機器學習-貝葉斯新聞分類例項
基礎知識儲備:
匯入常用python package
匯入文章content,匯入停用詞表
使用jieba對content內容分詞
建立函式去除content中的停用詞(注意格式的不同 dataframe, series, list)
統計詞頻:使用詞雲畫圖
建立詞雲展示
使用IF-IDF提取關鍵字
構建LDA主題模型
import pandas as pd
import jieba
import numpy
df_news = pd.read_table('val.txt',names = ['category','theme','URL','content'],encoding='utf-8')
#過濾缺失資料
df_news = df_news.dropna()
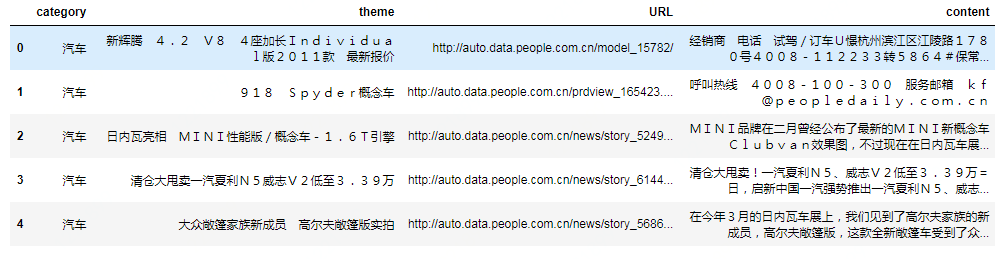
df_news.head()
df_news.shape
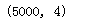
content = df_news.content.values.tolist()
print(content[1001])
#檢視第1001條新聞資訊

#對內容分詞處理
content_S = []
for line in content:
current_segment = jieba.lcut(line)
if len(current_segment) > 1 and current_segment != '\r\n': #換行符
content_S.append(current_segment)
content_S[1000]#分詞
#分詞後的內容,存在停用詞,需要做處理
df_content = pd.DataFrame({'content_S':content_S})
df_content.head()

#停用詞處理
stopwords = pd.read_csv("stopwords.txt",index_col = False,sep="\t",quoting=3,names=['stopword'], encoding='utf-8')
stopwords.head(20)
#對文字資料的停用詞做清洗
def drop_stopwords(contents,stopwords):
contents_clean = []
all_words = []
for line in contents:
line_clean = []
for word in line:
if word in stopwords:
continue
line_clean.append(word)
all_words.append(str(word))#清洗後所有詞
contents_clean.append(line_clean)#清洗後的文字
return contents_clean,all_words
contents = df_content.content_S.values.tolist()
stopwords = stopwords.stopword.values.tolist()
contents_clean,all_words = drop_stopwords(contents,stopwords)
df_content=pd.DataFrame({'contents_clean':contents_clean})
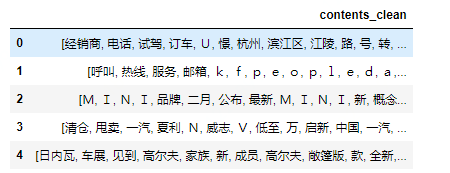
df_content.head()
#統計所有詞
df_all_words=pd.DataFrame({'all_words':all_words})
df_all_words.head()
#統計每個詞的詞頻,並按從高到低排列
words_count=df_all_words.groupby(by=['all_words'])['all_words'].agg({"count":numpy.size})
words_count=words_count.reset_index().sort_values(by=["count"],ascending=False)
words_count.head()

#製作雲圖視覺化詞頻統計,這裡自定義了一個模型
from wordcloud import WordCloud
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
%matplotlib inline
import matplotlib
wordcloud = WordCloud("simhei.ttf",)
from wordcloud import WordCloud
fontpath='simhei.ttf'
import numpy as np
from PIL import Image
aimask=np.array(Image.open("AI.png"))
wc = WordCloud(font_path=fontpath, # 設定字型
background_color="white", # 背景顏色
max_words=1000, # 詞雲顯示的最大詞數
max_font_size=100, # 字型最大值
min_font_size=10, #字型最小值
random_state=42, #隨機數
collocations=False, #避免重複單詞
mask=aimask, #造型遮蓋
width=1200,height=800,margin=2, #影象寬高,字間距,需要配合下面的plt.figure(dpi=xx)放縮才有效
)
word_frequence = {x[0]:x[1] for x in words_count.head(100).values}
word_cloud=wc.fit_words(word_frequence)
plt.figure(dpi=100) #通過這裡可以放大或縮小
plt.axis("off") #隱藏座標
plt.imshow(word_cloud)

#提取關鍵字 這裡只提取了五個 topk=5 ,隨便拿了一篇
import jieba.analyse
index = 2400
print (df_news['content'][index])
content_S_str = "".join(content_S[index])
print (" ".join(jieba.analyse.extract_tags(content_S_str, topK=5, withWeight=False)))

#關鍵字

#LDA :主題模型
from gensim import corpora, models, similarities
import gensim
#http://radimrehurek.com/gensim/
#做對映,相當於詞袋
dictionary = corpora.Dictionary(contents_clean)
corpus = [dictionary.doc2bow(sentence) for sentence in contents_clean]
lda = gensim.models.ldamodel.LdaModel(corpus=corpus, id2word=dictionary, num_topics=10) #類似Kmeans自己指定K值
#一號分類結果
print (lda.print_topic(1, topn=5))
0.006*"中" + 0.005*"比賽" + 0.003*"說" + 0.002*"該劇" + 0.002*"考生"
#分10堆主題
for topic in lda.print_topics(num_topics=10, num_words=5):
print (topic[1])
0.007*"電影" + 0.007*"中" + 0.006*"中國" + 0.005*"觀眾" + 0.004*"導演" 0.006*"中" + 0.005*"比賽" + 0.003*"說" + 0.002*"該劇" + 0.002*"考生" 0.005*"中" + 0.003*"面板" + 0.003*"肌膚" + 0.003*"V" + 0.003*"食物" 0.006*"中國" + 0.004*"中" + 0.002*"市場" + 0.002*"發展" + 0.002*"文化" 0.006*"中" + 0.005*"說" + 0.003*"男人" + 0.003*"女人" + 0.002*"學校" 0.016*"a" + 0.015*"e" + 0.011*"n" + 0.011*"o" + 0.011*"i" 0.004*"中" + 0.003*"B" + 0.002*"天籟" + 0.002*"球隊" + 0.002*"C" 0.004*"中" + 0.004*"節目" + 0.003*"男人" + 0.003*"萬" + 0.003*"公司" 0.009*"男人" + 0.005*"中" + 0.005*"女人" + 0.004*"P" + 0.003*"S" 0.005*"說" + 0.005*"中" + 0.004*"孩子" + 0.003*"中國" + 0.002*"做"
df_train=pd.DataFrame({'contents_clean':contents_clean,'label':df_news['category']})
df_train.tail()
#這裡顯示最後的5條

#已有新聞類別
df_train.label.unique()
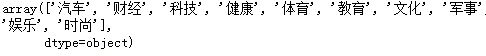
#將類別做數值轉換
label_mapping = {"汽車": 1, "財經": 2, "科技": 3, "健康": 4, "體育":5, "教育": 6,"文化": 7,"軍事": 8,"娛樂": 9,"時尚": 0}
df_train['label'] = df_train['label'].map(label_mapping)
df_train.head()
#重點!!! 建立模型一樣分訓練集和測試集
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(df_train['contents_clean'].values, df_train['label'].values, random_state=1)
#x_train[0][1]
words = []
for line_index in range(len(x_train)):
try:
#x_train[line_index][word_index] = str(x_train[line_index][word_index])
words.append(' '.join(x_train[line_index]))
except:
print (line_index,word_index)
words[1000]

from sklearn.feature_extraction.text import CountVectorizer
vec = CountVectorizer(analyzer='word', max_features=4000, lowercase = False)
vec.fit(words)
from sklearn.naive_bayes import MultinomialNB
classifier = MultinomialNB()
classifier.fit(vec.transform(words), y_train)
test_words = []
for line_index in range(len(x_test)):
try:
#x_train[line_index][word_index] = str(x_train[line_index][word_index])
test_words.append(' '.join(x_test[line_index]))
except:
print (line_index,word_index)
test_words[40]
classifier.score(vec.transform(test_words), y_test)
#不做TF-IDF的準確率稍低
‘’‘
TF-IDF是一種統計方法,用以評估一字詞對於一個檔案集或一個語料庫中的其中一份檔案的重要程度。字詞的重要性隨著它在檔案中出現的次數成正比增加,但同時會隨著它在語料庫中出現的頻率成反比下降。TF-IDF加權的各種形式常被搜尋引擎應用,作為檔案與使用者查詢之間相關程度的度量或評級。除了TF-IDF以外,因特網上的搜尋引擎還會使用基於連結分析的評級方法,以確定檔案在搜尋結果中出現的順序’
‘’‘’
0.804
from sklearn.feature_extraction.text import TfidfVectorizer
vectorizer = TfidfVectorizer(analyzer='word', max_features=4000, lowercase = False)
vectorizer.fit(words)
from sklearn.naive_bayes import MultinomialNB
classifier = MultinomialNB()
classifier.fit(vectorizer.transform(words), y_train)
#這裡發現使用貝葉斯逆概 TF-IDF 精確度達到了81.52%
classifier.score(vectorizer.transform(test_words), y_test)
0.8152
