【原】Andrew Ng斯坦福機器學習(1)——Lecture 1_Introduction and Basic Concepts
Lecture 1 Introduction and Basic Concepts
Lecture1 分4個視訊,主要講了
- 視訊1 - 2 - What is Machine Learning_ (7 min)
0、機器學習定義
• Arthur Samuel (1959). Machine Learning: Field of study that gives computers the ability to learn without being explicitly programmed. 機器學習:在進行特定程式設計的情況下,給予計算機學習能力的領域。 • Tom Mitchell (1998) Well-posed Learning Problem: A computer program is said to learn from
experience E with respect to some task T and some performance measure
P, if its performance on T, as measured by P, improves with experience
E. 卡內基梅隆大學Tom 定義:一個程式被認為能從經驗 E 中學習,解決任務 T,達到效能度量值P, 當且僅當,有了經驗 E 後,經過 P 評判,程式在處理 T 時的效能有所提升。
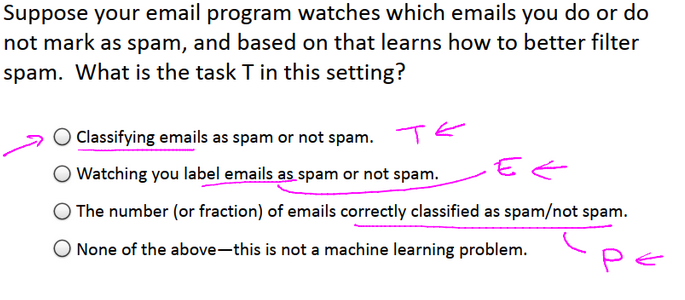
1、以垃圾郵件監測為例,解釋Tom 定義中字母的對應
例題:
2、機器學習演算法
常用:
- Supervised learning 監督學習 - Unsupervised learning 無監督學習
其他:
Reinforcement learning, recommender systems 強化學習和推薦系統
3、課程目的
If you actually tried to develop a machine learning system, how to make those best practices type decisions about the way in which you build your system。
如何在構建機器學習系統的時候選擇最好的實踐型別決策,節省時間。
- 1 - 3 - Supervised Learning (12 min)
1、Regression迴歸問題
迴歸問題:預測連續的輸出值
Housing price prediction
在歷史房價資料的基礎上,預測房屋價格。可以使用直線擬合(粉色),也可以使用二次曲線擬合(藍色)。
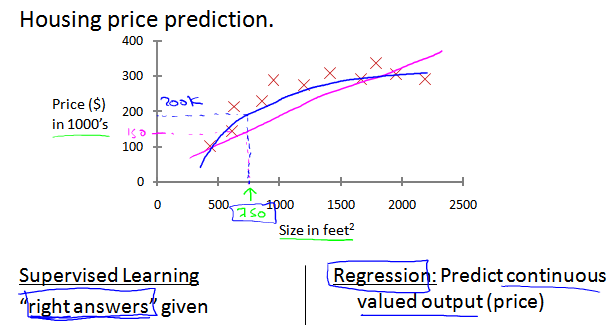
監督學習:基於已有的正確結果。 迴歸問題:預測連續的輸出值
2、Classification分類問題
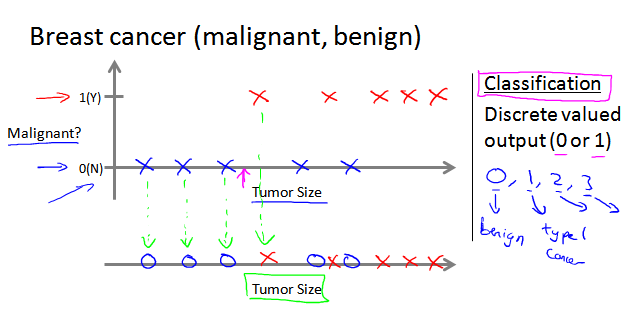
分類問題的預測結果是離散的多個值
腫瘤良性預測
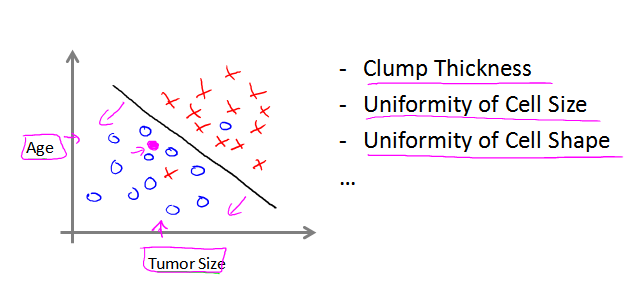
下圖是基於兩個特徵(兩個維度)進行預測的例子, 右邊是可能的其他維度(維度可能有無窮多個)
3、區分“分類問題”和“迴歸問題”
例題:

- 1 - 4 - Unsupervised Learning (14 min)
1、區分“監督學習”和“無監督學習”
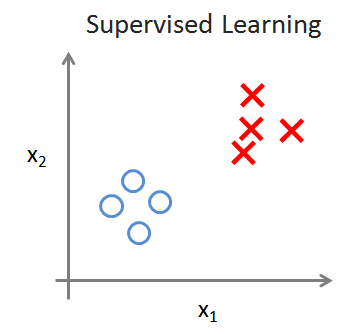
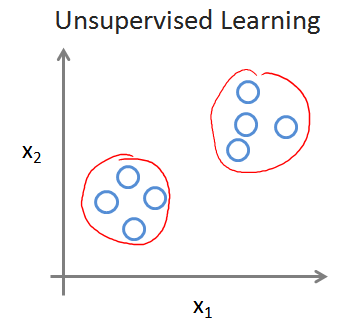
Supervised Learning:學習資料帶有標籤
Unsupervised Learning:沒有任何的標籤,或者有相同的標籤。已知資料集,不知如何處理,也未告知每個資料點是什麼。(右側的例子,無監督學習將資料劃分為兩個集合,也就是聚類clustering algorithm)
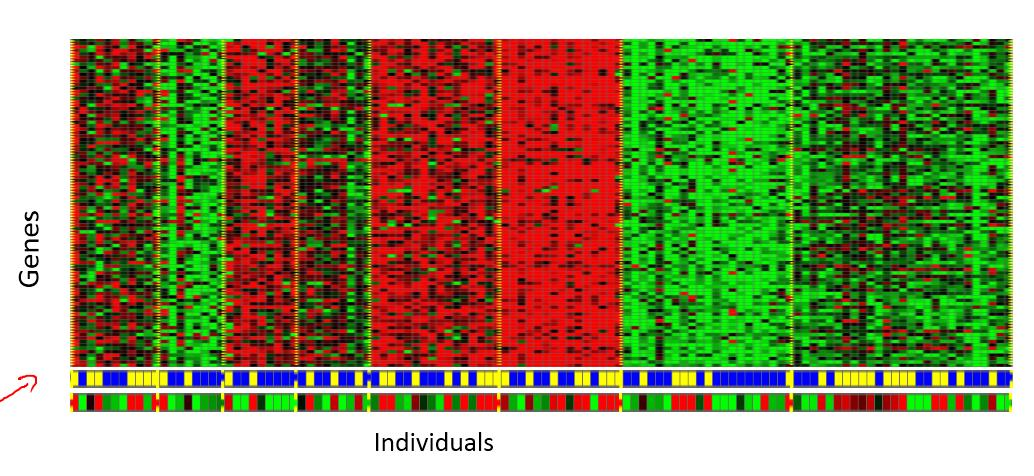
2、聚類演算法的例子
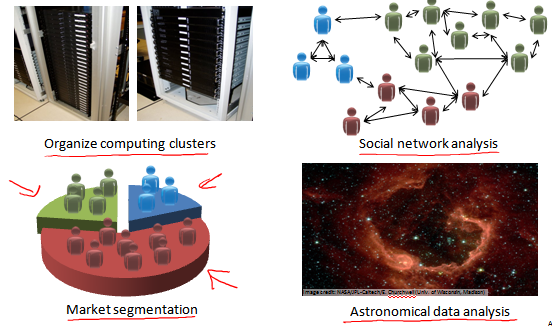
Google News 每天將爬來的網址分為一個個的新聞專題。 基因資訊分組。組織大型計算機叢集。 社交網路的分析。市場分割。天文資料分析
雞尾酒party問題,將混在一起的多個音訊源拆開。

在Octave裡只需要一行程式碼
[W,s,v] = svd((repmat(sum(x.*x,1),size(x,1),1).*x)*x');
