安卓之佈局總結
Adroid佈局
有人形象地比喻,Android開發中的佈局就相當於一棟建築的外觀架構。佈局用得好,這棟建築的外觀才美觀高大上。
Android佈局管理器
Android佈局管理器本身是一個介面控制元件,所有的佈局管理器都是ViewGroup類的子類,都是可以當做容器類來使用的。因此一個佈局管理器中可以巢狀其他的佈局管理器。
這是谷歌上找的一張佈局管理器層級圖

每一個ViewGroup都可以巢狀其他的ViewGroup和View(檢視)。一個ViewGroup的大小是相對的,它即可以是其他ViewGroup的父容器,也可以是其他ViewGroup的子容器。在Android中,ViewGroup指代的是佈局管理器,也就是下面要講的佈局樣式,View指代的是佈局管理器中的一個個控制元件。在Android中,控制元件可以在XML檔案中定義,也可以程式設計師根據自己的需要去定義一個類。本文重點先不討論檢視中的控制元件,還是迴歸到佈局。
Android六大基本佈局管理器分別是:
線性佈局(LinearLayout)、表格佈局(TableLayout)、網格佈局(GridLayout)、相對佈局(RelativeLayout)、絕對佈局(AbsoluteLayout)、層佈局(FrameLayout)
其中,表格佈局是線性佈局的子類。網格佈局是android 4.0後新增的佈局。
(1)線性佈局
線性佈局會將容器內的所有控制元件一個挨著一個地排列。
屬性:
1. 排列方向
android:orienation = “ horizontal/vertical”
水平排列和垂直排列,Android中預設為垂直排列vertical
注意:預設情況下水平和垂直方向的排列只佔一行,如果用android:layout_width來設定控制元件的寬度,如果控制元件寬度太大,超出螢幕的顯示範圍,螢幕是不會顯示超出的範圍的。
2. 對齊方式
用於控制元素(例如文字)在該控制元件裡的顯示位置。
屬性值:
可選的值有:top、bottom、left、right、center_vertical、fill_vertical、center_horizontal、fill_horizontal、center、fill、clip_vertical
也可以同時使用兩個屬性值,中間用 | 豎線隔開
例如:
android:gravity = “buttom|center_horizontal”
如果定義在控制元件中的底部,垂直居中
舉一個簡單例子,我用LinearLayout線性佈局來實現常用的計算器
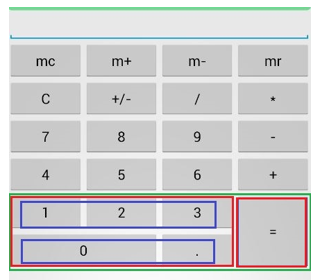
前面四行都很容易理解,用一個Linearout來包裹4個button控制元件,並且設定排列方向為水平方向。這裡只列出其中一行的佈局程式碼,其他三行的程式碼與第一行幾乎相同。
<LinearLayout android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:orientation="horizontal" > <Button android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="mc" android:layout_weight="1"> //layout_weight設定水平佈局中控制元件的佔比 </Button> <Button android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="m+" android:layout_weight="1"> </Button> <Button android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="m-" android:layout_weight="1"> </Button> <Button android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="mr" android:layout_weight="1"> </Button> </LinearLayout>
最關鍵的是下面兩行,即用綠色框框住的那一部分控制元件如何佈局。這裡我使用佈局控制器內部巢狀佈局控制器的方法。首先將綠色框內部的控制元件分成三個層級(我分別用不同顏色標註出來了)。第一個層級是綠色框,包含兩個兩列,即兩個紅色框。第二個層級是紅色框,每個紅色框看成一個整體的列,第一個列是左邊的紅色框,其內部包含兩個行;第二個列是右邊的紅色框,即“=”號,包含一個垂直佈局的列,佔位兩行。再對左邊的紅色框進行第三層級的拆分。可以拆分成兩行,每一行佔3個位。
於是就有下面的程式碼:
<!--綠色框--> <LinearLayout android:orientation="horizontal" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content"> <!--紅色框--> <LinearLayout android:orientation="vertical" android:layout_weight="3" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content"> <!--藍色框--> <LinearLayout android:orientation="horizontal" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content"> <Button android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_weight="1" android:text="1"></Button> <Button android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_weight="1" android:text="2"></Button> <Button android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_weight="1" android:text="3"></Button> </LinearLayout> <!--藍色框 --> <LinearLayout android:orientation="horizontal" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content"> <Button android:layout_width="0px" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_weight="2" android:text="0"> </Button> <Button android:layout_width="0px" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_weight="1" android:text="."> </Button> </LinearLayout> </LinearLayout> <!--紅色框,=號--> <LinearLayout android:orientation="vertical" android:layout_weight="1" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="match_parent"> <Button android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:text="="> </Button> </LinearLayout> </LinearLayout>
(2)相對佈局
相對佈局是最靈活的一種佈局方式,可以相對父容器和相對與其他控制元件進行佈局。
主要引數有:
1. 是否對齊父容器的語法格式為true/false:
例如:android:layout_alignParentLeft = “true”
2. 為於給定ID控制元件不同方位的語法格式:
例如:android:layout_above="@id/btn1"
@id/btn1 控制元件的ID必須是事前已經定義好的
android:layout_alignParentLeft 該控制元件是否對齊父容器的左端
android:layout_alignParentRight 該控制元件是否齊其父容器的右端
android:layout_alignParentTop 該控制元件是否對齊父容器的頂部
android:layout_alignParentBottom 該控制元件是否對齊父容器的底部
android:layout_centerInParent 該控制元件是否相對於父容器居中
android:layout_toLeftOf 該控制元件位於給定ID控制元件的左方
android:layout_toRightOf 該控制元件位於給定ID控制元件的右方
android:layout_above 該控制元件位於給定ID控制元件的上方
android:layout_below 該控制元件位於給定ID控制元件的下方
android:layout_centerHorizontal 該控制元件是否橫向居中
android:layout_centerVertical 該控制元件是否垂直居中
例項程式碼:
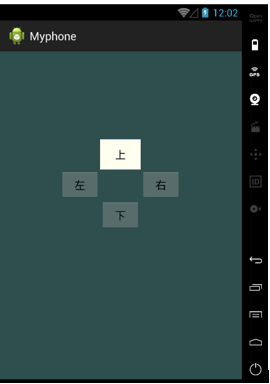
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:background="@color/darkslategray" > <Button android:id="@+id/btn1" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_centerInParent="true" android:layout_centerHorizontal="true" android:text="下"> </Button> <Button android:id="@+id/btn2" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_toLeftOf="@id/btn1" android:layout_above="@id/btn1" android:text="左"> </Button> <Button android:id="@+id/btn3" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_toRightOf="@id/btn1" android:layout_above="@id/btn1" android:text="右"> </Button> <Button android:id="@+id/btn4" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_toRightOf="@id/btn2" android:layout_above="@id/btn2" android:background="@color/white" android:text="上"> </Button> </RelativeLayout>
效果圖
(3)表格佈局
表格佈局是最規整的一種佈局方式。想象一下EXCEL表格規整的行和列,android佈局管理器中的TableLayout與EXCEL中的單元格有不少相似之處。如果學過HTML,用過tbale,tr,td標籤,應該也會對下面的用法有更好的理解。
表格佈局由一個TableLayout包裹起來,內部是一行行的控制元件,每一行用一個TableRow來包裹,每一行的元素個數(即列數)都是可以不同的。預設情況下,一行中的所有控制元件是等寬的。
控制元件屬性,在TableLayout中定義,對所有行起作用:
1. android:collapseColumns=”” #指定被隱藏的列的序號
2. android:shrinkColumns=”” #指定被收縮的列的列序號
3. android:stretchColumns=”” #指定被拉伸的列的列序號
4. android:layout_column="3": #表示跳過第三個控制元件,直接顯示下一個控制元件,注意:這個屬性從1開始計數
5. android:layout_span="3" #表示合併3個單元格,也就說這個元件佔3個單元格
注意:上面屬性的使用場合,是在TableLayout還是在TableRow中使用;如果是在TableRow中使用,需要在TableRow的子控制元件中新增屬性。前四個屬性都是新增在TableLayout中的,最是新增在TableRow的子控制元件中。
例項:
就以我們平常用的日曆為案例(由於螢幕太小,放不下最後一列星期六的日期)
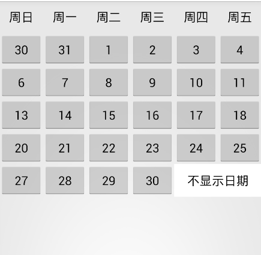
例項程式碼:
由於以下程式碼有很多相似之處,我只截取了比較重要的一部分
1. 總體框架
<TableLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:id="@+id/TableLayout2" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" > <TableRow> <Button android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="週日" android:background="#00000000"/> #去除button控制元件的樣式 <Button android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="週一" android:background="#00000000"/> <Button android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="週二" android:background="#00000000"/> <Button android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="週三" android:background="#00000000" /> <Button android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="週四" android:background="#00000000"/> <Button android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="週五" android:background="#00000000" /> <Button android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="週六" android:background="#00000000" /> </TableRow> <TableRow> ... ... </TableRow> ... ... ... ... </TableLayout>
2. 最後一行“不顯示日期”的合併單元格樣式
<Button android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="30" /> <Button android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_span="2" android:background="#ffffff" android:text="不顯示日期" />
(4)絕對佈局
絕對佈局指定每個控制元件在手機上的具體座標,每個控制元件的位置和大小是固定的。由於不同手機螢幕大小可能不同,所以絕對佈局只適用於固定的手機螢幕。平常用得比較少,這裡就不做詳細介紹了。
(5)層佈局
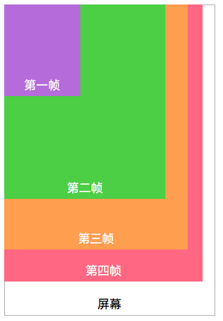
層佈局也叫幀佈局。每個控制元件佔據一層,後面新增的層會覆蓋前面的層。如果後面的層的大小大於或者等於前面的層,那麼前面的層就會被完全覆蓋。後面層中的控制元件就看不到了。實際應用中如果想要得到一個空間浮現在另一個控制元件的上方,可以在控制元件內部巢狀層佈局。
下面是層佈局的原理圖:
例項程式碼:
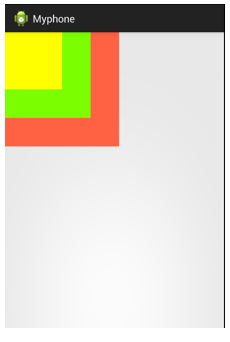
<FrameLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:id="@+id/FrameLayout1" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" tools:context=".MainActivity" android:foregroundGravity="right|bottom"> <TextView android:layout_width="200dp" android:layout_height="200dp" android:background="#FF6143" /> //橙色 <TextView android:layout_width="150dp" android:layout_height="150dp" android:background="#7BFE00" /> //綠色 <TextView android:layout_width="100dp" android:layout_height="100dp" android:background="#FFFF00" /> //黃色 </FrameLayout>
效果圖,每一個textview都會被前一個textview覆蓋:
實際應用:
在手機程式設計中,絕對佈局基本上不用,用得相對較多的是線性佈局和相對佈局。
