Virtual apk外掛化架構分析
其基本原理,就是hook系統的activity service等關鍵元件,當需要啟動外掛內的一些元件式,走自定義邏輯,當啟動本地apk中的元件時,走原生邏輯。
一、系統相關。
在分析滴滴外掛化框架之前,需要弄清楚android系統中應用的啟動流程,以及和系統的通訊排程相關。
有幾個關鍵類需要了解下:ActivityThread.java ApplicationThread.java ActivityManagerService.java Instrumentation.java
啟動流程如下:
在laucher裡面啟動一個新的app時,流程參考老羅文章:
整個應用程式的啟動過程要執行很多步驟,但是整體來看,主要分為以下五個階段:
一. Step1 -Step 11:Launcher通過Binder程序間通訊機制通知ActivityManagerService,它要啟動一個Activity;
二. Step 12 -Step 16:ActivityManagerService通過Binder程序間通訊機制通知Launcher進入Paused狀態;
三. Step 17 -Step 24:Launcher通過Binder程序間通訊機制通知ActivityManagerService,它已經準備就緒進入Paused狀態,於是ActivityManagerService就建立一個新的程序,用來啟動一個ActivityThread例項,即將要啟動的Activity就是在這個ActivityThread例項中執行;
四. Step 25 -Step 27:ActivityThread通過Binder程序間通訊機制將一個ApplicationThread型別的Binder物件傳遞給ActivityManagerService,以便以後ActivityManagerService能夠通過這個Binder物件和它進行通訊;
五. Step 28 -Step 35:ActivityManagerService通過Binder程序間通訊機制通知ActivityThread,現在一切備就緒,它可以真正執行Activity的啟動
ActivityManagerService:
這個是系統核心類,幾乎掌管了整個系統啟動相關的事宜。
ActivityThread:
它是一個應用程序的主執行緒,有一個死迴圈來分發程序需要處理的工作。
ApplicationThread:
用途參照啟動流程中的step4.
Instrumentation:
裡面的方法如下截圖,基本上管理了所有與Activity的相關互動工作。So,這個類需要被hook
二、原始碼分析。
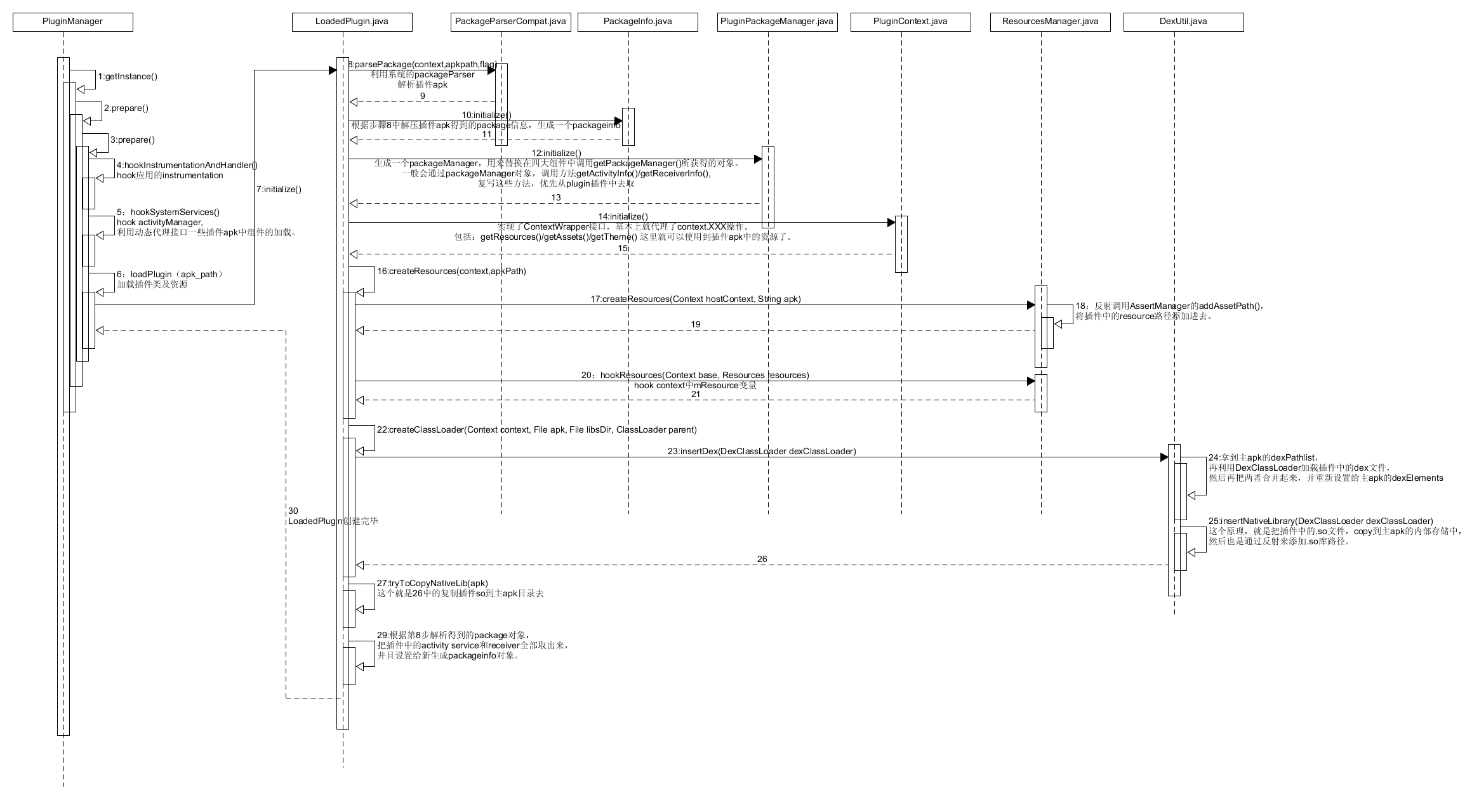
如果想從主apk裡面啟動外掛apk相關的activity或service,那麼首先必須先把外掛中的相關activity和service載入進來,整個載入流程如下。
針對hook的這幾個系統類,Instrumentation使用了一個子類物件(VAInstrumentation)來代替原本的instrumentation,這個子類裡面做的事情很簡單。複寫了父類的newActivity()(就是當我們建立activity時呼叫的方法),利用try catch捕捉classnotfoundexception,正常情況下說明我們想載入的是外掛apk中的activity,但是預設情況,我們的應用是沒有把外掛apk中的類載入進來的,所以報找不到類的錯誤。So,這個時候,我們就可以去外掛apk中載入對應的activity了。
當需要啟動一個activity時,一般使用startActivity(),那麼就跟隨這個方法,看看其呼叫鏈。
public void startActivityForResult(Intentintent, int requestCode, @Nullable Bundle options) {
if(mParent == null) {
//在這裡看到呼叫了instrumentation的execStartActivity(),那麼我們就需要針對instrumentation的這個方法進行處理,可以看到在virtualapk程式碼中,確實是這樣處理的。
Instrumentation.ActivityResult ar =
mInstrumentation.execStartActivity(
this,mMainThread.getApplicationThread(), mToken, this,
intent, requestCode, options);
…………
}
Instrumentation.java
publicActivityResult execStartActivity(
Context who, IBinder contextThread, IBinder token, Activity target,
Intent intent, int requestCode, Bundle options) {
IApplicationThread whoThread = (IApplicationThread) contextThread;
Uri referrer = target != null ? target.onProvideReferrer() : null;
if(referrer != null) {
intent.putExtra(Intent.EXTRA_REFERRER, referrer);
}
…………
try {
intent.migrateExtraStreamToClipData();
intent.prepareToLeaveProcess();
//實際呼叫的是ActivityManagerNative,其實就是系統呼叫ActivityManagerService來啟動activity.
//這個就不深究了。既然啟動activity需要呼叫Instrumentation的這個方法,so 我們需要處理這個方法。
int result =ActivityManagerNative.getDefault()
.startActivity(whoThread,who.getBasePackageName(), intent,
intent.resolveTypeIfNeeded(who.getContentResolver()),
token, target != null ?target.mEmbeddedID : null,
requestCode, 0, null,options);
checkStartActivityResult(result, intent);
}catch (RemoteException e) {
throw new RuntimeException("Failure from system", e);
}
return null;
}
Instrumentation.java
//複寫的父類中的方法.
publicActivityResult execStartActivity(
Context who, IBinder contextThread, IBinder token, Activity target,
Intent intent, int requestCode, Bundle options) {
mPluginManager.getComponentsHandler().transformIntentToExplicitAsNeeded(intent);
//null component is an implicitly intent
if(intent.getComponent() != null) {
Log.i(TAG, String.format("execStartActivity[%s : %s]",intent.getComponent().getPackageName(),
intent.getComponent().getClassName()));
// resolve intent with Stub Activity if needed
//啟動一個本地預置的activity,不過在其intent中加入了 plugin標誌位,以及目標包名,目標類名
//接下來繼續走正常的activity啟動流程,直到newActivity()
this.mPluginManager.getComponentsHandler().markIntentIfNeeded(intent);
}
ActivityResult result = realExecStartActivity(who, contextThread, token,target,
intent, requestCode, options);
return result;
}
整個呼叫流程如下圖片:
@Override
publicActivity newActivity(ClassLoader cl, String className, Intent intent) throwsInstantiationException, IllegalAccessException, ClassNotFoundException {
try {
//先從主apk的classloader中載入類,注意此時的類名是<activityandroid:name=".B$1" android:launchMode="singleTop"/>,又因為本地是沒有建立這個類的,所以肯定會報找不到類的錯誤 cl.loadClass(className);
}catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
//可以看下LoadedPlugin的實現,它是怎樣把外掛apk中的類載入進來的。
LoadedPlugin plugin = this.mPluginManager.getLoadedPlugin(intent);
//從載入的外掛資源中,找到對應的activity
String targetClassName = PluginUtil.getTargetActivity(intent);
Log.i(TAG, String.format("newActivity[%s : %s]", className,targetClassName));
if (targetClassName != null) {
//plugin.getClassLoader() 已經是載入過外掛資源的classloader了,這裡就建立了一個外掛activity例項
//相當於這個時候就用外掛apk中的activity代替了預置的<activity android:name=".B$1"android:launchMode="singleTop"/>
//之所以要這樣操作,是因為如果不預置activity,即不在manifest中宣告,那麼就會報activityNotFound的錯誤。
//所以採取的策略是,先騙過系統,防止出現activityNotFound的錯誤 Activity activity =mBase.newActivity(plugin.getClassLoader(), targetClassName, intent);
activity.setIntent(intent);
try {
// for 4.1+
//通過反射修改mResources為載入了外掛資源的resource
ReflectUtil.setField(ContextThemeWrapper.class, activity,"mResources", plugin.getResources());
} catch (Exception ignored) {
// ignored.
}
return activity;
}
}
return mBase.newActivity(cl, className, intent);
}
至此,外掛apk中的activity的啟動就分析完畢了。
針對service,是hook了系統的利用動態代理實現的。
/**
*hookSystemServices, but need to compatible with Android O in future.
*/
private void hookSystemServices() {
try {
Singleton<IActivityManager> defaultSingleton =(Singleton<IActivityManager>)ReflectUtil.getField(ActivityManagerNative.class, null, "gDefault");
IActivityManager activityManagerProxy =ActivityManagerProxy.newInstance(this, defaultSingleton.get());
// Hook IActivityManager from ActivityManagerNative
//把singleton的內部的物件用代理物件代替。
ReflectUtil.setField(defaultSingleton.getClass().getSuperclass(),defaultSingleton, "mInstance", activityManagerProxy);
if (defaultSingleton.get() == activityManagerProxy) {
this.mActivityManager = activityManagerProxy;
}
}catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
看下自己定義的動態代理類。
ActivityManagerProxy.java
@Override
publicObject invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
if("startService".equals(method.getName())) {
try {
return startService(proxy, method, args);
} catch (Throwable e) {
Log.e(TAG, "Start serviceerror", e);
}
}else if ("stopService".equals(method.getName())) {
try {
return stopService(proxy, method, args);
} catch (Throwable e) {
Log.e(TAG, "Stop Service error", e);
}
}else if ("stopServiceToken".equals(method.getName())) {
try {
return stopServiceToken(proxy, method, args);
} catch (Throwable e) {
Log.e(TAG, "Stop service token error", e);
}
}else if ("bindService".equals(method.getName())) {
try {
return bindService(proxy, method, args);
} catch (Throwable e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}else if ("unbindService".equals(method.getName())) {
try {
return unbindService(proxy, method, args);
} catch (Throwable e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}else if ("getIntentSender".equals(method.getName())) {
try {
getIntentSender(method, args);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}else if ("overridePendingTransition".equals(method.getName())){
try {
overridePendingTransition(method, args);
} catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
try {
// sometimes system binder has problems.
return method.invoke(this.mActivityManager, args);
}catch (Throwable th) {
Throwable c = th.getCause();
if (c != null && c instanceof DeadObjectException) {
// retry connect to systembinder
IBinder ams = ServiceManager.getService(Context.ACTIVITY_SERVICE);
if (ams != null) {
IActivityManager am =ActivityManagerNative.asInterface(ams);
mActivityManager = am;
}
}
Throwable cause = th;
do {
if (cause instanceof RemoteException) {
throw cause;
}
} while ((cause = cause.getCause()) != null);
throw c != null ? c : th;
}
}
ActivityManagerProxy.java
private Object startService(Object proxy, Methodmethod, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
IApplicationThread appThread = (IApplicationThread) args[0];
Intent target = (Intent) args[1];
//先在外掛service集合中查詢,找不到就說明是主apk中的service
ResolveInfo resolveInfo = this.mPluginManager.resolveService(target, 0);
//啟動的是主apk中的service
if(null == resolveInfo || null == resolveInfo.serviceInfo) {
// is host service
return method.invoke(this.mActivityManager, args);
}
return startDelegateServiceForTarget(target, resolveInfo.serviceInfo,null, RemoteService.EXTRA_COMMAND_START_SERVICE);
}
wrapperTargetIntent():
private Intent wrapperTargetIntent(Intenttarget, ServiceInfo serviceInfo, Bundle extras, int command) {
//fill in service with ComponentName
target.setComponent(new ComponentName(serviceInfo.packageName,serviceInfo.name));
String pluginLocation =mPluginManager.getLoadedPlugin(target.getComponent()).getLocation();
//start delegate service to run plugin service inside
boolean local = PluginUtil.isLocalService(serviceInfo);
Class<? extends Service> delegate = local ? LocalService.class :RemoteService.class;
Intent intent = new Intent();
//啟動本地代理service
intent.setClass(mPluginManager.getHostContext(), delegate);
intent.putExtra(RemoteService.EXTRA_TARGET, target);
intent.putExtra(RemoteService.EXTRA_COMMAND, command);
intent.putExtra(RemoteService.EXTRA_PLUGIN_LOCATION, pluginLocation);
if(extras != null) {
intent.putExtras(extras);
}
return intent;
}
以其中的一個service作為例子來看:
/*
*Copyright (C) 2017 Beijing Didi Infinity Technology and Development Co.,Ltd.All rights reserved.
*
*Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
* you maynot use this file except in compliance with the License.
* You mayobtain a copy of the License at
*
*http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unlessrequired by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
*distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUTWARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See theLicense for the specific language governing permissions and
*limitations under the License.
*/
package com.didi.virtualapk.delegate;
import android.app.ActivityThread;
import android.app.Application;
import android.app.IActivityManager;
import android.app.IApplicationThread;
import android.app.IServiceConnection;
import android.app.Service;
import android.content.ComponentName;
import android.content.Context;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.os.Binder;
import android.os.Build;
import android.os.IBinder;
import android.util.Log;
import com.didi.virtualapk.PluginManager;
importcom.didi.virtualapk.internal.LoadedPlugin;
import com.didi.virtualapk.utils.PluginUtil;
import com.didi.virtualapk.utils.ReflectUtil;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
/**
* @authorjohnsonlee
*/
public class LocalService extends Service {
private static final String TAG = "LocalService";
/**
* Thetarget service, usually it's a plugin service intent
*/
publicstatic final String EXTRA_TARGET = "target";
publicstatic final String EXTRA_COMMAND = "command";
publicstatic final String EXTRA_PLUGIN_LOCATION = "plugin_location";
publicstatic final int EXTRA_COMMAND_START_SERVICE = 1;
publicstatic final int EXTRA_COMMAND_STOP_SERVICE = 2;
publicstatic final int EXTRA_COMMAND_BIND_SERVICE = 3;
publicstatic final int EXTRA_COMMAND_UNBIND_SERVICE = 4;
private PluginManager mPluginManager;
@Override
publicIBinder onBind(Intent intent) {
return new Binder();
}
@Override
publicvoid onCreate() {
super.onCreate();
mPluginManager = PluginManager.getInstance(this);
}
@Override
publicint onStartCommand(Intent intent, int flags, int startId) {
if(null == intent || !intent.hasExtra(EXTRA_TARGET) ||!intent.hasExtra(EXTRA_COMMAND)) {
return START_STICKY;
}
//獲取目標service
Intent target = intent.getParcelableExtra(EXTRA_TARGET);
int command = intent.getIntExtra(EXTRA_COMMAND, 0);
if(null == target || command <= 0) {
return START_STICKY;
}
ComponentName component = target.getComponent();
LoadedPlugin plugin = mPluginManager.getLoadedPlugin(component);
//ClassNotFoundException when unmarshalling in Android 5.1
target.setExtrasClassLoader(plugin.getClassLoader());
switch (command) {
case EXTRA_COMMAND_START_SERVICE: {
ActivityThread mainThread =(ActivityThread)ReflectUtil.getActivityThread(getBaseContext());
IApplicationThread appThread = mainThread.getApplicationThread();
Service service;
if (this.mPluginManager.getComponentsHandler().isServiceAvailable(component)){
service =this.mPluginManager.getComponentsHandler().getService(component);
} else {
try {
service = (Service)plugin.getClassLoader().loadClass(component.getClassName()).newInstance();
Application app =plugin.getApplication();
IBinder token =appThread.asBinder();
Method attach =service.getClass().getMethod("attach", Context.class,ActivityThread.class, String.class, IBinder.class, Application.class,Object.class);
IActivityManager am =mPluginManager.getActivityManager();
attach.invoke(service,plugin.getPluginContext(), mainThread, component.getClassName(), token, app,am);
service.onCreate();
this.mPluginManager.getComponentsHandler().rememberService(component,service);
} catch (Throwable t) {
return START_STICKY;
}
}
service.onStartCommand(target, 0,this.mPluginManager.getComponentsHandler().getServiceCounter(service).getAndIncrement());
break;
}
…………
}