AI探索(四)NumPy庫的使用
NumPy(Numerical Python)
是 Python 語言的一個擴充套件程式庫,支援大量的維度陣列與矩陣運算,此外也針對陣列運算提供大量的數學函式庫。
umPy 是一個執行速度非常快的數學庫,主要用於陣列計算,包含:
- 一個強大的N維陣列物件 ndarray
- 廣播功能函式
- 整合 C/C++/Fortran 程式碼的工具
- 線性代數、傅立葉變換、隨機數生成等功能
NumPy 通常與 SciPy(Scientific Python)和 Matplotlib(繪相簿)一起使用, 這種組合廣泛用於替代 MatLab,是一個強大的科學計算環境,有助於我們通過 Python 學習資料科學或者機器學習。
SciPy 是一個開源的 Python 演算法庫和數學工具包。
SciPy 包含的模組有最優化、線性代數、積分、插值、特殊函式、快速傅立葉變換、訊號處理和影象處理、常微分方程求解和其他科學與工程中常用的計算。
Matplotlib 是 Python 程式語言及其數值數學擴充套件包 NumPy 的視覺化操作介面。它為利用通用的圖形使用者介面工具包,如 Tkinter, wxPython, Qt 或 GTK+ 嚮應用程式嵌入式繪圖提供了應用程式介面(API)。
NumPy 最重要的一個特點是其 N 維陣列物件 ndarray,它是一系列同類型資料的集合,以 0 下標為開始進行集合中元素的索引。
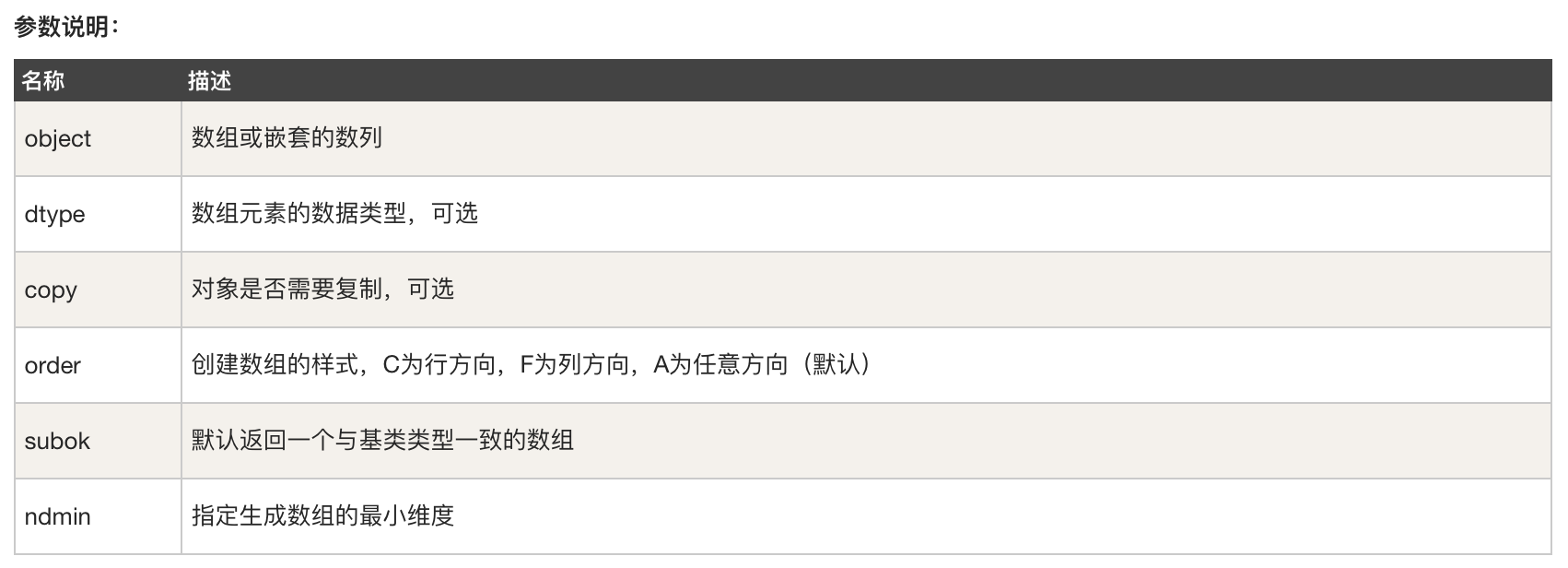
建立一個 ndarray 只需呼叫 NumPy 的 array 函式即可:
numpy.array(object, dtype = None, copy = True, order = None, subok = False, ndmin = 0)
示例1: 一維陣列
import numpy as np
a = np.array([1,2,3])
print a
輸出:
/usr/bin/python2.7 /Users/jackey/Documents/python/tensorflow/numpydemo.py
[1 2 3]
Process finished with exit code 0
示例2:二維陣列
import numpy as np
a = np.array([[1,2,3],[4,5,6]])
print a
輸出:
/usr/bin/python2.7 /Users/jackey/Documents/python/tensorflow/numpydemo.py
[[1 2 3]
[4 5 6]]
Process finished with exit code 0
示例3:二維陣列
import numpy as np
a = np.array([1,2,3],ndmin = 2)
print a
輸出:
/usr/bin/python2.7 /Users/jackey/Documents/python/tensorflow/numpydemo.py
[[1 2 3]]
Process finished with exit code 0
示例4:二維陣列
import numpy as np
a = np.array([1,2,3],ndmin = 2, dtype = complex)
print a
輸出:
/usr/bin/python2.7 /Users/jackey/Documents/python/tensorflow/numpydemo.py
[[1.+0.j 2.+0.j 3.+0.j]]
Process finished with exit code 0
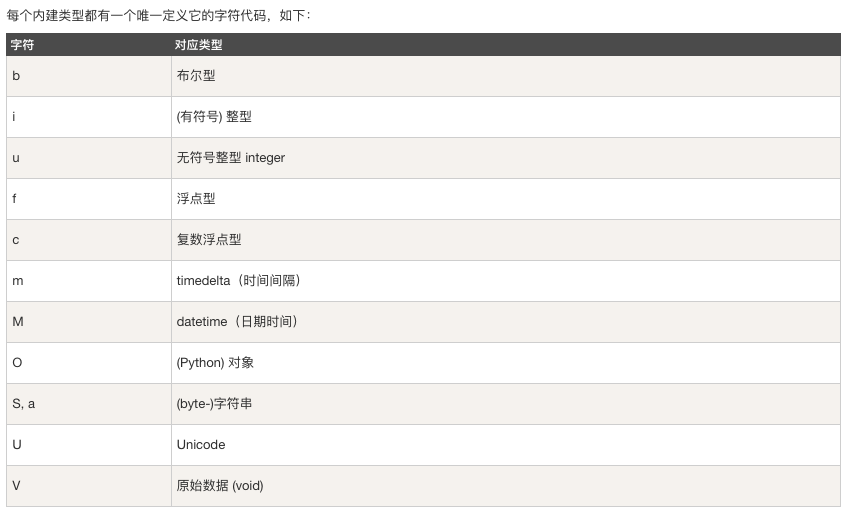
NumPy 資料型別
numpy 支援的資料型別比 Python 內建的型別要多很多,基本上可以和 C 語言的資料型別對應上,其中部分型別對應為 Python 內建的型別。
下表列舉了常用 NumPy 基本型別。

資料型別物件(dtype)
numpy.dtype(object, align, copy)
- object - 要轉換為的資料型別物件
- align - 如果為true, 填充欄位使其類似C的結構體
- copy - 複製dtype物件, 如果為false,則是對內建資料型別物件的引用
示例:
# -*- coding: UTF-8 -*-
import numpy as np
#使用標量型別
dt = np.dtype(np.int32)
print(dt)
# int8, int16, int32, int64 四種資料型別可以使用字串 'i1', 'i2','i4','i8' 代替
dt = np.dtype('i8')
print(dt)
輸出:
/usr/bin/python2.7 /Users/jackey/Documents/python/tensorflow/numpydemo.py
int32
int64
Process finished with exit code 0
下面例項展示結構化資料型別的使用,型別欄位和對應的實際型別將被建立
# -*- coding: UTF-8 -*- import numpy as np dt = np.dtype([('age',np.int8)]) print(dt) a = np.array([(10,),(20,),(30,)], dtype=dt) print(a) print(a['age'])
輸出:
/usr/bin/python2.7 /Users/jackey/Documents/python/tensorflow/numpydemo.py [('age', 'i1')] [(10,) (20,) (30,)] [10 20 30] Process finished with exit code 0
示例:
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*- import numpy as np student = np.dtype([('name','S20'), ('age','i1'), ('marks','f4')]) print(student) a = np.array([('abc',21,50),('xyz',18,75)], dtype=student) print(a)
輸出:
/usr/bin/python2.7 /Users/jackey/Documents/python/tensorflow/numpydemo.py [('name', 'S20'), ('age', 'i1'), ('marks', '<f4')] [('abc', 21, 50.) ('xyz', 18, 75.)] Process finished with exit code 0
Numpy陣列
NumPy 陣列的維數稱為秩(rank),一維陣列的秩為 1,二維陣列的秩為 2,以此類推。
在 NumPy中,每一個線性的陣列稱為是一個軸(axis),也就是維度(dimensions)。比如說,二維陣列相當於是兩個一維陣列,其中第一個一維陣列中每個元素又是一個一維陣列。所以一維陣列就是 NumPy 中的軸(axis),第一個軸相當於是底層陣列,第二個軸是底層數組裡的陣列。而軸的數量——秩,就是陣列的維數。
很多時候可以宣告 axis。axis=0,表示沿著第 0 軸進行操作,即對每一列進行操作;axis=1,表示沿著第1軸進行操作,即對每一行進行操作。
NumPy 的陣列中比較重要 ndarray 物件屬性有:
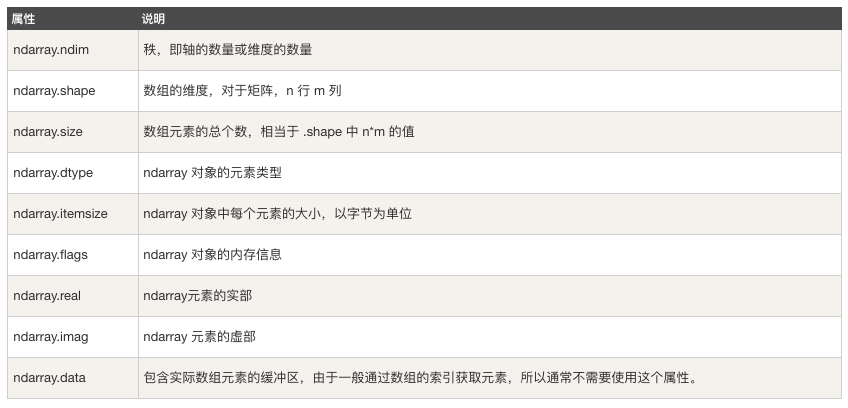
ndarray.ndim用於返回陣列的維數,等於秩
示例:
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*- import numpy as np a = np.arange(24) #a現在只有1個緯度 print(a.ndim)
輸出:
/usr/bin/python2.7 /Users/jackey/Documents/python/tensorflow/numpydemo.py 1 Process finished with exit code 0
ndarray.shape
ndarray.shape 表示陣列的維度,返回一個元組,這個元組的長度就是維度的數目,即 ndim 屬性(秩)。比如,一個二維陣列,其維度表示"行數"和"列數"。
ndarray.shape 也可以用於調整陣列大小。
示例:
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*- import numpy as np a = np.array([[1,2,3],[4,5,6]]) print(a.shape) a.shape = (6,1) print(a) a.shape = (1,6) print(a)
輸出:
/usr/bin/python2.7 /Users/jackey/Documents/python/tensorflow/numpydemo.py (2, 3) [[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] [6]] [[1 2 3 4 5 6]] Process finished with exit code 0
ndarray.itemsize
ndarray.itemsize 以位元組的形式返回陣列中每一個元素的大小。
例如,一個元素型別為 float64 的陣列 itemsiz 屬性值為 8(float64 佔用 64 個 bits,每個位元組長度為 8,所以 64/8,佔用 8 個位元組),又如,一個元素型別為 complex32 的陣列 item 屬性為 4(32/8)。
示例:
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*- import numpy as np x = np.array([1,2,3,4,5],dtype=np.int8) print(x) print(x.itemsize) y = np.array([1,2,3,4,5], dtype=np.float64) print(y) print(y.itemsize)
輸出:
/usr/bin/python2.7 /Users/jackey/Documents/python/tensorflow/numpydemo.py [1 2 3 4 5] 1 [1. 2. 3. 4. 5.] 8 Process finished with exit code 0
ndarray 陣列除了可以使用底層 ndarray 構造器來建立外,也可以通過以下幾種方式來建立。
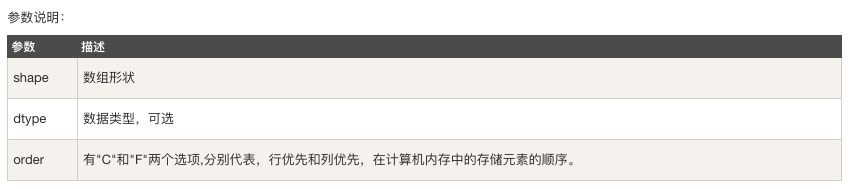
numpy.empty 方法用來建立一個指定形狀(shape)、資料型別(dtype)且未初始化的陣列:
numpy.empty(shape, dtype = float, order = 'C')
示例:
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*- import numpy as np x = np.empty([3,2], dtype=int) print(x)
輸出:
/usr/bin/python2.7 /Users/jackey/Documents/python/tensorflow/numpydemo.py [[ 0 -9223363263373412019] [ 140375703420932 140375703442528] [ 4345035248 140375703442504]] Process finished with exit code 0
注意 − 陣列元素為隨機值,因為它們未初始化。
numpy.zeros
建立指定大小的陣列,陣列元素以 0 來填充:
numpy.zeros(shape, dtype = float, order = 'C')
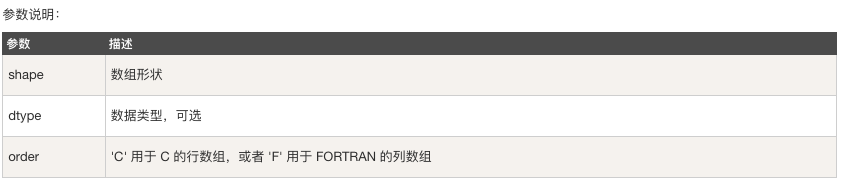
示例:
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*- import numpy as np # 預設為浮點數 x = np.zeros(5) print(x) # 設定型別為整數 y = np.zeros((5,), dtype=np.int) print(y) # 自定義型別 z = np.zeros((2,2), dtype=[('x', 'i4'), ('y','i4')]) print(z)
輸出:
/usr/bin/python2.7 /Users/jackey/Documents/python/tensorflow/numpydemo.py [0. 0. 0. 0. 0.] [0 0 0 0 0] [[(0, 0) (0, 0)] [(0, 0) (0, 0)]] Process finished with exit code 0
numpy.ones
建立指定形狀的陣列,陣列元素以 1 來填充:
numpy.ones(shape, dtype = None, order = 'C')
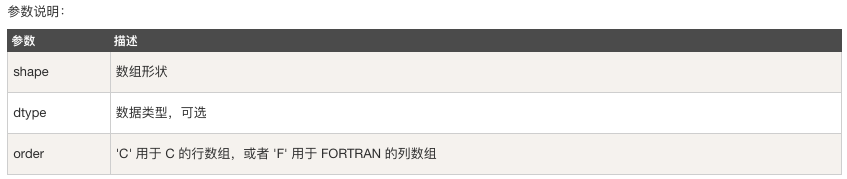
示例:
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*- import numpy as np # 預設為浮點數 x = np.ones(5) print(x) # 自定義型別 x = np.ones([2,2],dtype=int) print(x)
輸出:
/usr/bin/python2.7 /Users/jackey/Documents/python/tensorflow/numpydemo.py [1. 1. 1. 1. 1.] [[1 1] [1 1]] Process finished with exit code 0
建立標準正態分佈陣列:
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*- import numpy as np a = np.random.randn(2,3) print(a)
輸出:
/usr/bin/python2.7 /Users/jackey/Documents/python/tensorflow/numpydemo.py [[-0.16777072 1.15536929 0.15206009] [ 0.36466659 0.39643679 -1.06021005]] Process finished with exit code 0
建立隨機分佈整數型陣列。
利用 randint([low,high],size) 建立一個整數型指定範圍在 [low.high] 之間的陣列:
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*- import numpy as np a = np.random.randint(100,200,(3,3)) print(a)
輸出:
/usr/bin/python2.7 /Users/jackey/Documents/python/tensorflow/numpydemo.py [[172 166 115] [191 126 165] [195 171 198]] Process finished with exit code 0
從已有的陣列建立陣列
numpy.asarray
numpy.asarray 類似 numpy.array,但 numpy.asarray 只有三個,比 numpy.array 少兩個。
numpy.asarray(a, dtype = None, order = None)
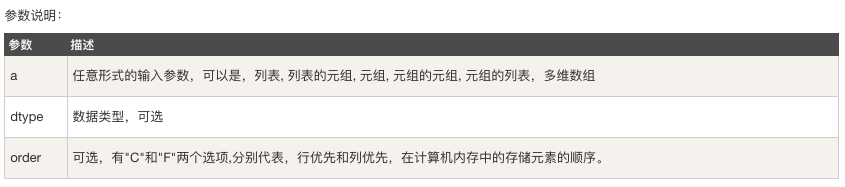
示例:
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*- import numpy as np # 將列表轉換為ndarray x = [1,2,3] a = np.asarray(x) print(a) # 將元組列表轉換為 ndarray x = [(1,2,3),(4,5)] a = np.asarray(x) print(a) # 設定了dtype引數 x = [1,2,3] a = np.asarray(x, dtype=float) print(a)
輸出:
/usr/bin/python2.7 /Users/jackey/Documents/python/tensorflow/numpydemo.py [1 2 3] [(1, 2, 3) (4, 5)] [1. 2. 3.] Process finished with exit code 0
numpy.frombuffer
numpy.frombuffer 用於實現動態陣列。
numpy.frombuffer 接受 buffer 輸入引數,以流的形式讀入轉化成 ndarray 物件。
numpy.frombuffer(buffer, dtype = float, count = -1, offset = 0)
注意:buffer 是字串的時候,Python3 預設 str 是 Unicode 型別,所以要轉成 bytestring 在原 str 前加上 b。
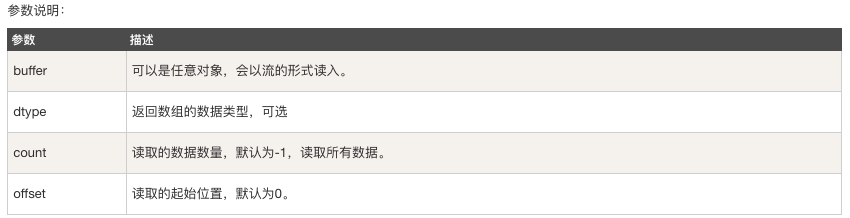
示例:
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*- import numpy as np s = 'Hello world!' a = np.frombuffer(s, dtype='S1') print(a)
輸出:
/usr/bin/python2.7 /Users/jackey/Documents/python/tensorflow/numpydemo.py ['H' 'e' 'l' 'l' 'o' ' ' 'w' 'o' 'r' 'l' 'd' '!'] Process finished with exit code 0
numpy.fromiter
numpy.fromiter 方法從可迭代物件中建立 ndarray 物件,返回一維陣列。
numpy.fromiter(iterable, dtype, count=-1)
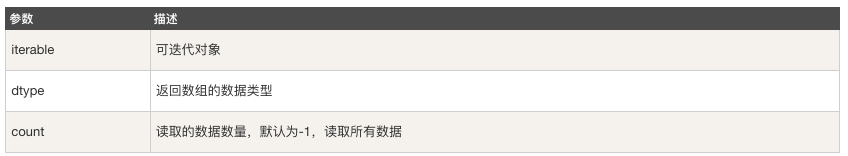
示例:
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*- import numpy as np # 使用 range 函式建立列表物件 list = range(5) it = iter(list) # 使用迭代器建立 ndarray x = np.fromiter(it, dtype=float) print(x)
輸出:
/usr/bin/python2.7 /Users/jackey/Documents/python/tensorflow/numpydemo.py [0. 1. 2. 3. 4.] Process finished with exit code 0
