二叉樹序列化/反序列化
阿新 • • 發佈:2018-12-19
二叉樹被記錄成檔案的過程,為二叉樹的序列化
通過檔案重新建立原來的二叉樹的過程,為二叉樹的反序列化
設計方案並實現。
(已知結點型別為32位整型)
思路:先序遍歷實現。
因為要寫入檔案,我們要把二叉樹序列化為一個字串。
首先,我們要規定,一個結點結束後的標誌:“!”
然後就可以通過先序遍歷生成先序序列了。
但是,眾所周知,只靠先序序列是無法確定一個唯一的二叉樹的,原因分析如下:
比如序列1!2!3!
我們知道1是根,但是對於2,可以作為左孩子,也可以作為右孩子:
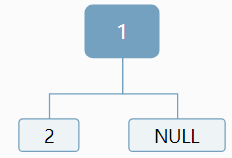
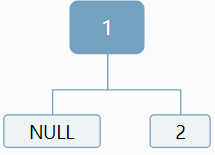
對於3,我們仍然無法確定,應該作為左孩子還是右孩子,情況顯得更加複雜:
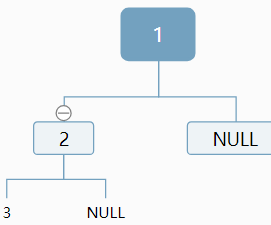
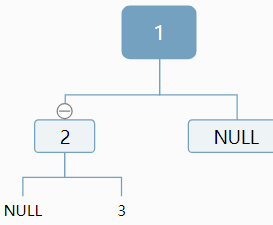

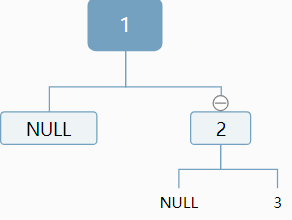
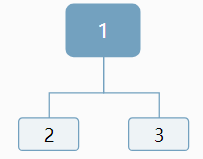
原因:我們對於當前結點,插入新結點是無法判斷插入位置,是應該作為左孩子,還是作為右孩子。
因為我們的NULL並未表示出來。
如果我們把NULL也用一個符號表示出來:
比如

1!2!#!#!3!#!#!
我們再按照先序遍歷的順序重建:
對於1,插入2時,就確定要作為左孩子,因為左孩子不為空。
然後接下來兩個#,我們就知道了2的左右孩子為空,然後重建1的右子樹即可。
我們定義結點:
public static class Node { public int value; public Node left; public Node right; public Node(int data) { this.value = data; } }
序列化:
public static String serialByPre(Node head) {
if (head == null) {
return "#!";
}
String res = head.value + "!";
res += serialByPre(head.left);
res += serialByPre(head.right);
return res;
}
public static Node reconByPreString(String preStr) { //先把字串轉化為結點序列 String[] values = preStr.split("!"); Queue<String> queue = new LinkedList<String>(); for (int i = 0; i != values.length; i++) { queue.offer(values[i]); } return reconPreOrder(queue); } public static Node reconPreOrder(Queue<String> queue) { String value = queue.poll(); if (value.equals("#")) { return null;//遇空 } Node head = new Node(Integer.valueOf(value)); head.left = reconPreOrder(queue); head.right = reconPreOrder(queue); return head; }
這樣並未改變先序遍歷的時空複雜度,解決了先序序列確定唯一一顆樹的問題,實現了二叉樹序列化和反序列化。
