【資訊科技】【2006.12】人工耳蝸在噪聲環境中更好地識別旋律並改善語音理解的訊號處理策略
本文為美國德克薩斯大學達拉斯分校(作者:KALYAN S. KASTURI)的電子工程碩士論文,共194頁。
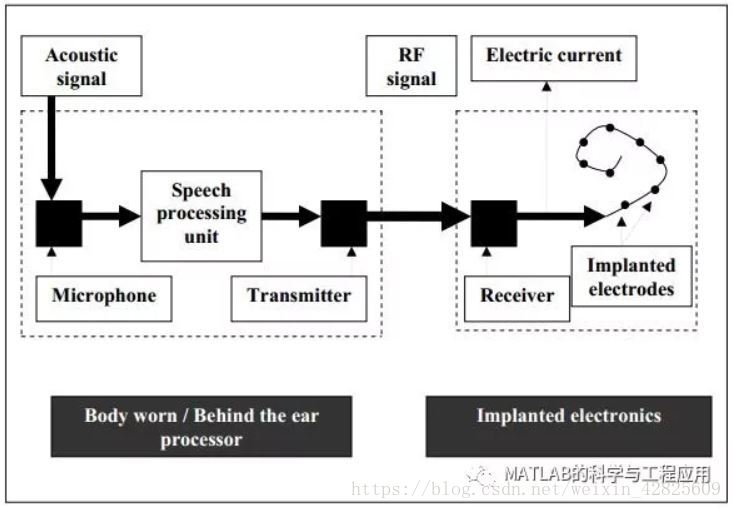
人工耳蝸是由植入電極和訊號處理器組成的裝置,設計用於恢復深度耳聾人群的部分聽力。自上世紀70年代初人工耳蝸誕生以來,逐漸得到廣泛普及,因此已經進行了大量的研究來推動並改進人工耳蝸技術。到目前為止,在人工耳蝸領域進行的大部分研究主要集中於改善安靜無噪聲(或低噪聲)狀態下的語音感知。在嘈雜的聽力環境下,音樂和言語感知仍然是極具挑戰性的問題。許多研究表明人工耳蝸在簡單旋律識別任務中的識別分數較低。大多數人工耳蝸裝置採用訊號的包絡幅度來提供電刺激。瞭解人工耳蝸植入過程中各種因素對旋律識別的影響,對於改進現有的編碼策略具有重要意義。
本文研究了濾波器間距、相對相位、譜上移、載頻和相位擾動等因素對聲學聽覺旋律識別的影響。目前用於人工耳蝸的濾波器間距大於音樂半音階梯,因此並非所有音符都能夠被解析。在當前的工作中,我們研究了稱為“半音階濾波器間距”的新技術,其中濾波器頻寬根據音樂半音階梯變化。迄今為止所研究的用於人工耳蝸的降噪方法大多是預處理方法。在這些方法中,首先使用降噪增強語音訊號,然後使用語音處理器處理增強的訊號。一種更好和更有效的方法是將降噪機制整合到人工耳蝸訊號處理中。本文研究了兩種嵌入設計的噪聲抑制方法,即“信噪比加權法”和“S形壓縮法”,分析了兩種方法在噪聲環境下改善語音感知的效果。信噪比加權降噪方法是一種指數加權法,使用瞬時信噪比(SNR)估計實現人工耳蝸中特定電極對應的每個頻帶的降噪。S形壓縮法基於噪聲估計將壓縮曲線劃分為兩個區域,該方法對噪聲部分和語音部分應用不同型別的壓縮,因此與常規冪律壓縮相比能夠更好地抑制噪聲。
Cochlear implants are prosthetic devices, consisting of implantedelectrodes and a signal processor and are designed to restore partial hearingto the profoundly deaf community. Since their inception in early 1970s cochlearimplants have gradually gained popularity and consequently considerableresearch has been done to advance and improve the cochlear implant technology.Most of the research conducted so far in the field of cochlear implants hasbeen primarily focused on improving speech perception in quiet. Musicperception and speech perception in noisy listening conditions with cochlearimplants are still highly challenging problems. Many research studies havereported low recognition scores in the task of simple melody recognition. Mostof the cochlear implant devices use envelope cues to provide electricstimulation. Understanding the effect of various factors on melody recognitionin the context of cochlear implants is important to improve the existing codingstrategies. In the present work we investigate the effect of various factorssuch as filter spacing, relative phase, spectral up-shifting, carrier frequencyand phase perturbation on melody recognition in acoustic hearing. The filterspacing currently used in the cochlear implants is larger than the musicalsemitone steps and hence not all musical notes can be resolved. In the currentwork we investigate the use of new filter spacing techniques called the‘Semitone filter spacing techniques’ in which filter bandwidths are varied in correspondenceto the musical semitone steps. Noise reduction methods investigated so far foruse with cochlear implants are mostly pre-processing methods. In these methods,the speech signal is first enhanced using the noise reduction method and theenhanced signal is then processed using the speech processor. A better and moreefficient approach is to integrate the noise reduction mechanism into thecochlear implant signal processing. In this dissertation we investigate the useof two such embedded noise reduction methods namely, the ‘SNR weighting method’and the ‘S-shaped compression’ to improve speech perception in noisy listeningconditions. The SNR weighting noise reduction method is an exponential weightingmethod that uses the instantaneous signal to noise ratio (SNR) estimate toperform noise reduction in each frequency band that corresponds to a particularelectrode in the cochlear implant. The S-shaped compression technique dividesthe compression curve into two regions based on the noise estimate. This methodapplies a different type of compression for the noise portion and the speechportion and hence better suppresses the noise compared to the regular power-lawcompression.
1 引言
2 人工耳蝸簡介
3 文獻回顧
4 利用人工耳蝸改善旋律識別的策略
5 噪聲環境下人工耳蝸實現更優語音感知的策略
6 結論
下載英文原文地址:
更多精彩文章請關注微訊號: