201771010134楊其菊《面向物件程式設計(java)》第十七週學習總結
第十七週學習總結
1. 程式是一段靜態的程式碼,它是應用程式執行的藍本。程序是程式的一次動態執行,它對應了從程式碼載入、執行至執行完畢的一個完整過程。作業系統為每個程序分配一段獨立的記憶體空間和系統資源,包括:程式碼資料以及堆疊等資源。每一個程序的內部資料和狀態都是完全獨立的。多工作業系統中,程序切換對CPU資源消耗較大。
2. 多執行緒是程序執行過程中產生的多條執行線索。執行緒是比程序執行更小的單位。執行緒不能獨立存在,必須存在於程序中,同一程序的各執行緒間共享程序空間的資料。每個執行緒有它自身的產生、存在和消亡的過程,是一個動態的概念。多執行緒意味著一個程式的多行語句可以看上去幾乎在同一時間內同時執行。執行緒建立、銷燬和切換的負荷遠小於程序,又稱為輕量級程序。
3. Java實現多執行緒有兩種途徑:建立Thread類的子類;在程式中定義實現Runnable介面的類。
4. 用Thread類的子類建立執行緒:首先需從Thread類派生出一個子類,在該子類中重寫run()方法。然後用建立該子類的物件Lefthand left=new Lefthand(); Righthand right=new Righthand();最後用start()方法啟動執行緒 left.start(); right.start();
5. 用Thread類的子類建立多執行緒的關鍵性操作:定義Thread類的子類並實現使用者執行緒操作,即run()方法的實現。在適當的時候啟動執行緒。由於Java只支援單重繼承,用這種方法定義的類不可再繼承其他父類。
6.用Runnable()介面實現執行緒:首先設計一個實現Runnable介面的類;然後在類中根據需要重寫run方法;再建立該類物件,以此物件為引數建立Thread 類的物件;呼叫Thread類物件的start方法啟動執行緒,將 CPU執行權轉交到run方法。
7.Thread(Runnable r):建立一個新執行緒,它呼叫r的run(), r是一個實現了Runnable介面的類的例項。
8.執行緒兩種建立方法比較:實現Runnable介面的優勢:符合OO設計的思想;便於用extends繼承其它類。採用繼承Thread類方法的優點:程式碼簡單。
9. 執行緒的終止:當執行緒的run方法執行方法體中最後一條語句後,或者出現了在run方法中沒有捕獲的異常時,執行緒將終止,讓出CPU使用權。呼叫interrupt()方法也可終止執行緒。 void interrupt() :向一個執行緒傳送一箇中斷請求,同時把這個執行緒的“interrupted”狀態置為true。若該執行緒處於 blocked 狀 態,會丟擲 InterruptedException。
10. 測試執行緒是否被中斷的方法:static boolean interrupted() :檢測當前執行緒是否已被中斷,並重置狀態 “interrupted”值為false。 boolean isInterrupted() :檢測當前執行緒是否已被中斷 , 不改變狀態 “interrupted”值 利用各執行緒的狀態變換,可以控制各個執行緒輪流 使用CPU,體現多執行緒的並行性特徵。
11. 執行緒有如下7種狀態:New (新建);Runnable (可執行);Running(執行) ;Blocked (被阻塞) ;Waiting (等待) ;Timed waiting (計時等待) ; Terminated (被終止)。
new(新建):執行緒物件剛剛建立,還沒有啟動,此時執行緒還處於不可執行狀態。例如: Thread thread=new Thread(r); 此時執行緒thread處於新建狀態,有了相應的記憶體空間以及其它資源。
runnable(可執行狀態):此時執行緒已經啟動,處於執行緒的run()方法之中。此時的執行緒可能執行,也可能不執行,只要 CPU一空閒,馬上就會執行。呼叫執行緒的start()方法可使執行緒處於“可執行”狀態。例如: thread.start();
12. blocked (被阻塞):一個正在執行的執行緒因特殊原因,被暫停執行,進入阻塞狀態。阻塞時執行緒不能進入佇列排隊,必須等到引起阻塞的原因消除,才可重新進入排隊佇列。引起阻塞的原因很多,不同原因要用不同的方法解除。sleep(),wait()是兩個常用引起執行緒阻塞的方法。
13. 執行緒阻塞的三種情況:等待阻塞:通過呼叫執行緒的wait()方法,讓執行緒等待某工作的完成。同步阻塞:執行緒在獲取synchronized同步鎖失敗(因為鎖被其它執行緒所佔用),它會進入同步阻 塞狀態。 其他阻塞:通過呼叫執行緒的sleep()或join() 或發出了I/O請求時,執行緒會進入到阻塞狀態。當 sleep()狀態超時、join()等待執行緒終止或者超時、或者I/O處理完畢時,執行緒重新轉入就緒狀態。
14. Terminated (被終止) :執行緒被終止的原因有二:一是run()方法中最後一個語句執行完畢而自 然死亡。二是因為一個沒有捕獲的異常終止了run方法而意外死亡。可以呼叫執行緒的 stop 方法殺死一個執行緒(thread.stop();),但是,stop方法已過時,不要在自己的程式碼中呼叫它。
15. Java 的執行緒排程採用優先順序策略:優先順序高的先執行,優先順序低的後執行;多執行緒系統會自動為每個執行緒分配一個優先順序,預設時,繼承其父類的優先順序; 任務緊急的執行緒,其優先順序較高; 同優先順序的執行緒按“先進先出”的佇列原則。
16.Thread類有三個與執行緒優先順序有關的靜態量: MAX_PRIORITY:最大優先權,值為10; MIN_PRIORITY:最小優先權,值為1; NORM _PRIORITY:預設優先權,值為5。
呼叫setPriority(int a)重置當前執行緒的優先順序,a取值可以是前述的三個靜態量。呼叫getPriority()獲得當前執行緒優先順序。
17.下面幾種情況下,當前執行執行緒會放棄CPU:執行緒呼叫了yield() 或sleep() 方法;搶先式系統下,有高優先順序的執行緒參與排程;由於當前執行緒進行I/O訪問、外存讀寫、等待用 戶輸入等操作導致執行緒阻塞;或者是為等候一個條件變數,以及執行緒呼叫wait() 方法。
18.守護執行緒的惟一用途是為其他執行緒提供服務。例如計時執行緒。在一個執行緒啟動之前,呼叫setDaemon方法可將執行緒轉換為守護執行緒。例如:setDaemon(true);
19.多執行緒併發執行中的問題:多個執行緒相對執行的順序是不確定的。執行緒執行順序的不確定性會產生執行結果的不確定性。在多執行緒對共享資料操作時常常會產生這種不確定性
2.多執行緒併發執行不確定性問題解決方案:引入執行緒同步機制,使得另一執行緒要使用該方法,就只能等待。
21. 在Java中解決多執行緒同步問題的方法有兩種:J ava SE 5.0中引入ReentrantLock類。 在共享記憶體的類方法前加synchronized修飾符。
22.有關鎖物件和條件物件的關鍵要點:鎖用來保護程式碼片段,保證任何時刻只能有一個執行緒執行被保護的程式碼。鎖管理試圖進入被保護程式碼段的執行緒。鎖可擁有一個或多個相關條件物件。每個條件物件管理那些已經進入被保護的程式碼 段但還不能執行的執行緒。
23.synchronized關鍵字作用: 某個類內方法用synchronized 修飾後,該方法被稱為同步方法;只要某個執行緒正在訪問同步方法,其他執行緒欲要訪問同步方法就被阻塞,直至執行緒從同 步方法返回前喚醒被阻塞執行緒,其他執行緒方可能進入同步方法。
24.在同步方法中使用wait()、notify 和notifyAll()方法:一個執行緒在使用的同步方法中時,可能根據問題的需要,必須使用wait()方法使本執行緒等待,暫時讓出CPU的使用權,並允許其它執行緒使用這個同步方法。執行緒如果用完同步方法,應當執行notifyAll()方 法通知所有由於使用這個同步方法而處於等待的 執行緒結束等待
實驗十七 執行緒同步控制
實驗時間 2018-12-10
1、實驗目的與要求
(1) 掌握執行緒同步的概念及實現技術;
(2) 執行緒綜合程式設計練習
2、實驗內容和步驟
實驗1:測試程式並進行程式碼註釋。
測試程式1:
l 在Elipse環境下除錯教材651頁程式14-7,結合程式執行結果理解程式;
l 掌握利用鎖物件和條件物件實現的多執行緒同步技術。
1 package synch; 2 3 import java.util.*; 4 import java.util.concurrent.locks.*; 5 6 /** 7 * A bank with a number of bank accounts that uses locks for serializing access. 8 * @version 1.30 2004-08-01 9 * @author Cay Horstmann 10 */ 11 public class Bank 12 { 13 private final double[] accounts; 14 private Lock bankLock; 15 private Condition sufficientFunds; 16 17 /** 18 * Constructs the bank. 19 * @param n the number of accounts 20 * @param initialBalance the initial balance for each account 21 */ 22 public Bank(int n, double initialBalance) 23 { 24 accounts = new double[n]; 25 Arrays.fill(accounts, initialBalance); 26 bankLock = new ReentrantLock(); 27 sufficientFunds = bankLock.newCondition(); 28 } 29 30 /** 31 * Transfers money from one account to another. 32 * @param from the account to transfer from 33 * @param to the account to transfer to 34 * @param amount the amount to transfer 35 */ 36 public void transfer(int from, int to, double amount) throws InterruptedException 37 { 38 //加鎖; 39 bankLock.lock(); 40 try//臨界區互斥訪問; 41 { 42 while (accounts[from] < amount) 43 sufficientFunds.await();//將執行緒放到條件的等待等待;有兩個以上使得臨界區程式碼執行不下去的原因,針對每個原因設定一個條件物件; 44 System.out.print(Thread.currentThread()); 45 accounts[from] -= amount; 46 System.out.printf(" %10.2f from %d to %d", amount, from, to); 47 accounts[to] += amount; 48 System.out.printf(" Total Balance: %10.2f%n", getTotalBalance()); 49 //sufficientFunds.signalAll(); 50 sufficientFunds.signal();//喚醒所有執行緒,由阻塞狀態進入執行; 51 } 52 finally 53 { 54 bankLock.unlock();//解鎖,放在finally語句中,以是得出現異常時其他執行緒能正常使用臨界區; 55 } 56 } 57 58 /** 59 * Gets the sum of all account balances. 60 * @return the total balance 61 */ 62 public double getTotalBalance() 63 { 64 bankLock.lock();//加鎖; 65 try 66 { 67 double sum = 0; 68 69 for (double a : accounts) 70 sum += a; 71 72 return sum; 73 } 74 finally 75 { 76 bankLock.unlock();//解鎖; 77 } 78 } 79 80 /** 81 * Gets the number of accounts in the bank. 82 * @return the number of accounts 83 */ 84 public int size() 85 { 86 return accounts.length; 87 } 88 }
1 package synch; 2 3 /** 4 * This program shows how multiple threads can safely access a data structure. 5 * @version 1.31 2015-06-21 6 * @author Cay Horstmann 7 */ 8 public class SynchBankTest 9 { 10 public static final int NACCOUNTS = 100; 11 public static final double INITIAL_BALANCE = 1000; 12 public static final double MAX_AMOUNT = 1000; 13 public static final int DELAY = 10; 14 15 public static void main(String[] args) 16 { 17 Bank bank = new Bank(NACCOUNTS, INITIAL_BALANCE); 18 for (int i = 0; i < NACCOUNTS; i++) 19 { 20 int fromAccount = i; 21 Runnable r = () -> { 22 try 23 { 24 while (true) 25 { 26 int toAccount = (int) (bank.size() * Math.random()); 27 double amount = MAX_AMOUNT * Math.random(); 28 bank.transfer(fromAccount, toAccount, amount); 29 Thread.sleep((int) (DELAY * Math.random())); 30 } 31 } 32 catch (InterruptedException e) 33 { 34 } 35 }; 36 Thread t = new Thread(r); 37 t.start(); 38 } 39 } 40 }

有兩個以上使得臨界區程式碼執行不下去的原因,針對每個原因設定一個條件物件
測試程式2:
l 在Elipse環境下除錯教材655頁程式14-8,結合程式執行結果理解程式;
l 掌握synchronized在多執行緒同步中的應用。
1 package synch2; 2 3 import java.util.*; 4 5 /** 6 * A bank with a number of bank accounts that uses synchronization primitives. 7 * @version 1.30 2004-08-01 8 * @author Cay Horstmann 9 */ 10 public class Bank 11 { 12 private final double[] accounts; 13 14 /** 15 * Constructs the bank. 16 * @param n the number of accounts 17 * @param initialBalance the initial balance for each account 18 */ 19 public Bank(int n, double initialBalance) 20 { 21 accounts = new double[n]; 22 Arrays.fill(accounts, initialBalance); 23 } 24 25 /** 26 * Transfers money from one account to another. 27 * @param from the account to transfer from 28 * @param to the account to transfer to 29 * @param amount the amount to transfer 30 */ 31 public synchronized void transfer(int from, int to, double amount) throws InterruptedException 32 {//同步方法; 33 while (accounts[from] < amount) 34 wait();//導致執行緒進入等待狀態直到他被通知;容許其他執行緒使用這個同步方法;如果當前執行緒不是物件鎖的持有者,該方法丟擲InterruptedException異常; 35 System.out.print(Thread.currentThread()); 36 accounts[from] -= amount; 37 System.out.printf(" %10.2f from %d to %d", amount, from, to); 38 accounts[to] += amount; 39 System.out.printf(" Total Balance: %10.2f%n", getTotalBalance()); 40 notifyAll();//解除那些在該物件上呼叫方法的執行緒的阻塞狀態,如果當前執行緒不是物件鎖的持有者,該方法丟擲InterruptedException異常; 41 } 42 43 /** 44 * Gets the sum of all account balances. 45 * @return the total balance 46 */ 47 public synchronized double getTotalBalance() 48 { 49 double sum = 0; 50 51 for (double a : accounts) 52 sum += a; 53 54 return sum; 55 } 56 57 /** 58 * Gets the number of accounts in the bank. 59 * @return the number of accounts 60 */ 61 public int size() 62 { 63 return accounts.length; 64 } 65 }
1 package synch2; 2 3 /** 4 * This program shows how multiple threads can safely access a data structure, 5 * using synchronized methods. 6 * @version 1.31 2015-06-21 7 * @author Cay Horstmann 8 */ 9 public class SynchBankTest2 10 { 11 public static final int NACCOUNTS = 100; 12 public static final double INITIAL_BALANCE = 1000; 13 public static final double MAX_AMOUNT = 1000; 14 public static final int DELAY = 10; 15 16 public static void main(String[] args) 17 { 18 Bank bank = new Bank(NACCOUNTS, INITIAL_BALANCE); 19 for (int i = 0; i < NACCOUNTS; i++) 20 { 21 int fromAccount = i; 22 Runnable r = () -> { 23 try 24 { 25 while (true) 26 { 27 int toAccount = (int) (bank.size() * Math.random()); 28 double amount = MAX_AMOUNT * Math.random(); 29 bank.transfer(fromAccount, toAccount, amount); 30 Thread.sleep((int) (DELAY * Math.random())); 31 } 32 } 33 catch (InterruptedException e) 34 { 35 } 36 }; 37 Thread t = new Thread(r); 38 t.start(); 39 } 40 } 41 }

測試程式3:
l 在Elipse環境下執行以下程式,結合程式執行結果分析程式存在問題;
l 嘗試解決程式中存在問題。
| class Cbank { private static int s=2000; public static void sub(int m) { int temp=s; temp=temp-m; try { Thread.sleep((int)(1000*Math.random())); } catch (InterruptedException e) { } s=temp; System.out.println("s="+s); } }
class Customer extends Thread { public void run() { for( int i=1; i<=4; i++) Cbank.sub(100); } } public class Thread3 { public static void main(String args[]) { Customer customer1 = new Customer(); Customer customer2 = new Customer(); customer1.start(); customer2.start(); } } |
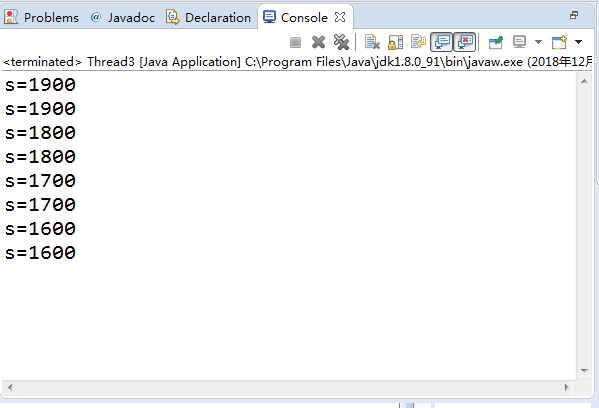
顯示結果不合邏輯;
修改後:

1 class Cbank 2 { 3 private static int s=2000; 4 public synchronized static void sub(int m) 5 { 6 int temp=s; 7 temp=temp-m; 8 try { 9 Thread.sleep((int)(1000*Math.random())); 10 } 11 catch (InterruptedException e) { } 12 s=temp; 13 System.out.println("s="+s); 14 } 15 } 16 17 18 class Customer extends Thread 19 { 20 public void run() 21 { 22 for( int i=1; i<=4; i++) 23 Cbank.sub(100); 24 } 25 } 26 public class Thread3 27 { 28 public static void main(String args[]) 29 { 30 Customer customer1 = new Customer(); 31 Customer customer2 = new Customer(); 32 customer1.start(); 33 customer2.start(); 34 } 35 }Cbank

實驗2 程式設計練習
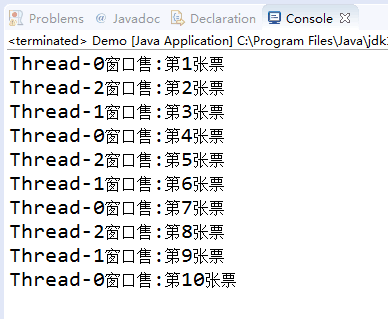
利用多執行緒及同步方法,編寫一個程式模擬火車票售票系統,共3個視窗,賣10張票,程式輸出結果類似(程式輸出不唯一,可以是其他類似結果)。
Thread-0視窗售:第1張票
Thread-0視窗售:第2張票
Thread-1視窗售:第3張票
Thread-2視窗售:第4張票
Thread-2視窗售:第5張票
Thread-1視窗售:第6張票
Thread-0視窗售:第7張票
Thread-2視窗售:第8張票
Thread-1視窗售:第9張票
Thread-0視窗售:第10張票
1 package xaincheng; 2 3 import java.nio.charset.MalformedInputException; 4 5 public class Demo { 6 public static void main(String[] args) 7 { 8 Mythread mythread= new Mythread(); 9 Thread t1 = new Thread(mythread); 10 Thread t2 = new Thread(mythread); 11 Thread t3 = new Thread(mythread); 12 t1.start(); 13 t2.start(); 14 t3.start(); 15 16 } 17 18 19 } 20 21 class Mythread implements Runnable{ 22 23 int t=1; 24 boolean flag=true; 25 26 public void run() { 27 28 while(flag) { 29 try { 30 31 Thread.sleep(500); 32 } 33 catch (InterruptedException e) 34 { 35 e.printStackTrace(); 36 } 37 38 39 40 synchronized (this) { 41 42 if(t<=10){ 43 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"視窗售:第"+t+"張票"); 44 t++; 45 } 46 if(t>10){ 47 flag=false; 48 } 49 50 } 51 52 } 53 } 54 }