二十四點小遊戲
阿新 • • 發佈:2018-12-12
##第3章 作業
24點遊戲是經典的紙牌益智遊戲。
完整程式碼在最後
常見遊戲規則: 從撲克中每次取出4張牌。使用加減乘除,第一個能得出24者為贏。(其中,J代表11,Q代表12,K代表13,A代表1),按照要求程式設計解決24點遊戲。 基本要求: 隨機生成4個代表撲克牌牌面的數字字母,程式自動列出所有可能算出24的表示式,用擅長的語言(C/C++/Java或其他均可)實現程式解決問題。
-
1.程式風格良好(使用自定義註釋模板)
-
2.列出表示式無重複。
提高要求:使用者初始生命值為一給定值(比如3),初始分數為0。隨機生成4個代表撲克牌牌面的數字或字母,由使用者輸入包含這4個數字或字母的運算表示式(可包含括號),如果表示式計算結果為24則代表使用者贏了此局。
-
- 程式風格良好(使用自定義註釋模板)
- 2.使用計時器要求使用者在規定時間內輸入表示式,如果規定時間內運算正確則加分,超時或運算錯誤則進入下一題並減少生命值(不扣分)。
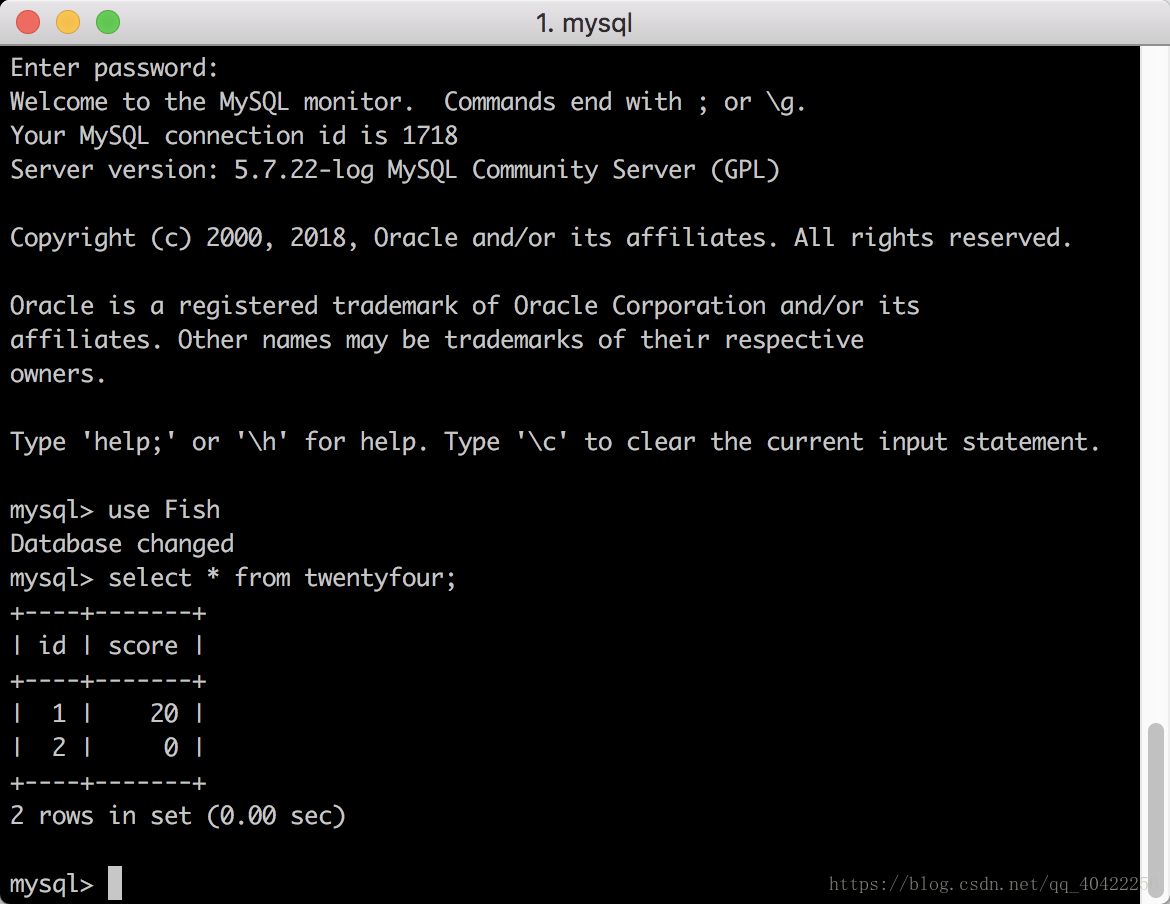
- 3.所有成績均可記錄在TopList.txt檔案中。
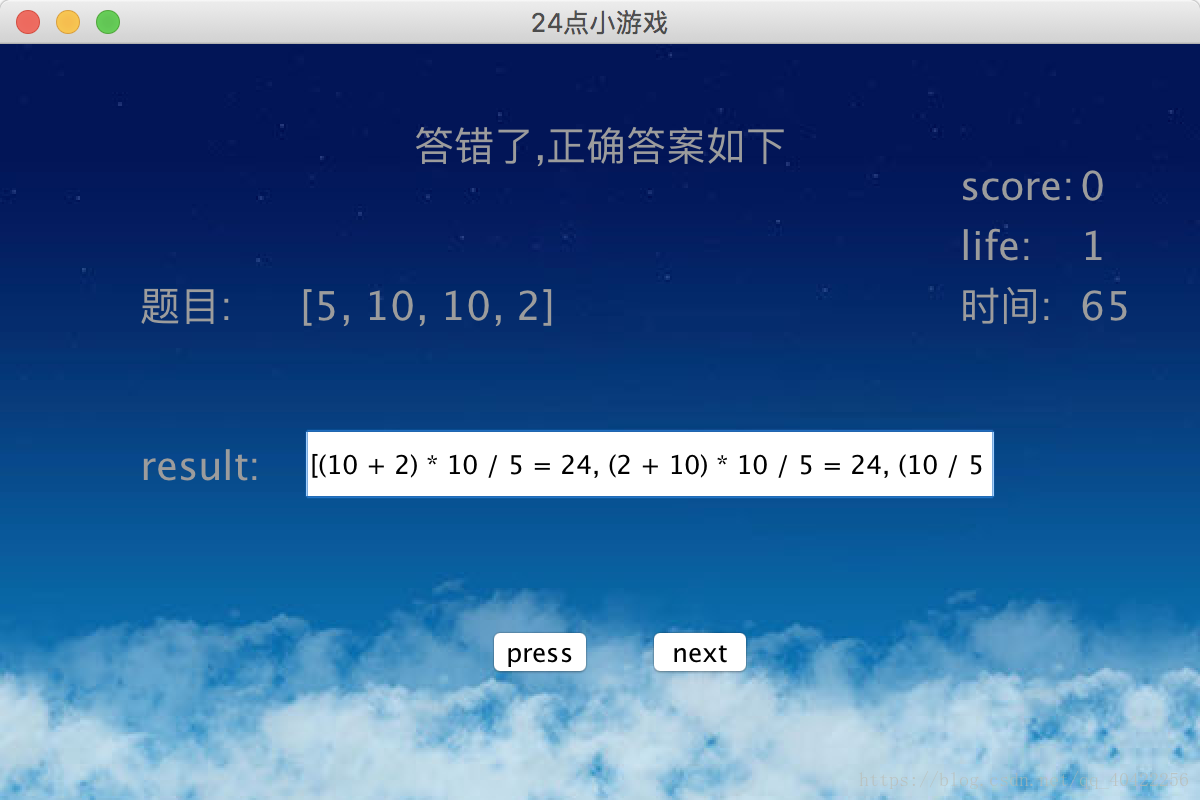
先展示一下執行結果:
思路:我們首先完成基本要求,首先用map初始化一下撲克牌,之後隨機生成4張撲克牌,之後對4張撲克牌的值和操作符進行全排列,之後進行組合,進行判斷是否值為24,並將值為24的儲存在結果集中。然後是提高要求,我們使用java的圖形使用者介面來做,設定一些基本的控制元件之後,通過之前的方法,我們獲取到可以生成24的撲克牌,我們通過label為使用者顯示要計算的撲克牌,使用者輸入要計算的字串,之後我們獲取到字串,對字串進行整理,利用棧進行計算,判斷結果是否正確,最後我們再加上分數,生命值,計時功能,並將結果寫入資料庫。
- 初始化一些基本變數
static Integer score = 0; //分數 static Integer life = 3; //生命值 static Map<String, Integer> map = new HashMap<>(); //初始化撲克牌map static List<String> sourceList = new ArrayList<>(); //源list static List<String> targetList = new ArrayList<>(); //生成隨機的目標list static Set<String> set; //可以進行運算得到24的set集合 static JTextField countText; //輸入框 static JButton signIn; //press按鈕 static JButton nextQuestion; //next按鈕 static JLabel label; //標題label static JLabel scoreLabel1; //分數label static JLabel lifeLabel1; //生命值label static JLabel question; //問題label static String string; //獲取到輸入框的字串 static Set<String> resultSet1; //正確答案的結果集 static Integer time = 90; //時間 static JLabel timeLabel1; //時間label static Thread thread; //時間的執行緒 public static char[] op = { '+', '-', '*', '/', '(', ')' }; //操作符陣列 public static String[] strOp = { "+", "-", "*", "/", "(", ")" }; /** * 先初始化map */ static { map.put("A", 1); for (int i = 2; i <= 10; i++) { map.put(String.valueOf(i), i); } map.put("J", 11); map.put("Q", 12); map.put("K", 13); } /** * 利用執行緒實現計時功能 * @author yangjiaxin * */ class MyThread implements Runnable { public void run() { while (time > 0) { time--; timeLabel1.setText(time + ""); try { Thread.sleep(1000); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } //Jishi.this.dispose(); } };
- 將隨機的4張牌進行全排列組合
/**
* 獲取隨機的4張撲克牌
*/
public static void getrandom() {
for (String key : map.keySet()) {
sourceList.add(key);
}
Random random = new Random();
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
Integer integer = random.nextInt(13);
targetList.add(sourceList.get(integer));
}
// System.out.print("隨機的四張牌為:");
// for (String string : targetList) {
// System.out.print(string+" ");
// }
// System.out.println();
}
//
// /**
// * 列印結果集
// *
// * @param resultSet
// * 結果集
// */
// private static void printlnResultSet(Collection<String> resultSet) {
// for (String str : resultSet) {
// System.out.println(str);
// }
// }
/**
* 得到給定整形陣列的全排列情況
*
* @param numbers
* 給定的整形陣列
* @return 全排列陣列
*/
private static int[][] arrangeAllNumbers(int[] numbers) {
List<int[]> list = new ArrayList<int[]>();
allSort(numbers, 0, numbers.length - 1, list);
int[][] resultSet = new int[list.size()][list.get(0).length];
resultSet = list.toArray(resultSet);
return resultSet;
}
/**
* 得到給定的操作中出現的所有操作符排列情況
*
* @param operators
* 出現的操作符陣列
* @param number
* 每組操作符的數量
* @return 所有操作符排列陣列
*/
private static char[][] arrangeAllOperators(char[] operators, int number) {
int setSize = (int) Math.pow(operators.length, number);
int index = 0;
char[][] resultSet = new char[setSize][number];
for (int i = 0; i < operators.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < operators.length; j++) {
for (int k = 0; k < operators.length; k++) {
resultSet[index][0] = operators[i];
resultSet[index][1] = operators[j];
resultSet[index][2] = operators[k];
index++;
}
}
}
return resultSet;
}
/**
*
*
* @param numbers
* 給定進行運算的一組整數,4個數為一組
* @param targetNumber
* 想要得到的結果
* @return 所有可能得到想要的結果的所有運算形式的字串形式集合
* @throws Exception
* 如果不能得到想要的結果,則丟擲該異常,表明根據指定的一組數字通過一系列的加減乘除不能得到想要的結果
*/
public static Set<String> caculate(int[] numbers, int targetNumber)
throws Exception {
resultSet1 = new HashSet<String>();// 這裡用Set而不是用List,主要是因為當給定的一組數字中如果有重複數字的話,同一結果會被出現多次,如果用List存放的話,會將重複的結果都存放起來,而Set會自動消除重複值
char[][] operatorsArrangement = arrangeAllOperators(new char[] { '+',
'-', '*', '/' }, 3);
int[][] numbersArrangement = arrangeAllNumbers(numbers);
for (int[] nums : numbersArrangement)
for (char[] operators : operatorsArrangement) {
int result = 0;
try {
result = caculate(nums, operators);
} catch (Exception e) {// 出現非精確計算
continue;
}
if (result == targetNumber)
resultSet1.add(buildString(nums, operators, targetNumber));// 如果計算後的結果等於想要的結果,就存放到集合中
}
if (resultSet1.isEmpty())
throw new Exception("給定的數字:" + Arrays.toString(numbers)
+ "不能通過加減乘除運算得到結果:" + targetNumber);
return resultSet1;
}
/**
* 將一組整型數字以給定的操作符按順序拼接為一個完整的表示式字串
*
* @param nums
* 一組整型數字
* @param operators
* 一組操作符
* @param target
* 目標值
* @return 拼接好的表示式字串
*/
private static String buildString(int[] nums, char[] operators, int target) {
String str = String.valueOf(nums[0]);
for (int i = 0; i < operators.length; i++) {
if (operators[i] == '+' || operators[i] == '-' ) {
str = "("+ str + ' ' + operators[i] + ' ' + nums[i + 1] +")";
} else {
str = str + ' ' + operators[i] + ' ' + nums[i + 1];
}
}
str = str + " = " + target;
return str;
}
/**
* 將給定的一組數字以給定的操作符按順序進行運算,如:int result = caculate(new int[]{3,4,5,8}, new
* char[]{'+','-','*'});
*
* @param nums
* 一組數字
* @param operators
* 一組運算子,數量為數字的個數減1
* @return 最後的計算結果
* @throws Exception
* 當計算結果不精確時,丟擲該異常,主要是針對除法運算,例如18 / 8 = 2,諸如這樣不精確計算將丟擲該異常
*/
private static int caculate(int[] nums, char[] operators) throws Exception {
int result = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < operators.length; i++) {
if (i == 0) {
result = caculate(nums[i], nums[i + 1], operators[i]);
} else {
result = caculate(result, nums[i + 1], operators[i]);
}
}
return result;
}
/**
* 根據指定操作符將兩個給定的數字進行計算
*
* @param num1
* 數字1
* @param num2
* 數字2
* @param operator
* 操作符,只能從“+、-、*、/”4個操作符中取值
* @return 計算結果
* @throws Exception
* 當計算結果不精確時,丟擲該異常,主要是針對除法運算,例如18 / 8 = 2,諸如這樣不精確計算將丟擲該異常
*/
private static int caculate(int num1, int num2, char operator)
throws Exception {
double result = 0;
switch (operator) {// 根據操作符做相應的計算操作
case '+':
result = num1 + num2;
break;
case '-':
result = num1 - num2;
break;
case '*':
result = num1 * num2;
break;
case '/':
result = (double) num1 / (double) num2;
break;
}
if (!check(result))
throw new Exception("不精確的計算數字");
return (int) result;
}
/**
* 檢查指定的浮點數是否可以直接轉換為整型數字而不損失精度
*
* @param result
* 要檢查的浮點數
* @return 如果可以進行無損轉換,返回true,否則返回false
*/
private static boolean check(double result) {
String str = String.valueOf(result);
int pointIndex = str.indexOf(".");// 小數點的下標值
String fraction = str.substring(pointIndex + 1);
return fraction.equals("0") ? true : false;// 通過判斷小數點後是否只有一個0來確定是否可以無損轉換為整型數值
}
/**
* 對傳入的整型陣列buf進行全排列
*
* @param buf
* 要進行全排列的整型陣列
* @param start
* 開始的下標值
* @param end
* 結束下標值
* @param list
* 儲存最後全排列結果的集合
*/
private static void allSort(int[] buf, int start, int end, List<int[]> list) {
if (start == end) {// 當只要求對陣列中一個字母進行全排列時,只要就按該陣列輸出即可
int[] a = new int[buf.length];
System.arraycopy(buf, 0, a, 0, a.length);
list.add(a);
} else {// 多個字母全排列
for (int i = start; i <= end; i++) {
int temp = buf[start];// 交換陣列第一個元素與後續的元素
buf[start] = buf[i];
buf[i] = temp;
allSort(buf, start + 1, end, list);// 後續元素遞迴全排列
temp = buf[start];// 將交換後的陣列還原
buf[start] = buf[i];
buf[i] = temp;
}
}
}
- 利用棧進行計算
/**
* 判斷是否為數字
* @param c
* @return
*/
public static boolean isDigit(char c) {
if (c >= '0' && c <= '9') {
return true;
}
return false;
}
/**
* 判斷是否為操作符
* @param c
* @return
*/
public static boolean isOp(char c) {
for (int i = 0; i < op.length; i++) {
if (op[i] == c) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
public static boolean isOp(String s) {
for (int i = 0; i < strOp.length; i++) {
if (strOp[i].equals(s)) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
/**
* 處理輸入的計算式
*
* @param str
* @return
*/
public static List<String> work(String str) {
List<String> list = new ArrayList<String>();
char c;
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
for (int i = 0; i < str.length(); i++) {
c = str.charAt(i);
if (isDigit(c)) {
sb.append(c);
}
if (isOp(c)) {
if (sb.toString().length() > 0) {
list.add(sb.toString());
sb.delete(0, sb.toString().length());
}
list.add(c + "");
}
}
if (sb.toString().length() > 0) {
list.add(sb.toString());
sb.delete(0, sb.toString().length());
}
return list;
}
// public static void printList(List<String> list) {
// for (String o : list) {
// System.out.print(o + " ");
// }
// }
/**
* 中綴表示式轉化為字尾表示式 1,遇到數字輸出 2,遇到高優先順序的全部出棧 3,最後全部出棧
*/
public static List<String> InfixToPostfix(List<String> list) {
List<String> Postfixlist = new ArrayList<String>();// 存放字尾表示式
Stack<String> stack = new Stack<String>();// 暫存操作符
// stack.push('#');
for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {
String s = list.get(i);
if (s.equals("(")) {
stack.push(s);
} else if (s.equals("*") || s.equals("/")) {
stack.push(s);
} else if (s.equals("+") || s.equals("-")) {
if (!stack.empty()) {
while (!(stack.peek().equals("("))) {
Postfixlist.add(stack.pop());
if (stack.empty()) {
break;
}
}
stack.push(s);
} else {
stack.push(s);
}
} else if (s.equals(")")) {
while (!(stack.peek().equals("("))) {
Postfixlist.add(stack.pop());
}
stack.pop();
} else {
Postfixlist.add(s);
}
if (i == list.size() - 1) {
while (!stack.empty()) {
Postfixlist.add(stack.pop());
}
}
}
return Postfixlist;
}
/**
* 字尾表示式計算
*/
public static int doCal(List<String> list) {
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<Integer>();
for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {
String s = list.get(i);
int t = 0;
if (!isOp(s)) {
t = Integer.parseInt(s);
stack.push(t);
} else {
if (s.equals("+")) {
int a1 = stack.pop();
int a2 = stack.pop();
int v = a2 + a1;
stack.push(v);
} else if (s.equals("-")) {
int a1 = stack.pop();
int a2 = stack.pop();
int v = a2 - a1;
stack.push(v);
} else if (s.equals("*")) {
int a1 = stack.pop();
int a2 = stack.pop();
int v = a2 * a1;
stack.push(v);
} else if (s.equals("/")) {
int a1 = stack.pop();
int a2 = stack.pop();
int v = a2 / a1;
stack.push(v);
}
}
}
return stack.pop();
}
/**
* 判斷使用者輸入的字串是否可以得到24點
* @return
*/
public static boolean cal() {
List<String> list = work(string);
List<String> list2 = InfixToPostfix(list);
// System.out.println("原式為:" + string);
// System.out.print("字尾表示式為:");
// printList(list2);
// System.out.println(" ");
//System.out.println("計算結果為:" + doCal(list2));
if (doCal(list2) == 24) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
/**
* 獲取到可以組成24點的有效撲克牌
* @return
*/
public static boolean getUsefulRandom() {
getrandom();
int[] a = new int[4];
int i = 0;
for (String string : targetList) {
a[i] = map.get(string);
i++;
}
try {
set = caculate(a, 24);
return true;
} catch (Exception e) {
//e.printStackTrace();//開發期間方便查詢錯誤,測試通過後就無需列印錯誤資訊了
//System.err.println(e.getMessage());
targetList.clear();
return false;
}
}
public static void getUserfulRandom1() {
boolean b = false;
while (!b) {
b = getUsefulRandom();
}
System.out.print("有效的四張牌為:");
for (String string : targetList) {
System.out.print(string+" ");
}
System.out.println();
//printlnResultSet(set);
}
最後的是全部的程式碼:
package shilaoshi;
import java.awt.Color;
import java.awt.Font;
import java.awt.event.ActionEvent;
import java.awt.event.ActionListener;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Random;
import java.util.Set;
import java.util.Stack;
import java.util.TreeSet;
import javax.swing.ImageIcon;
import javax.swing.JButton;
import javax.swing.JFrame;
import javax.swing.JLabel;
import javax.swing.JPanel;
import javax.swing.JTextField;
public class TwentyFour extends JFrame{
static Integer score = 0; //分數
static Integer life = 3; //生命值
static Map<String, Integer> map = new HashMap<>(); //初始化撲克牌map
static List<String> sourceList = new ArrayList<>(); //源list
static List<String> targetList = new ArrayList<>(); //生成隨機的目標list
static Set<String> set; //可以進行運算得到24的set集合
static JTextField countText; //輸入框
static JButton signIn; //press按鈕
static JButton nextQuestion; //next按鈕
static JLabel label; //標題label
static JLabel scoreLabel1; //分數label
static JLabel lifeLabel1; //生命值label
static JLabel question; //問題label
static String string; //獲取到輸入框的字串
static Set<String> resultSet1; //正確答案的結果集
static Integer time = 90; //時間
static JLabel timeLabel1; //時間label
static Thread thread; //時間的執行緒
public static char[] op = { '+', '-', '*', '/', '(', ')' }; //操作符陣列
public static String[] strOp = { "+", "-", "*", "/", "(", ")" };
/**
* 先初始化map
*/
static {
map.put("A", 1);
for (int i = 2; i <= 10; i++) {
map.put(String.valueOf(i), i);
}
map.put("J", 11);
map.put("Q", 12);
map.put("K", 13);
}
/**
* 利用執行緒實現計時功能
* @author yangjiaxin
*
*/
class MyThread implements Runnable {
public void run() {
while (time > 0) {
time--;
timeLabel1.setText(time + "");
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
//Jishi.this.dispose();
}
};
/**
* 構造方法初始化視覺化圖形介面
*/
public TwentyFour() {
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
setBg();
this.setTitle("24點小遊戲");
this.setSize(600, 400);
this.setLocation(300, 100);
this.setLayout(null);
JLabel timeLabel = new JLabel("時間:");
timeLabel.setFont(new Font("宋體", Font.PLAIN, 20));
timeLabel.setForeground(Color.decode("#9C9C9C"));
timeLabel.setBounds(480, 110, 60, 40);
timeLabel1 = new JLabel(time.toString());
timeLabel1.setFont(new Font("宋體", Font.PLAIN, 20));
timeLabel1.setForeground(Color.decode("#9C9C9C"));
timeLabel1.setBounds(540, 110, 60, 40);
label = new JLabel("24點小遊戲",JLabel.CENTER);
label.setFont(new Font("宋體",Font.PLAIN,20));
label.setForeground(Color.decode("#9C9C9C"));
label.setBounds( 200, 10, 200, 80);
this.add(label);
JLabel questionLabel = new JLabel("題目:");
questionLabel.setFont(new Font("宋體", Font.PLAIN, 20));
questionLabel.setForeground(Color.decode("#9C9C9C"));
questionLabel.setBounds(70, 110, 90, 40);
question = new JLabel("");
question.setBounds(150, 110, 350, 40);
question.setFont(new Font("宋體", Font.PLAIN, 20));
question.setForeground(Color.decode("#9C9C9C"));
getUserfulRandom1();
question.setText(targetList.toString());
JLabel result = new JLabel("result:");
result.setFont(new Font("宋體", Font.PLAIN, 20));
result.setForeground(Color.decode("#9C9C9C"));
result.setBounds(70, 190, 90, 40);
JLabel scoreLabel = new JLabel("score:");
scoreLabel.setFont(new Font("宋體", Font.PLAIN, 20));
scoreLabel.setForeground(Color.decode("#9C9C9C"));
scoreLabel.setBounds(480, 50, 60, 40);
scoreLabel1 = new JLabel(score.toString());
scoreLabel1.setFont(new Font("宋體", Font.PLAIN, 20));
scoreLabel1.setForeground(Color.decode("#9C9C9C"));
scoreLabel1.setBounds(540, 50, 60, 40);
JLabel lifeLabel = new JLabel("life:");
lifeLabel.setFont(new Font("宋體", Font.PLAIN, 20));
lifeLabel.setForeground(Color.decode("#9C9C9C"));
lifeLabel.setBounds(480, 80, 60, 40);
lifeLabel1 = new JLabel(life.toString());
lifeLabel1.setFont(new Font("宋體", Font.PLAIN, 20));
lifeLabel1.setForeground(Color.decode("#9C9C9C"));
lifeLabel1.setBounds(540, 80, 60, 40);
countText = new JTextField(200);
countText.setBounds(150, 190, 350, 40);
nextQuestion = new JButton("next");
nextQuestion.setBounds(320, 290, 60, 30);
signIn = new JButton("press");
signIn.setBounds(240, 290, 60, 30);
// signIn.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
//
// @Override
// public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
// // TODO Auto-generated method stub
// string = countText.getText();
// boolean b = cal();
// if (b) {
// label.setText("恭喜你答對了");
// score = score + 20;
// scoreLabel1.setText(score.toString());
// }else {
// label.setText("答錯了");
// life--;
// lifeLabel1.setText(life.toString());
//
// }
// }
//
// });
this.add(timeLabel1);
this.add(timeLabel);
this.add(questionLabel);
this.add(countText);
this.add(signIn);
this.add(question);
this.add(result);
this.add(scoreLabel);
this.add(scoreLabel1);
this.add(lifeLabel);
this.add(lifeLabel1);
this.add(nextQuestion);
this.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
this.setVisible(true);
thread = new Thread(new MyThread()); //開啟執行緒
thread.start();
start(); //開始答題
}
/**
* 開始答題的方法
*/
public void start() {
signIn.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
string = countText.getText();
boolean b = cal();
if (b) {
label.setText("恭喜你答對了");
score = score + 20;
scoreLabel1.setText(score.toString());
}else {
label.setText("答錯了,正確答案如下");
countText.setText(resultSet1.toString());
life = life - 1;
System.out.println("life-----"+life);
lifeLabel1.setText(life.toString());
}
if (life<0) {
save(score);
label.setText("life out");
score = 0;
life = 3;
}
}
});
nextQuestion.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
time = 90;
label.setText("24點小遊戲");
if (life == 3) {
scoreLabel1.setText(score.toString());
lifeLabel1.setText(life.toString());
}
targetList.clear();
getUserfulRandom1();
question.setText(targetList.toString());
countText.setText("");
}
});
}
/**
* 建立連線
*
* @return
*/
public static Connection getConnection() {
Connection conn = null;
try {
// 1.註冊驅動
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
// 2.建立連線
conn = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/Fish?useSSL=yes", "root", "1234");
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
System.out.println("註冊驅動失敗");
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (SQLException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
return conn;
}
/**
* save函式,將score存入資料庫
*
* @param strDate
* @param state
*/
public static void save(Integer score) {
PreparedStatement ps = null;
Connection conn = null;
String sql = "insert into twentyFour(score) values(?)";
try {
conn = getConnection();
ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
ps.setInt(1, score);
ps.executeUpdate();
} catch (SQLException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
if (conn != null) {
conn.close();
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
/**
* 獲取隨機的4張撲克牌
*/
public static void getrandom() {
for (String key : map.keySet()) {
sourceList.add(key);
}
Random random = new Random();
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
Integer integer = random.nextInt(13);
targetList.add(sourceList.get(integer));
}
// System.out.print("隨機的四張牌為:");
// for (String string : targetList) {
// System.out.print(string+" ");
// }
// System.out.println();
}
//
// /**
// * 列印結果集
// *
// * @param resultSet
// * 結果集
// */
// private static void printlnResultSet(Collection<String> resultSet) {
// for (String str : resultSet) {
// System.out.println(str);
// }
// }
/**
* 得到給定整形陣列的全排列情況
*
* @param numbers
* 給定的整形陣列
* @return 全排列陣列
*/
private static int[][] arrangeAllNumbers(int[] numbers) {
List<int[]> list = new ArrayList<int[]>();
allSort(numbers, 0, numbers.length - 1, list);
int[][] resultSet = new int[list.size()][list.get(0).length];
resultSet = list.toArray(resultSet);
return resultSet;
}
/**
* 得到給定的操作中出現的所有操作符排列情況
*
* @param operators
* 出現的操作符陣列
* @param number
* 每組操作符的數量
* @return 所有操作符排列陣列
*/
private static char[][] arrangeAllOperators(char[] operators, int number) {
int setSize = (int) Math.pow(operators.length, number);
int index = 0;
char[][] resultSet = new char[setSize][number];
for (int i = 0; i < operators.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < operators.length; j++) {
for (int k = 0; k < operators.length; k++) {
resultSet[index][0] = operators[i];
resultSet[index][1] = operators[j];
resultSet[index][2] = operators[k];
index++;
}
}
}
return resultSet;
}
/**
*
*
* @param numbers
* 給定進行運算的一組整數,4個數為一組
* @param targetNumber
* 想要得到的結果
* @return 所有可能得到想要的結果的所有運算形式的字串形式集合
* @throws Exception
* 如果不能得到想要的結果,則丟擲該異常,表明根據指定的一組數字通過一系列的加減乘除不能得到想要的結果
*/
public static Set<String> caculate(int[] numbers, int targetNumber)
throws Exception {
resultSet1 = new HashSet<String>();// 這裡用Set而不是用List,主要是因為當給定的一組數字中如果有重複數字的話,同一結果會被出現多次,如果用List存放的話,會將重複的結果都存放起來,而Set會自動消除重複值
char[][] operatorsArrangement = arrangeAllOperators(new char[] { '+',
'-', '*', '/' }, 3);
int[][] numbersArrangement = arrangeAllNumbers(numbers);
for (int[] nums : numbersArrangement)
for (char[] operators : operatorsArrangement) {
int result = 0;
try {
result = caculate(nums, operators);
} catch (Exception e) {// 出現非精確計算
continue;
}
if (result == targetNumber)
resultSet1.add(buildString(nums, operators, targetNumber));// 如果計算後的結果等於想要的結果,就存放到集合中
}
if (resultSet1.isEmpty())
throw new Exception("給定的數字:" + Arrays.toString(numbers)
+ "不能通過加減乘除運算得到結果:" + targetNumber);
return resultSet1;
}
/**
* 將一組整型數字以給定的操作符按順序拼接為一個完整的表示式字串
*
* @param nums
* 一組整型數字
* @param operators
* 一組操作符
* @param target
* 目標值
* @return 拼接好的表示式字串
*/
private static String buildString(int[] nums, char[] operators, int target) {
String str = String.valueOf(nums[0]);
for (int i = 0; i < operators.length; i++) {
if (operators[i] == '+' || operators[i] == '-' ) {
str = "("+ str + ' ' + operators[i] + ' ' + nums[i + 1] +")";
} else {
str = str + ' ' + operators[i] + ' ' + nums[i + 1];
}
}
str = str + " = " + target;
return str;
}
/**
* 將給定的一組數字以給定的操作符按順序進行運算,如:int result = caculate(new int[]{3,4,5,8}, new
* char[]{'+','-','*'});
*
* @param nums
* 一組數字
* @param operators
* 一組運算子,數量為數字的個數減1
* @return 最後的計算結果
* @throws Exception
* 當計算結果不精確時,丟擲該異常,主要是針對除法運算,例如18 / 8 = 2,諸如這樣不精確計算將丟擲該異常
*/
private static int caculate(int[] nums, char[] operators) throws Exception {
int result = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < operators.length; i++) {
if (i == 0) {
result = caculate(nums[i], nums[i + 1], operators[i]);
} else {
result = caculate(result, nums[i + 1], operators[i]);
}
}
return result;
}
/**
* 根據指定操作符將兩個給定的數字進行計算
*
* @param num1
* 數字1
* @param num2
* 數字2
* @param operator
* 操作符,只能從“+、-、*、/”4個操作符中取值
* @return 計算結果
* @throws Exception
* 當計算結果不精確時,丟擲該異常,主要是針對除法運算,例如18 / 8 = 2,諸如這樣不精確計算將丟擲該異常
*/
private static int caculate(int num1, int num2, char operator)
throws Exception {
double result = 0;
switch (operator) {// 根據操作符做相應的計算操作
case '+':
result = num1 + num2;
break;
case '-':
result = num1 - num2;
break;
case '*':
result = num1 * num2;
break;
case '/':
result = (double) num1 / (double) num2;
break;
}
if (!check(result))
throw new Exception("不精確的計算數字");
return (int) result;
}
/**
* 檢查指定的浮點數是否可以直接轉換為整型數字而不損失精度
*
* @param result
* 要檢查的浮點數
* @return 如果可以進行無損轉換,返回true,否則返回false
*/
private static boolean check(double result) {
String str = String.valueOf(result);
int pointIndex = str.indexOf(".");// 小數點的下標值
String fraction = str.substring(pointIndex + 1);
return fraction.equals("0") ? true : false;// 通過判斷小數點後是否只有一個0來確定是否可以無損轉換為整型數值
}
/**
* 對傳入的整型陣列buf進行全排列
*
* @param buf
* 要進行全排列的整型陣列
* @param start
* 開始的下標值
* @param end
* 結束下標值
* @param list
* 儲存最後全排列結果的集合
*/
private static void allSort(int[] buf, int start, int end, List<int[]> list) {
if (start == end) {// 當只要求對陣列中一個字母進行全排列時,只要就按該陣列輸出即可
int[] a = new int[buf.length];
System.arraycopy(buf, 0, a, 0, a.length);
list.add(a);
} else {// 多個字母全排列
for (int i = start; i <= end; i++) {
int temp = buf[start];// 交換陣列第一個元素與後續的元素
buf[start] = buf[i];
buf[i] = temp;
allSort(buf, start + 1, end, list);// 後續元素遞迴全排列
temp = buf[start];// 將交換後的陣列還原
buf[start] = buf[i];
buf[i] = temp;
}
}
}
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
/**
* 判斷是否為數字
* @param c
* @return
*/
public static boolean isDigit(char c) {
if (c >= '0' && c <= '9') {
return true;
}
return false;
}
/**
* 判斷是否為操作符
* @param c
* @return
*/
public static boolean isOp(char c) {
for (int i = 0; i < op.length; i++) {
if (op[i] == c) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
public static boolean isOp(String s) {
for (int i = 0; i < strOp.length; i++) {
if (strOp[i].equals(s)) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
/**
* 處理輸入的計算式
*
* @param str
* @return
*/
public static List<String> work(String str) {
List<String> list = new ArrayList<String>();
char c;
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
for (int i = 0; i < str.length(); i++) {
c = str.charAt(i);
if (isDigit(c)) {
sb.append(c);
}
if (isOp(c)) {
if (sb.toString().length() > 0) {
list.add(sb.toString());
sb.delete(0, sb.toString().length());
}
list.add(c + "");
}
}
if (sb.toString().length() > 0) {
list.add(sb.toString());
sb.delete(0, sb.toString().length());
}
return list;
}
// public static void printList(List<String> list) {
// for (String o : list) {
// System.out.print(o + " ");
// }
// }
/**
* 中綴表示式轉化為字尾表示式 1,遇到數字輸出 2,遇到高優先順序的全部出棧 3,最後全部出棧
*/
public static List<String> InfixToPostfix(List<String> list) {
List<String> Postfixlist = new ArrayList<String>();// 存放字尾表示式
Stack<String> stack = new Stack<String>();// 暫存操作符
// stack.push('#');
for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {
String s = list.get(i);
if (s.equals("(")) {
stack.push(s);
} else if (s.equals("*") || s.equals("/")) {
stack.push(s);
} else if (s.equals("+") || s.equals("-")) {
if (!stack.empty()) {
while (!(stack.peek().equals("("))) {
Postfixlist.add(stack.pop());
if (stack.empty()) {
break;
}
}
stack.push(s);
} else {
stack.push(s);
}
} else if (s.equals(")")) {
while (!(stack.peek().equals("("))) {
Postfixlist.add(stack.pop());
}
stack.pop();
} else {
Postfixlist.add(s);
}
if (i == list.size() - 1) {
while (!stack.empty()) {
Postfixlist.add(stack.pop());
}
}
}
return Postfixlist;
}
/**
* 字尾表示式計算
*/
public static int doCal(List<String> list) {
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<Integer>();
for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {
String s = list.get(i);
int t = 0;
if (!isOp(s)) {
t = Integer.parseInt(s);
stack.push(t);
} else {
if (s.equals("+")) {
int a1 = stack.pop();
int a2 = stack.pop();
int v = a2 + a1;
stack.push(v);
} else if (s.equals("-")) {
int a1 = stack.pop();
int a2 = stack.pop();
int v = a2 - a1;
stack.push(v);
} else if (s.equals("*")) {
int a1 = stack.pop();
int a2 = stack.pop();
int v = a2 * a1;
stack.push(v);
} else if (s.equals("/")) {
int a1 = stack.pop();
int a2 = stack.pop();
int v = a2 / a1;
stack.push(v);
}
}
}
return stack.pop();
}
/**
* 判斷使用者輸入的字串是否可以得到24點
* @return
*/
public static boolean cal() {
List<String> list = work(string);
List<String> list2 = InfixToPostfix(list);
// System.out.println("原式為:" + string);
// System.out.print("字尾表示式為:");
// printList(list2);
// System.out.println(" ");
//System.out.println("計算結果為:" + doCal(list2));
if (doCal(list2) == 24) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
/**
* 獲取到可以組成24點的有效撲克牌
* @return
*/
public static boolean getUsefulRandom() {
getrandom();
int[] a = new int[4];
int i = 0;
for (String string : targetList) {
a[i] = map.get(string);
i++;
}
try {
set = caculate(a, 24);
return true;
} catch (Exception e) {
//e.printStackTrace();//開發期間方便查詢錯誤,測試通過後就無需列印錯誤資訊了
//System.err.println(e.getMessage());
targetList.clear();
return false;
}
}
public static void getUserfulRandom1() {
boolean b = false;
while (!b) {
b = getUsefulRandom();
}
System.out.print("有效的四張牌為:");
for (String string : targetList) {
System.out.print(string+" ");
}
System.out.println();
//printlnResultSet(set);
}
/**
* 設定背景圖片
*/
public void setBg(){
((JPanel)this.getContentPane()).setOpaque(false);
ImageIcon img = new ImageIcon
("bg.jpg");
JLabel background = new JLabel(img);
this.getLayeredPane().add(background, new Integer(Integer.MIN_VALUE));
background.setBounds(0, 0, img.getIconWidth(), img.getIconHeight());
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new TwentyFour();
}
}