Hessian的使用以及理解(轉)
Hessian的使用以及理解
- Hessian版本:3.1.5
將包括如下的內容:
- Hessian的基本使用
- Hessian的原理
- Hessian和Spring 的結合使用
- 擴充套件
簡單說來,Hessian是一個輕量級的RPC框架(RPC是什麼?請參考這裡)。
它基於HTTP協議傳輸,使用Hessian二進位制序列化,對於資料包比較大的情況比較友好。
但是它的引數和返回值都需要實現Serializable介面。
簡單實現一個Hessian的例子:
- 建立介面和實現類
public interface Basic {
String sayHello(String name);
} public class BasicImpl implements Basic{
public String sayHello(String name) {
return "This is Hello words from HESSIAN Server. " + name;
}
}- 配置HessianServlet, web.xml中:
<servlet>
<servlet-name>HessianServlet</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>com.caucho.hessian.server.HessianServlet</servlet-class 我們將會把Servlet部署在Tomcat上,埠8080。
- 編寫客戶端程式碼:
public class BasicClient {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
String url = "http://localhost:8080/hessian";
HessianProxyFactory factory = new HessianProxyFactory();
factory.setOverloadEnabled(true);
Basic basic = (Basic) factory.create(Basic.class, url);
System.out.println(basic.sayHello("SW"));
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}建立HessianProxyFactory物件,建立Basic “物件”,然後呼叫sayHello()方法。
整個過程感覺很簡單,並沒有什麼配置。
啟動Tomcat,執行Client。
輸出如下:
This is Hello words from HESSIAN Server. SW
可見是呼叫成功了。
等等,這個過程到底發生了些什麼?
我們先從服務端說起,主要是有這幾個步驟:
- 編寫介面和實現類
- 在web.xml中宣告HessianServlet,並且將上一步的實現類設定為Servlet的[service-class]屬性值
- 將Servlet部署在Tomcat容器中
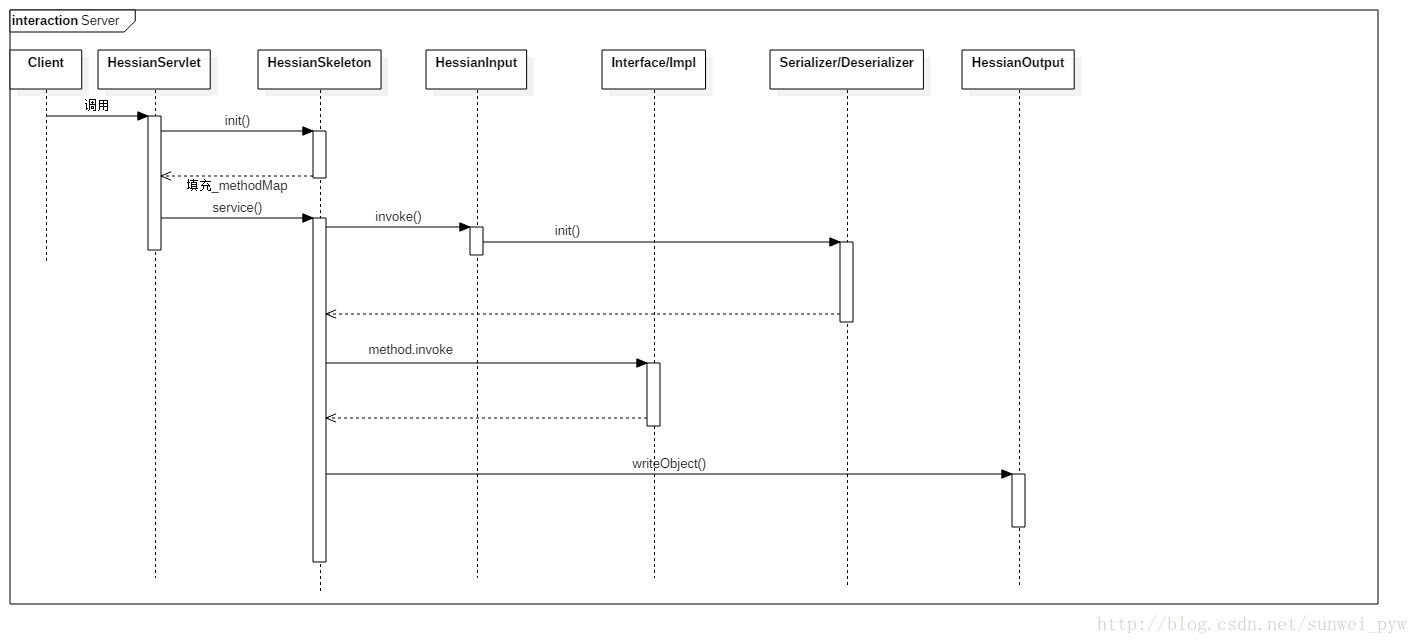
可見我們所有的工作都圍繞在HessianServlet在展開。該Servlet中有兩個比較重要的方法:init()、service();
init方法初始化服務和服務物件,主要分為3步:
通過home-class或者service-class建立服務端的實現類例項;
if (_homeImpl != null) {
}
else if (getInitParameter("home-class") != null) {
String className = getInitParameter("home-class");
Class homeClass = loadClass(className);
_homeImpl = homeClass.newInstance();
init(_homeImpl);
}
else if (getInitParameter("service-class") != null) {
String className = getInitParameter("service-class");
Class homeClass = loadClass(className);
_homeImpl = homeClass.newInstance();
init(_homeImpl);
}
else {
if (getClass().equals(HessianServlet.class))
throw new ServletException("server must extend HessianServlet");
_homeImpl = this;
}通過home-api或者api-class載入實現類的介面物件;
if (_homeAPI != null) {
}
else if (getInitParameter("home-api") != null) {
String className = getInitParameter("home-api");
_homeAPI = loadClass(className);
}
else if (getInitParameter("api-class") != null) {
String className = getInitParameter("api-class");
_homeAPI = loadClass(className);
}
else if (_homeImpl != null)
_homeAPI = _homeImpl.getClass();init方法還會建立HessianSkeleton物件,這是Hessian服務端的核心功能部分。
HessianSkeleton繼承自AbstractSkeleton,其構造方法,將會從實現類中抽取方法和方法的Method物件,並且儲存到_methodMap中。
對於一個Servlet來說其service方法是對外提供服務的方法:
/**
* Execute a request. The path-info of the request selects the bean.
* Once the bean's selected, it will be applied.
*/
public void service(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response)
throws IOException, ServletException
{
HttpServletRequest req = (HttpServletRequest) request;
HttpServletResponse res = (HttpServletResponse) response;
if (! req.getMethod().equals("POST")) {
res.setStatus(500, "Hessian Requires POST");
PrintWriter out = res.getWriter();
res.setContentType("text/html");
out.println("<h1>Hessian Requires POST</h1>");
return;
}
String serviceId = req.getPathInfo();
String objectId = req.getParameter("id");
if (objectId == null)
objectId = req.getParameter("ejbid");
ServiceContext.begin(req, serviceId, objectId);
try {
InputStream is = request.getInputStream();
OutputStream os = response.getOutputStream();
HessianInput in = new HessianInput(is);
HessianOutput out = new HessianOutput(os);
if (objectId != null)
_objectSkeleton.invoke(in, out);
else
_homeSkeleton.invoke(in, out);
} catch (RuntimeException e) {
throw e;
} catch (ServletException e) {
throw e;
} catch (Throwable e) {
throw new ServletException(e);
} finally {
ServiceContext.end();
}
}最主要的是呼叫HessianSkeleton物件的invoke方法。注意,Servlet例項中有兩個HessianSkeleton變數,分別是:_objectSkeleton和 _homeSkeleton,呼叫誰,是由objectid決定的。此處還有不明白的地方。
invoke方法:
首先從HessianInput物件中獲取到Method資訊,獲取到真正的service物件。
根據反射機制,呼叫service物件的invoke方法,獲取到返回值。
最後呼叫HessianOutput物件將結果寫回到呼叫方。
客戶端程式碼
Hessian原生API編寫客戶端HessianClient:
public class BasicClient {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
String url = "http://localhost:8080/hessian";
HessianProxyFactory factory = new HessianProxyFactory();
factory.setOverloadEnabled(true);
Basic basic = (Basic) factory.create(Basic.class, url);
System.out.println(basic.sayHello("SW"));
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}建立HessianProxyFacotry,建立介面Basic的代理物件,然後呼叫sayHello()方法。
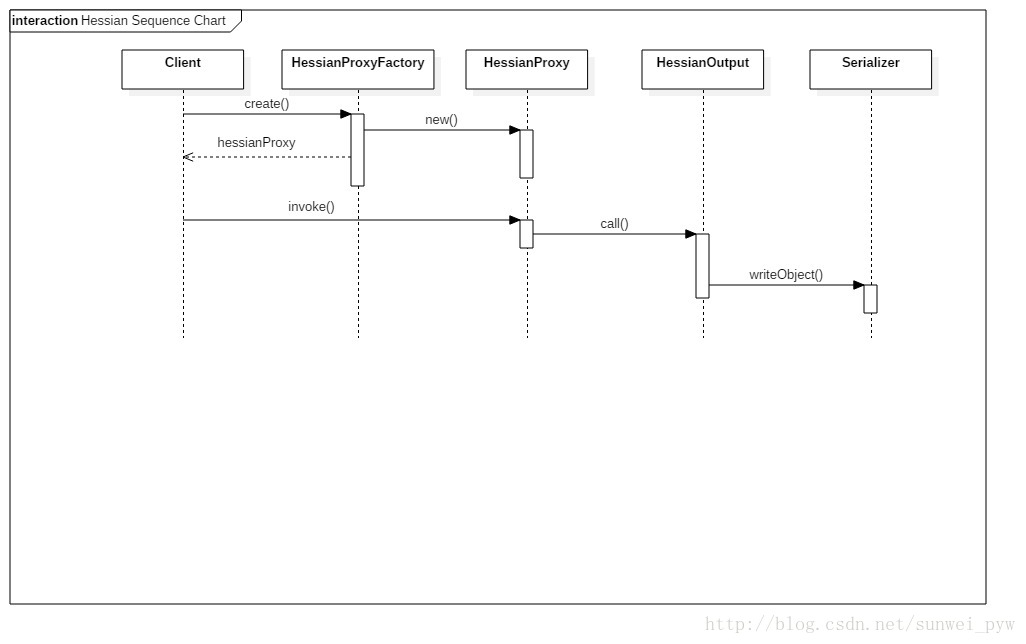
那麼重點就在於建立代理物件,首先建立HessianProxyFacotry物件,構造方法中建立了一個HessianProxyResolver物件,這個物件的lookup方法將用來查詢遠端服務。此外HessianProxyFacotry還有包括許可權驗證方面的支援。
建立了factory之後,接下來就是通過Class物件和遠端服務的URL建立代理物件了。
HessianProxyFactory使用HessianProxy物件作為代理的Handler,也就是說,我們對代理物件的所有操作,都會由這個handler來處理。handler的invoke方法,在進行一些方法名和引數的確認之後,建立HttpURLConnection物件,呼叫sendRequest方法,將方法名和引數用HessianOutput物件(設定序列化的方式)的call方法,寫入到服務端。
主要程式碼如下:
protected URLConnection sendRequest(String methodName, Object []args)
throws IOException
{
URLConnection conn = null;
conn = _factory.openConnection(_url);
// Used chunked mode when available, i.e. JDK 1.5.
if (_factory.isChunkedPost() && conn instanceof HttpURLConnection) {
try {
HttpURLConnection httpConn = (HttpURLConnection) conn;
httpConn.setChunkedStreamingMode(8 * 1024);
} catch (Throwable e) {
}
}
addRequestHeaders(conn);
OutputStream os = null;
try {
os = conn.getOutputStream();
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new HessianRuntimeException(e);
}
try {
if (log.isLoggable(Level.FINEST)) {
PrintWriter dbg = new PrintWriter(new LogWriter(log));
os = new HessianDebugOutputStream(os, dbg);
}
AbstractHessianOutput out = _factory.getHessianOutput(os);
out.call(methodName, args);
out.flush();
return conn;
} catch (IOException e) {
if (conn instanceof HttpURLConnection)
((HttpURLConnection) conn).disconnect();
throw e;
} catch (RuntimeException e) {
if (conn instanceof HttpURLConnection)
((HttpURLConnection) conn).disconnect();
throw e;
}
}服務端拿到請求,進行反序列化,然後將方法呼叫,再將結果序列化之後寫回到connection。所以,客戶端在sendRequest之後,所要做的就是將返回的結果進行解析,看返回的code是不是200:
conn = sendRequest(mangleName, args);
if (conn instanceof HttpURLConnection) {
httpConn = (HttpURLConnection) conn;
int code = 500;
try {
code = httpConn.getResponseCode();
} catch (Exception e) {
}
parseResponseHeaders(conn);
if (code != 200) {
StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer();
int ch;
.....
AbstractHessianInput in = _factory.getHessianInput(is);
in.startReply();
Object value = in.readObject(method.getReturnType());
if (value instanceof InputStream) {
value = new ResultInputStream(httpConn, is, in, (InputStream) value);
is = null;
httpConn = null;
}
else
in.completeReply();
return value;解析HessianInput物件,並且從中讀取到結果返回。
至此,服務端和客戶端的互動過程已經簡單地介紹完畢。
Spring也為Hessian提供了很友好的支援,通過使用spring-remoting包,我們可以很方便地釋出和呼叫服務。
這部分提供一個簡單的實現例子:
在web.xml中,我們配置SpringMVC的DispatcherServlet:
<servlet>
<servlet-name>SpringMVC</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>classpath:applicationContext.xml</param-value>
</init-param>
<load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>SpringMVC</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/remote/*</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>applicationContext.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.1.xsd"
default-lazy-init="true">
<bean id = "basicService" class="example.impl.BasicImpl"/>
<bean name="/basicHessianService" class="org.springframework.remoting.caucho.HessianServiceExporter">
<property name="service" ref="basicService"/>
<property name="serviceInterface" value="example.Basic"/>
</bean>
</beans>這裡,我們使用了org.springframework.remoting.caucho.HessianServiceExporter來發布服務。將程式部署在tomcat中。
客戶端,使用org.springframework.remoting.caucho.HessianProxyFactoryBean來代理請求:
client.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.1.xsd"
default-lazy-init="true">
<bean id="basicService" class="org.springframework.remoting.caucho.HessianProxyFactoryBean">
<property name="serviceUrl" value="http://localhost:8080/remote/basicHessianService"/>
<property name="serviceInterface" value="example.Basic"/>
</bean>
</beans>編寫客戶端:
public class SpringClient {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(new String[]{"classpath:client.xml"});
Basic basic = (Basic)context.getBean("basicService");
System.out.println(basic.sayHello("SUNWEI"));
}
}這樣,服務端/客戶端的程式碼都已經編寫完成。
最原始的實現,我們的服務是通過Servlet來繫結的,而Spring的實現,我們使用了SpringMVC的載入時機,將配置檔案載入。HessianServiceExporter
public class HessianServiceExporter extends RemoteExporter implements HttpRequestHandler, InitializingBean {
....這個類實現了InitializingBean介面,這是spring-beans包中很重要的一個擴充套件介面。
這個介面的說明如下:
Interface to be implemented by beans that need to react once all their
properties have been set by a BeanFactory: for example, to perform custom
initialization, or merely to check that all mandatory properties have been set.也就是說,它會隨著Spring容器(此處為Spring MVC容器)的啟動而被載入。看看HessianServiceExporter的實現:
public void prepare() {
HessianSkeleton skeleton = null;
try {
try {
Constructor ctor = (class$com$caucho$hessian$server$HessianSkeleton == null?(class$com$caucho$hessian$server$HessianSkeleton = class$("com.caucho.hessian.server.HessianSkeleton")):class$com$caucho$hessian$server$HessianSkeleton).getConstructor(new Class[]{class$java$lang$Object == null?(class$java$lang$Object = class$("java.lang.Object")):class$java$lang$Object, class$java$lang$Class == null?(class$java$lang$Class = class$("java.lang.Class")):class$java$lang$Class});
this.checkService();
this.checkServiceInterface();
skeleton = (HessianSkeleton)ctor.newInstance(new Object[]{this.getProxyForService(), this.getServiceInterface()});
} catch (NoSuchMethodException var4) {
Constructor ctor = (class$com$caucho$hessian$server$HessianSkeleton == null?(class$com$caucho$hessian$server$HessianSkeleton = class$("com.caucho.hessian.server.HessianSkeleton")):class$com$caucho$hessian$server$HessianSkeleton).getConstructor(new Class[]{class$java$lang$Object == null?(class$java$lang$Object = class$("java.lang.Object")):class$java$lang$Object});
skeleton = (HessianSkeleton)ctor.newInstance(new Object[]{this.getProxyForService()});
}
} catch (Throwable var5) {
throw new BeanInitializationException("Hessian skeleton initialization failed", var5);
}
if(hessian2Available) {
this.skeletonInvoker = new Hessian2SkeletonInvoker(skeleton, this.serializerFactory);
} else {
this.skeletonInvoker = new Hessian1SkeletonInvoker(skeleton, this.serializerFactory);
}
}
public void handleRequest(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
Assert.notNull(this.skeletonInvoker, "HessianServiceExporter has not been initialized");
if(!"POST".equals(request.getMethod())) {
throw new HttpRequestMethodNotSupportedException("POST", "HessianServiceExporter only supports POST requests");
} else {
try {
this.skeletonInvoker.invoke(request.getInputStream(), response.getOutputStream());
} catch (Throwable var4) {
throw new NestedServletException("Hessian skeleton invocation failed", var4);
}
}
}在prepare方法中,獲取service和serviceInterface的配置,建立HessianSkeleton物件。
同時,還實現了HttpRequestHandler,spring-web中的介面。
又因為實現了HttpRequestHandler介面,所以在handleRequest方法中,可以像HessianServlet的service方法一樣,呼叫Hessian2SkeletonInvoker的invoke方法進行實際的方法呼叫。
最後一點尾巴
定義一個自己的HttpRequestHandler物件,配置在applicationContext.xml中,然後通過頁面訪問:
public class MyHandler implements HttpRequestHandler, InitializingBean {
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
System.out.println("初始化 MyHandler");
}
public void handleRequest(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
System.out.println("執行 MyHandler");
}
}配置在applicationContext.xml中:
<bean id = "/myHandler" class="client.MyHandler"/>通過Spring MVC的上下文載入該Handler,啟動Tomcat的時候,可以看到控制檯輸出:
初始化 MyHandler
在瀏覽器中訪問:http://localhost:8080/remote/myHandler
將觸發執行:執行 MyHandler
-EOF-