranteed more reliability regardless of any physical or weather conditions.
SecurityIt is very difficult to intercept a signal being transmitted through fiber optic cable. Specialist skills and equipment are required to break through the physical network layer. With Wi-Fi, this barrier does not exist, so it is possible to drive around with a laptop and hack into other people’s Wi-Fi networks.
CapacityAt present, the current Wi-Fi standard by IEEE 802.11 can handle an absolute maximum of 1.3Gbit/sec. By contrast, fiber networks are being deployed today at speeds of 100Gbit/sec and currently being planned is a new 400Gbit/sec. Wi-Fi will never catch up with fibre optics.
DistanceWireless signals degrade with distance. The further away the user is from the broadcast station, the weaker the signal. Nevertheless, fiber optic cables can convey a clear signal much farther, and the users can get the same signal at any point.
SummaryFrom what we have discussed, both fiber optic cables and Wi-Fi offer several advantages. Wi-Fi seems to more convenient. However, the long-term benefits of fiber cables make them more compelling. Fiber optic cables are commonly used to extend the distance limitations while ensuring high data rates and minimizing electrical interference.
