SpringBoot整合SpringSecurity(附帶原始碼)
SpringBoot整合SpringSecurity
配置環境
配置idea
我使用的是idea,點選New Project
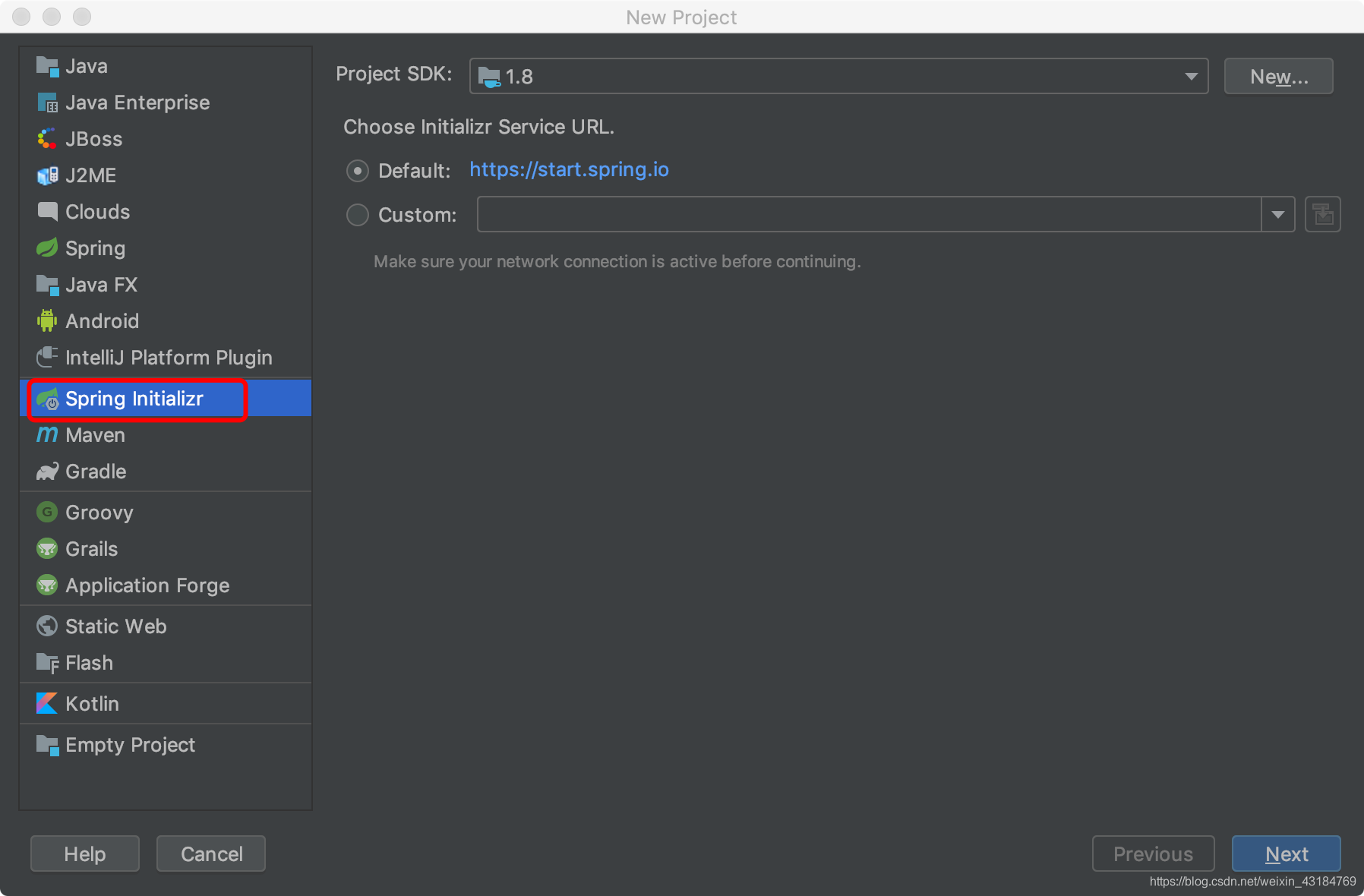 點選next專案資訊配置隨意,再下一步選上下圖所示的元件
點選next專案資訊配置隨意,再下一步選上下圖所示的元件
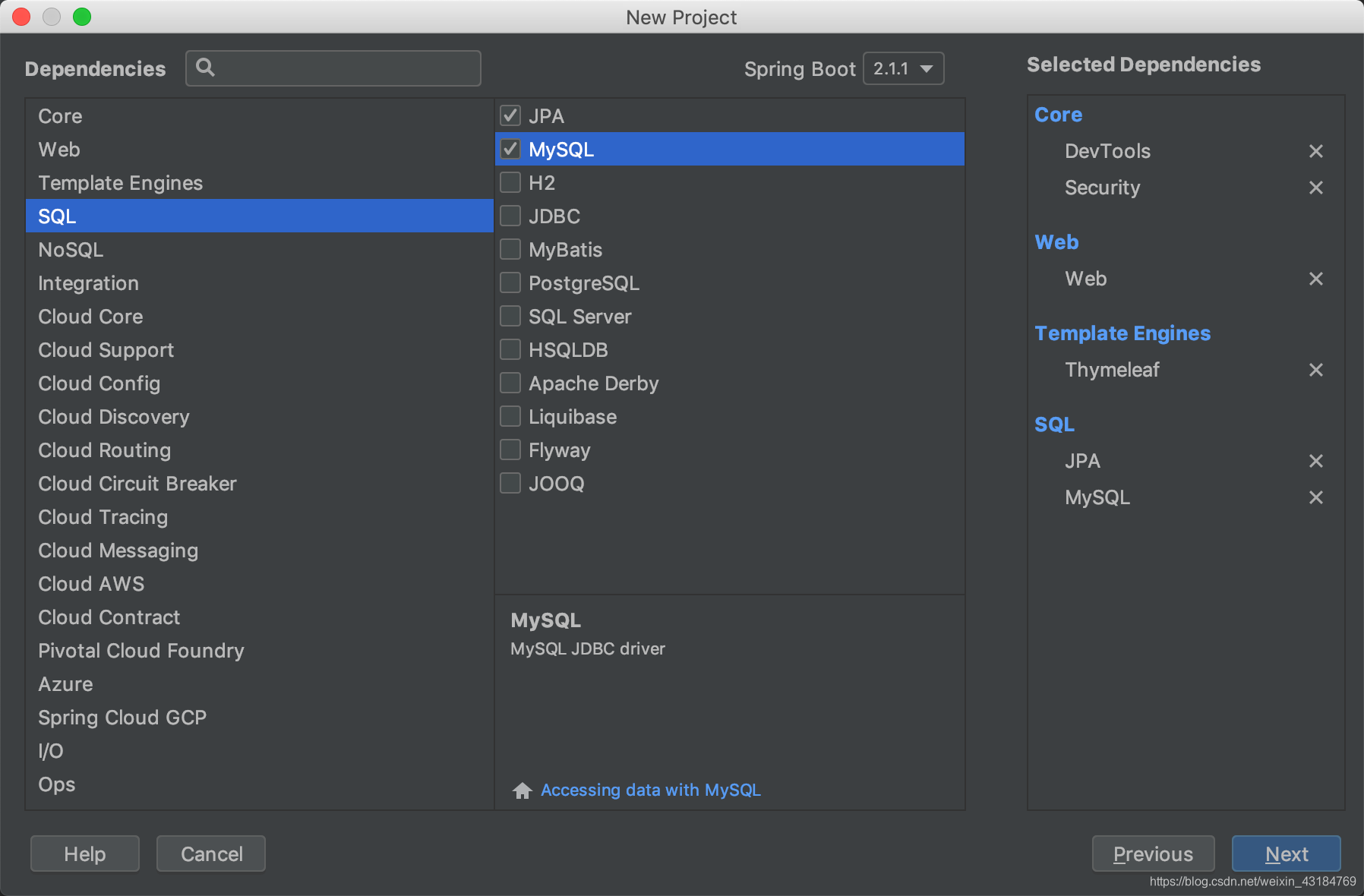
配置thymeleaf
在pom.xml中加入
<dependency>
<groupId>net.sourceforge.nekohtml</groupId>
<artifactId>nekohtml</artifactId>
<version>1.9.22</version>
</dependency>
在application.yml中加入
spring: thymeleaf: suffix: .html cache: false //設定為傳統模式,防止因為嚴格的語法檢測遇到的各種麻煩,例如<html />後習慣不會去加斜槓就會被當做錯誤檢測 mode: LEGACYHTML5
配置傳統檢測模式需要額外匯入上述的dependency並配合配置檔案
配置JPA
在application.yml中加入
spring: datasource: url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/springsecurity driver-class-name: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver username: root password: root jpa: show-sql: true //由於jpa預設將駝峰命名的entity轉化為帶下劃線的名稱去匹配資料庫中的表名,而我在資料庫中也是使用駝峰命名,所以需要下入下列的配置 hibernate: naming: physical-strategy: org.hibernate.boot.model.naming.PhysicalNamingStrategyStandardImpl
配置資料庫
匯入如下程式碼
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `Sys_permission`;
CREATE TABLE `Sys_permission` (
`id` int(11) unsigned NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`name` varchar(200) DEFAULT NULL,
`description` varchar(200) DEFAULT NULL,
`url` varchar(200) DEFAULT NULL,
`pid` int(11) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
LOCK TABLES `Sys_permission` WRITE;
/*!40000 ALTER TABLE `Sys_permission` DISABLE KEYS */;
INSERT INTO `Sys_permission` (`id`, `name`, `description`, `url`, `pid`)
VALUES
(1,'ROLE_HOME','index','/',NULL),
(2,'ROLE_ADMIN','admin','/admin',NULL),
(3,'ROLE_USER','user','/user',NULL);
/*!40000 ALTER TABLE `Sys_permission` ENABLE KEYS */;
UNLOCK TABLES;
# Dump of table Sys_permission_role
# ------------------------------------------------------------
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `Sys_permission_role`;
CREATE TABLE `Sys_permission_role` (
`id` int(11) unsigned NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`role_id` int(11) unsigned NOT NULL,
`permission_id` int(11) unsigned NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`),
KEY `role2` (`role_id`),
KEY `permission` (`permission_id`),
CONSTRAINT `permission` FOREIGN KEY (`permission_id`) REFERENCES `Sys_permission` (`id`),
CONSTRAINT `role2` FOREIGN KEY (`role_id`) REFERENCES `Sys_Role` (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
LOCK TABLES `Sys_permission_role` WRITE;
/*!40000 ALTER TABLE `Sys_permission_role` DISABLE KEYS */;
INSERT INTO `Sys_permission_role` (`id`, `role_id`, `permission_id`)
VALUES
(10,2,1),
(11,2,3),
(12,3,1),
(13,3,2),
(15,2,2);
/*!40000 ALTER TABLE `Sys_permission_role` ENABLE KEYS */;
UNLOCK TABLES;
# Dump of table Sys_Role
# ------------------------------------------------------------
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `Sys_Role`;
CREATE TABLE `Sys_Role` (
`id` int(11) unsigned NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`name` varchar(200) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
LOCK TABLES `Sys_Role` WRITE;
/*!40000 ALTER TABLE `Sys_Role` DISABLE KEYS */;
INSERT INTO `Sys_Role` (`id`, `name`)
VALUES
(2,'ROLE_USER'),
(3,'ROLE_ADMIN');
/*!40000 ALTER TABLE `Sys_Role` ENABLE KEYS */;
UNLOCK TABLES;
# Dump of table Sys_Role_User
# ------------------------------------------------------------
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `Sys_Role_User`;
CREATE TABLE `Sys_Role_User` (
`id` int(11) unsigned NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`Sys_User_id` int(11) unsigned NOT NULL,
`Sys_Role_id` int(11) unsigned NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`),
KEY `user` (`Sys_User_id`),
KEY `role` (`Sys_Role_id`),
CONSTRAINT `role` FOREIGN KEY (`Sys_Role_id`) REFERENCES `Sys_Role` (`id`),
CONSTRAINT `user` FOREIGN KEY (`Sys_User_id`) REFERENCES `Sys_User` (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
LOCK TABLES `Sys_Role_User` WRITE;
/*!40000 ALTER TABLE `Sys_Role_User` DISABLE KEYS */;
INSERT INTO `Sys_Role_User` (`id`, `Sys_User_id`, `Sys_Role_id`)
VALUES
(6,1,3),
(7,2,2);
/*!40000 ALTER TABLE `Sys_Role_User` ENABLE KEYS */;
UNLOCK TABLES;
# Dump of table Sys_User
# ------------------------------------------------------------
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `Sys_User`;
CREATE TABLE `Sys_User` (
`id` int(11) unsigned NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`username` varchar(200) DEFAULT NULL,
`password` varchar(200) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
LOCK TABLES `Sys_User` WRITE;
/*!40000 ALTER TABLE `Sys_User` DISABLE KEYS */;
INSERT INTO `Sys_User` (`id`, `username`, `password`)
VALUES
(1,'admin','6d789d4353c72e4f625d21c6b7ac2982'),
(2,'user','36f1cab655c5252fc4f163a1409500b8');
/*!40000 ALTER TABLE `Sys_User` ENABLE KEYS */;
UNLOCK TABLES;
最後會生成5個表,分別是使用者表,角色表,許可權表,使用者角色中間表,角色許可權中間表。
配置包目錄
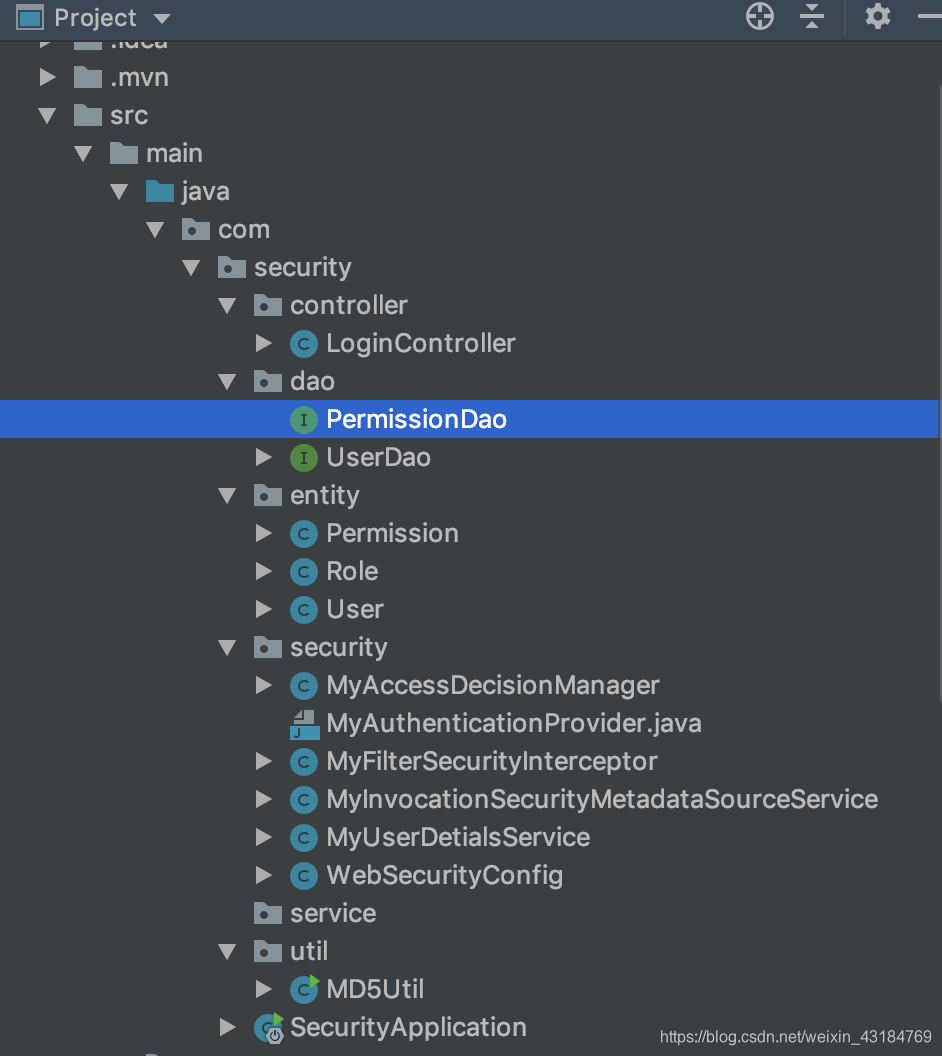
其中entity可以用idea進行生成,
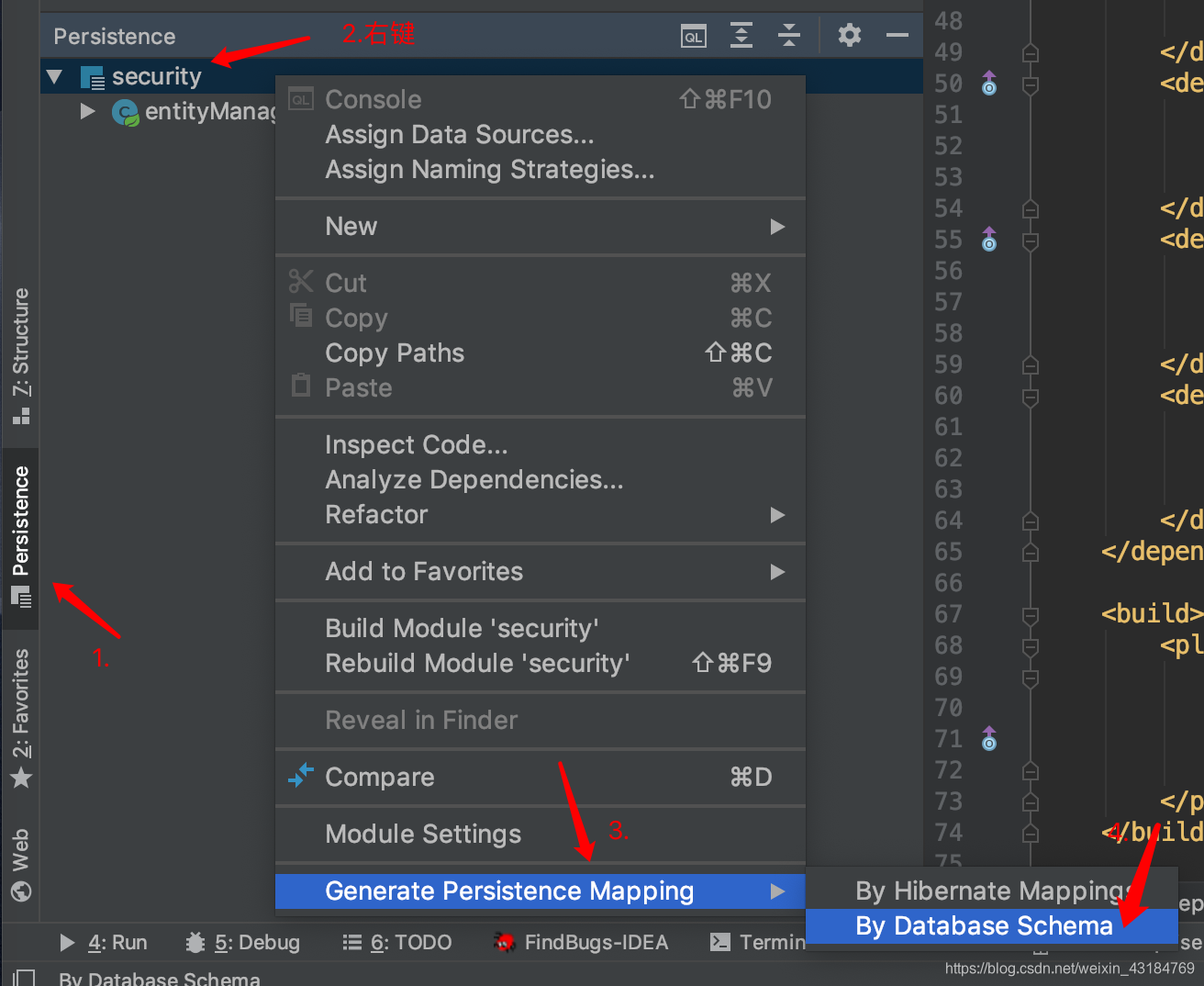
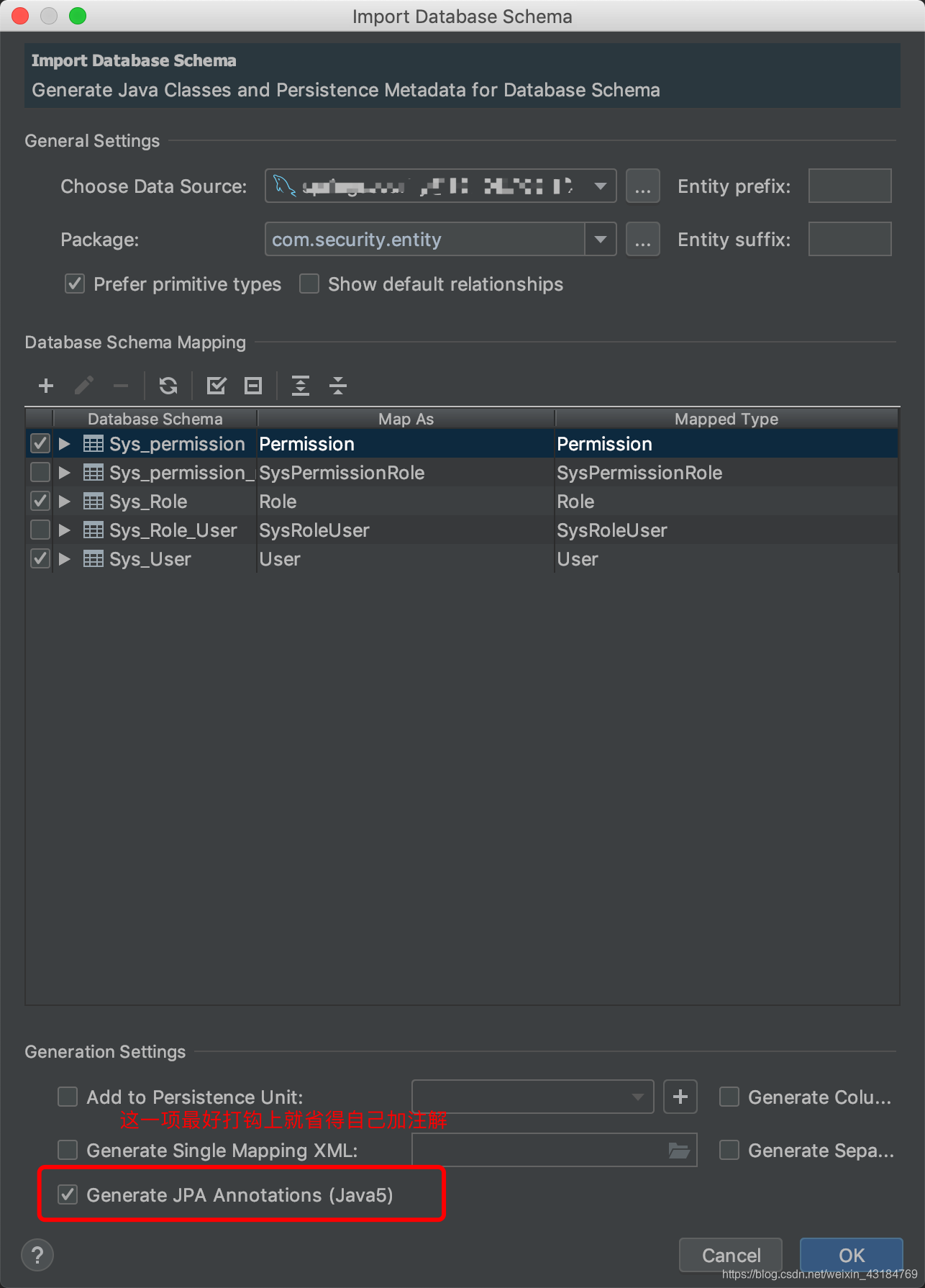
配置dao層
需要新建UserDao和PermissionDao兩個類
/**
* UserDao
*/
@Repository
public interface UserDao extends JpaRepository<User,Integer> {
//自定義一個根據姓名查詢使用者的方法
public User findByUsername(String userName);
}
/**
* PermissionDao
* 無需自定義方法,直接使用jpa封裝好的就可以
*/
public interface PermissionDao extends JpaRepository<Permission,Integer> {
}
配置Entity關係
在本demo中需要配置兩個關係,分別是使用者與角色的多對多關係,角色和許可權的多對多關係。
在User類中加入:
private List<Role> roles = new ArrayList<>();
/**
* @ManyToMany 表示多對多關係,fetch = FetchType.EAGER配置懶載入策略為立即載入,因為多對多涉及到樹形結構的第二層,
* 使用懶載入會在使用roles物件時才去資料庫查詢,但是在本專案中會出現no session,暫時無法解決,所以加上次配置
*
* @JoinTable name:中間表名, @joinColumn : name:在中間表中對應外來鍵名,referencedColumnName在原先表中的主鍵名
*
* inverseJoinColumns中的@joinColumn : name:多的另一方在中間表中對應的主鍵名,referencedColumnName在原先表中的主鍵名
*
* 此處的配置表明user和role的多對多關係由user維護
*/
@ManyToMany(fetch = FetchType.EAGER)
@JoinTable(name = "Sys_Role_User", joinColumns = {@JoinColumn(name = "Sys_User_id", referencedColumnName = "id")},
inverseJoinColumns = {@JoinColumn(name = "Sys_Role_id", referencedColumnName = "id")})
public List<Role> getRoles() {
return roles;
}
public void setRoles(List<Role> roles) {
this.roles = roles;
}
在Role中加入:
private List<User> users = new ArrayList<>();
//mappedBy:對映的名字為user中role集合的名字
@ManyToMany(mappedBy = "roles")
public List<User> getUsers() {
return users;
}
public void setUsers(List<User> users) {
this.users = users;
}
Permission和Role的多對多對映也是如此,就不貼出來了。
簡單的環境搭建就到此結束了,一切從簡所以沒有配置連線池。
SpringSecurity配置
我們先做個簡單的嘗試,在配置好以上步驟後,在template中加入一個名為index的頁面
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>登入成功</h1>
<h2><a href="/logout">退出</a></h2>
</body>
</html>
並建立一個LoginController,在controller中設定對映路徑為/index。
我們啟動專案,在位址列中輸入localhost:8080/index,你會發現自動跳轉到了一個登陸介面,我們完全沒有寫過 登陸介面,所以這個是springsecurity自帶的一個登入頁,登陸的使用者名稱為user,密碼是輸出在console中的uuid字串。
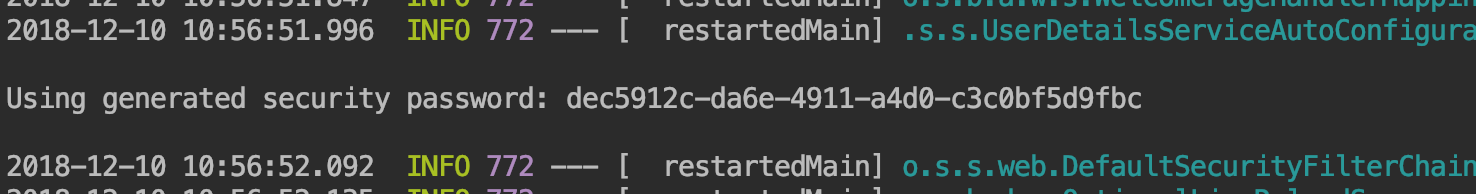 登陸以後就可以訪問Index頁面了。在我們配置Security之前,它預設攔截所有頁面並會自動生成一個登陸的賬號密碼,但這顯然不是我們想要的樣子。下面我們對它進行改造。
登陸以後就可以訪問Index頁面了。在我們配置Security之前,它預設攔截所有頁面並會自動生成一個登陸的賬號密碼,但這顯然不是我們想要的樣子。下面我們對它進行改造。
配置攔截策略
首先我們在security包下建立一個類,名字為WebSecurityConfig,繼承WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter
//這兩個註解缺一不可
@Configuration
@EnableWebSecurity
public class WebSecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
//重寫引數為HttpSecurity的configure方法,配置攔截策略
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http
//自定義登陸頁面
.formLogin().loginPage("/login")
//登陸成功後跳轉的頁面
.defaultSuccessUrl("/index")
//登陸失敗或無許可權跳轉頁面
.failureUrl("/login-error")
.permitAll()
//其他所有頁面必須驗證後才可以訪問
.and().authorizeRequests().anyRequest().authenticated()
//不加上不驗證。不知道為什麼
.and().csrf().disable();
}
}
引用網上的圖片
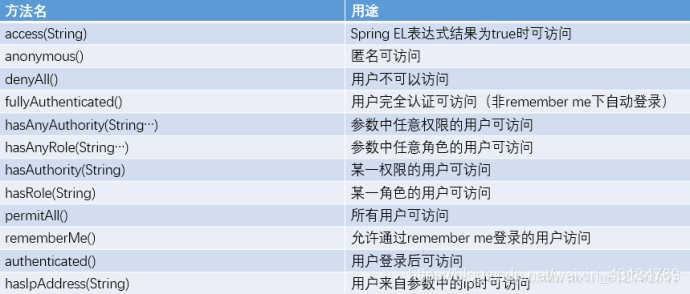 順帶建立兩個HTML
順帶建立兩個HTML
login.html
<form class="form-signin" action="/login" method="post">
<h2 class="form-signin-heading">使用者登入</h2>
<table>
<tr>
<td>使用者名稱:</td>
<td><input type="text" name="username" class="form-control" placeholder="請輸入使用者名稱"/></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>密碼:</td>
<td><input type="password" name="password" class="form-control" placeholder="請輸入密碼" /></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td colspan="2">
<button type="submit" class="btn btn-lg btn-primary btn-block" >登入</button>
</td>
</tr>
</table>
</form>
error.html
<h1>error</h1>
此時再執行專案,輸入localhost:8080/跳轉到的頁面就是我們剛才寫好的頁面了,隨便輸入賬號密碼點選登入的報錯頁面也是剛剛新增的error頁面。
自定義登陸賬號驗證
實際開發中我們需要在資料庫中儲存使用者的賬號密碼資訊,所以我們需要自定義驗證方式。
在security資料夾中建立MyUserDetialsService類 實現UserDetailsService介面
@Service
public class MyUserDetialsService implements UserDetailsService {
@Autowired
UserDao userDao;
@Override
public UserDetails loadUserByUsername(String userName) throws UsernameNotFoundException {
//此處的user是entity包中的user
com.security.entity.User user = userDao.findByUsername(userName);
if (user != null) {
List<GrantedAuthority> grantedAuthorities = new ArrayList<>();
//獲取使用者的角色集合
List<Role> roles = user.getRoles();
//遍歷角色集合,並獲取每個角色擁有的許可權
for (Role role : roles) {
List<Permission> permissions = role.getPermissions();
for (Permission permission :permissions) {
//為每個授權中心物件寫入許可權名
grantedAuthorities.add(new SimpleGrantedAuthority(permission.getName()));
}
}
/**此處的user是springsecurity中的一個實現了UserDetails介面的user類,因為我們沒有將entity中的user去實現
* UserDetails介面,所以只能在此處呼叫實現好的構造方法
*/
return new User(user.getUsername(), user.getPassword(), grantedAuthorities);
}
return null;
}
}
此處我們的密碼使用MD5配合加密鹽進行加密,所以需要在utils包中建立MD5Utils類
public class MD5Util {
private static final String SALT = "tamboo";
public static String encode(String password) {
password = password + SALT;
MessageDigest md5 = null;
try {
md5 = MessageDigest.getInstance("MD5");
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
char[] charArray = password.toCharArray();
byte[] byteArray = new byte[charArray.length];
for (int i = 0; i < charArray.length; i++)
byteArray[i] = (byte) charArray[i];
byte[] md5Bytes = md5.digest(byteArray);
StringBuffer hexValue = new StringBuffer();
for (int i = 0; i < md5Bytes.length; i++) {
int val = ((int) md5Bytes[i]) & 0xff;
if (val < 16) {
hexValue.append("0");
}
hexValue.append(Integer.toHexString(val));
}
return hexValue.toString();
}
}
在先前建立好的WebSecurityConfig中加入如下配置:
//注入我們剛才寫好的service類
@Autowired
MyUserDetialsService userService;
//配置加密
@Override
protected void configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception {
auth.userDetailsService(userService).passwordEncoder(new PasswordEncoder() {
//加密
@Override
public String encode(CharSequence rawPassword) {
return MD5Util.encode((String) rawPassword);
}
//解密,前者是輸入的密碼,後者是資料庫查詢的密碼
@Override
public boolean matches(CharSequence rawPassword, String encodedPassword) {
return encodedPassword.equals(MD5Util.encode((String) rawPassword));
}
});
}
實際上我們剛才寫的程式碼中並沒有對密碼進行驗證,SpringSecurity中已經在內部寫好了驗證程式碼,我們只需要將查詢到的user物件轉換為UserDetail物件返回給框架即可。此時再次執行demo登陸的賬號密碼就可以使用資料庫中自定義的了,我目前設定的預設賬號密碼為admin:admin,user:user。
配置自定義許可權驗證
在security包下建立MyInvocationSecurityMetadataSourceService實現FilterInvocationSecurityMetadataSource介面。該類用於載入許可權表中的url資訊,並和request的url進行對比,有匹配則將該URL所需要的許可權返回給decide()方法,不存在則返回空
@Service
public class MyInvocationSecurityMetadataSourceService implements FilterInvocationSecurityMetadataSource {
@Autowired
private PermissionDao permissionDao;
private HashMap<String, Collection<ConfigAttribute>> map = null;
//在demo啟動第一個使用者登陸後,載入所有許可權進map
public void loadResourceDefine() {
map = new HashMap<>();
Collection<ConfigAttribute> array;
ConfigAttribute cfg;
List<Permission> permissions = permissionDao.findAll();
for (Permission permission : permissions) {
array = new ArrayList<>();
//此處只添加了使用者的名字,其實還可以新增更多許可權的資訊,例如請求方法到ConfigAttribute的集合中去。此處新增的資訊將會作為MyAccessDecisionManager類的decide的第三個引數。
cfg = new SecurityConfig(permission.getName());
array.add(cfg);
//用許可權的getUrl() 作為map的key,用ConfigAttribute的集合作為 value
map.put(permission.getUrl(), array);
}
}
@Override
public Collection<ConfigAttribute> getAttributes(Object object) throws IllegalArgumentException {
if(map ==null) {
loadResourceDefine();
}
HttpServletRequest request = ((FilterInvocation) object).getHttpRequest();
AntPathRequestMatcher matcher;
//遍歷許可權表中的url
for (String url : map.keySet()) {
matcher = new AntPathRequestMatcher(url);
//與request對比,符合則說明許可權表中有該請求的URL
if(matcher.matches(request)) {
return map.get(url);
}
}
return null;
}
@Override
public Collection<ConfigAttribute> getAllConfigAttributes() {
return null;
}
@Override
public boolean supports(Class<?> aClass) {
return true;
}
}
接著在security下新建MyAccessDecisionManager類實現AccessDecisionManager介面。該類為決策類,決策該使用者的request是否有許可權訪問。
@Service
public class MyAccessDecisionManager implements AccessDecisionManager {
/**
* @param authentication UserService中迴圈新增到GrantedAuthority中的許可權資訊集合
* @param object 包含客戶端發起的請求的request資訊,可以轉換為HTTPRequest
* @param collection url所需的許可權集合
* @throws AccessDeniedException
* @throws InsufficientAuthenticationException
*/
@Override
public void decide(Authentication authentication, Object object, Collection<ConfigAttribute> collection) throws AccessDeniedException, InsufficientAuthenticationException {
//判斷URL所需的許可權集合是否為空,為空則放行
if (null == collection || collection.size() <= 0) {
return;
}
String needPermission;
for (ConfigAttribute c : collection) {
//獲得所需的許可權
needPermission = c.getAttribute();
//遍歷使用者擁有的許可權與URL所需的許可權進行對比
for (GrantedAuthority ga : authentication.getAuthorities()) {
if (needPermission.trim().equals(ga.getAuthority())){
return;
}
}
}
throw new AccessDeniedException("no permission");
}
@Override
public boolean supports(ConfigAttribute configAttribute) {
return true;
}
@Override
public boolean supports(Class<?> aClass) {
return true;
}
}
最後在security包下建立MyFilterSecurityInterceptor類
@Service
public class MyFilterSecurityInterceptor extends AbstractSecurityInterceptor implements Filter {
@Autowired
private FilterInvocationSecurityMetadataSource securityMetadataSource;
//設定決策器
@Autowired
public void setMyAccessDecisionManager(MyAccessDecisionManager myAccessDecisionManager) {
super.setAccessDecisionManager(myAccessDecisionManager);
}
@Override
public void init(FilterConfig filterConfig) throws ServletException {
}
@Override
public void doFilter(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response, FilterChain chain) throws IOException, ServletException {
FilterInvocation fi = new FilterInvocation(request, response, chain);
invoke(fi);
}
public void invoke(FilterInvocation fi) throws IOException, ServletException {
//fi裡面有一個被攔截的url
//裡面呼叫MyInvocationSecurityMetadataSource的getAttributes(Object object)這個方法獲取fi對應的所有許可權
//再呼叫MyAccessDecisionManager的decide方法來校驗使用者的許可權是否足夠
InterceptorStatusToken token = super.beforeInvocation(fi);
try {
//執行下一個攔截器
fi.getChain().doFilter(fi.getRequest(), fi.getResponse());
} finally {
super.afterInvocation(token, null);
}
}
@Override
public void destroy() {
}
@Override
public Class<?> getSecureObjectClass() {
return FilterInvocation.class;
}
//新增判斷url所需的許可權類
@Override
public SecurityMetadataSource obtainSecurityMetadataSource() {
return this.securityMetadataSource;
}
}
建立
admin.html
<p class="bg-info">Admin許可權訪問</p>
index2.html
<p>這是沒錄入資料庫的url</p>
user.html
<p>User許可權訪問</p>
將這些頁面加入controller對映。
資料庫中設定的關係為:
| 使用者 | 角色 | 許可權 |
|---|---|---|
| admin | ROLE_USER,ROLE_ADMIN | ROLE_ADMIN,ROLE_HOME,ROLE_User |
| user | ROLE_USER | ROLE_HOME,ROLE_User |
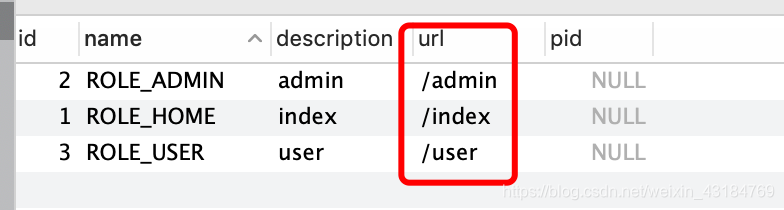 許可權表中對映的URL如圖。
許可權表中對映的URL如圖。
執行demo
結果如下:
登陸admin賬號,所有頁面都可以訪問
登陸user賬號,除了/admin無許可權訪問,其他都可以訪問。
/index2沒有錄入資料庫,但是在任何使用者登陸以後都可以訪問。
原始碼地址:
https://gitee.com/king176/springbootdemo_source_code/tree/master
