ADA:Algorithm Design and Analysis——review
1.Divide-and-Conquer
1.1Divide-and-Conquer
1.2 Karatsuba’s Algorithm


1.3Merge Sort
T(n) = 2T(n/2) + cn
1.4Binary Search
T(n) = T(n/2) + c
1.5Master Theorem
T(n) = aT(n/b) + f (n)
a ≥ 1, b > 1 are constants and f (n) is positive .
Case 1: f(n) < nlogba
T(n) = nlogba
Case 2: f(n) = nlogba
T(n) = nlogba
Case 3: f(n) > nlogba
T(n) = f(n)
1.6Matrix Multiplications
T(n) = 8T(n/2) + cn2.
By Master theorem, T(n) is Θ(n3).
1.7Strassen’s Algorithm
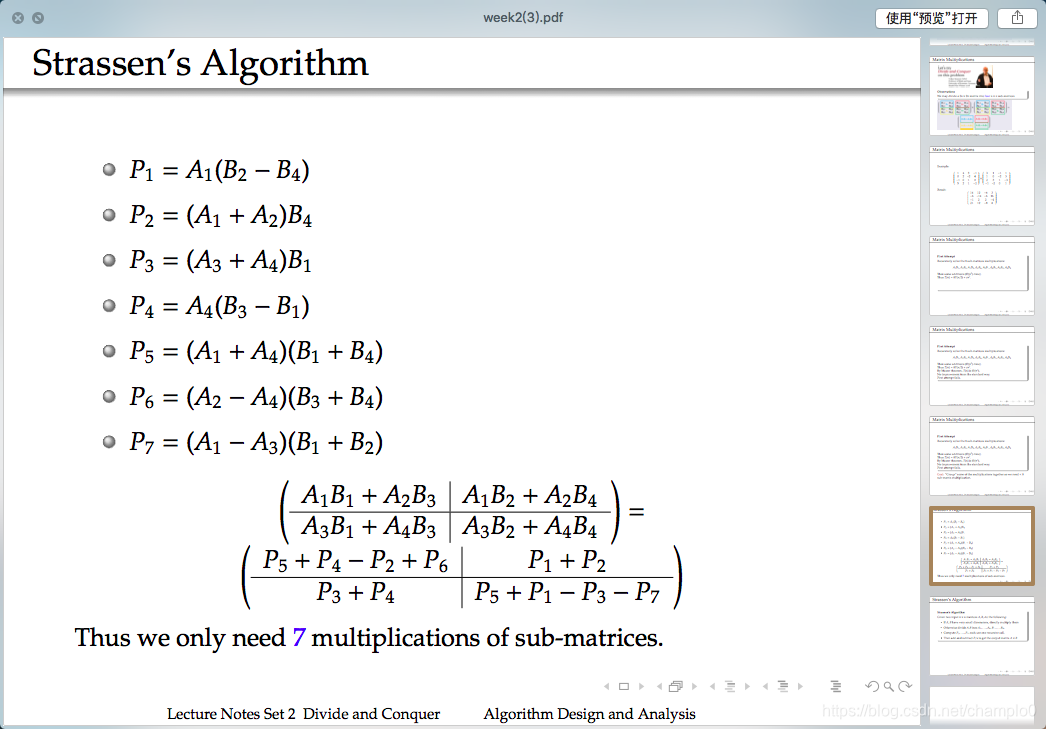
T(n) = 7T(n/2) + cn2
By Master theorem, T(n) is Θ(nlog 7) ≈ Θ(n2.808)
2.Graph
2.1 Graph
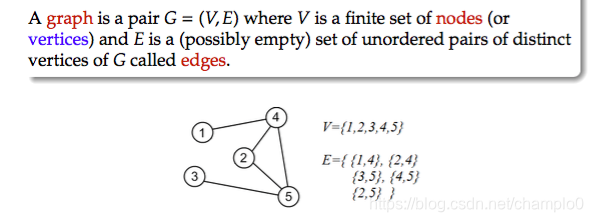
無向圖:{} 有向圖:()
2.1.1 Adjacency Matrix

Size:O(n2)
2.1.2 Adjacency List

Size:O(m)
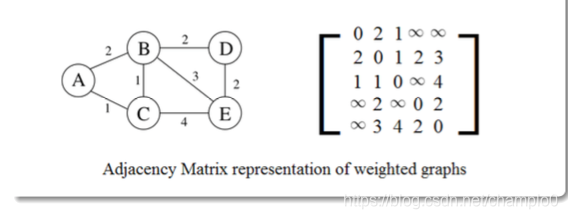
2.2 Weighted Graphs

2.3 DAGs
directed acyclic graph,有向無環圖。
acyclic:

時間複雜度:O(n + m)
2.4 edge 的分類

圖中藍色的即為tree edge。
2.5 Linearisations
有環不能被線性。
Linearizable ≡ Acyclicity ≡ No-Back-edgeness


The algorithm runs in time O(m + n).
2.6 SCC , Kosaraju-Sharir algorithm
strongly connected component
1.如果G是無環圖,則每個節點都是scc,G中有n個sccs。
2.如果G是個環,則G本身是scc,G中有1個scc。
3.如果G是無向圖,則檢查scc和檢查reachability一樣。
find scc

The algorithm runs in time O(m + n).
3. Depth First Search
3.1 Recursive Implementation 遞迴實現


3.2 Stack Implementation 堆疊實現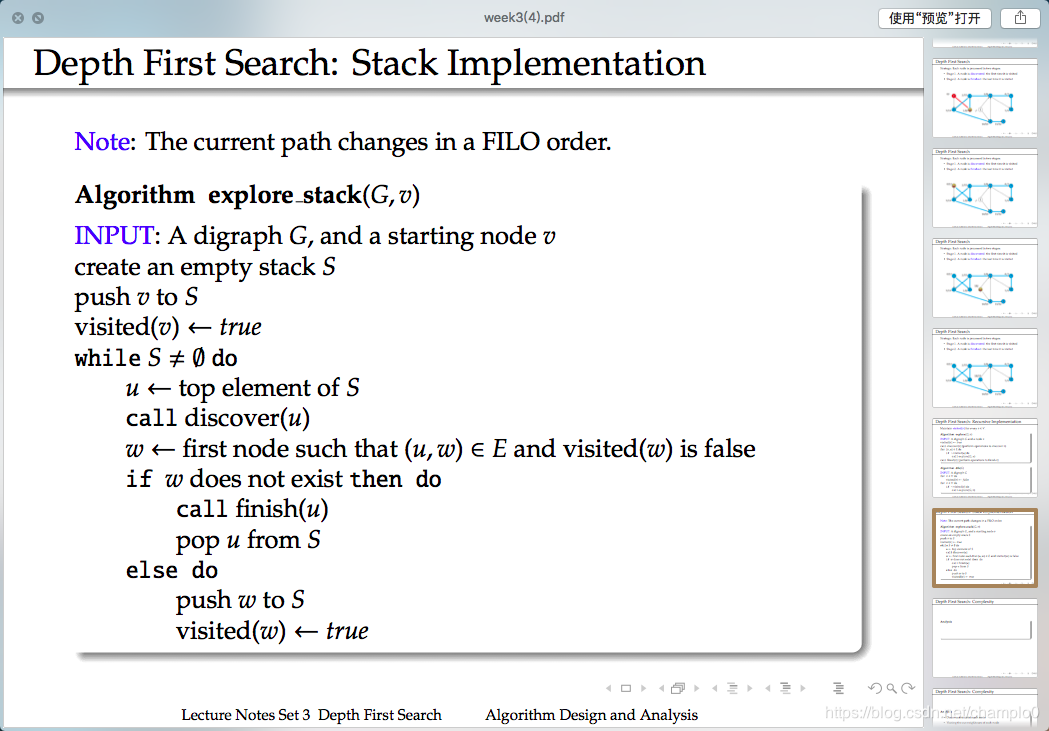
時間複雜度分析:
領接表:O(n + m) 鄰接矩陣: O(n2)
4. Breadth First Search
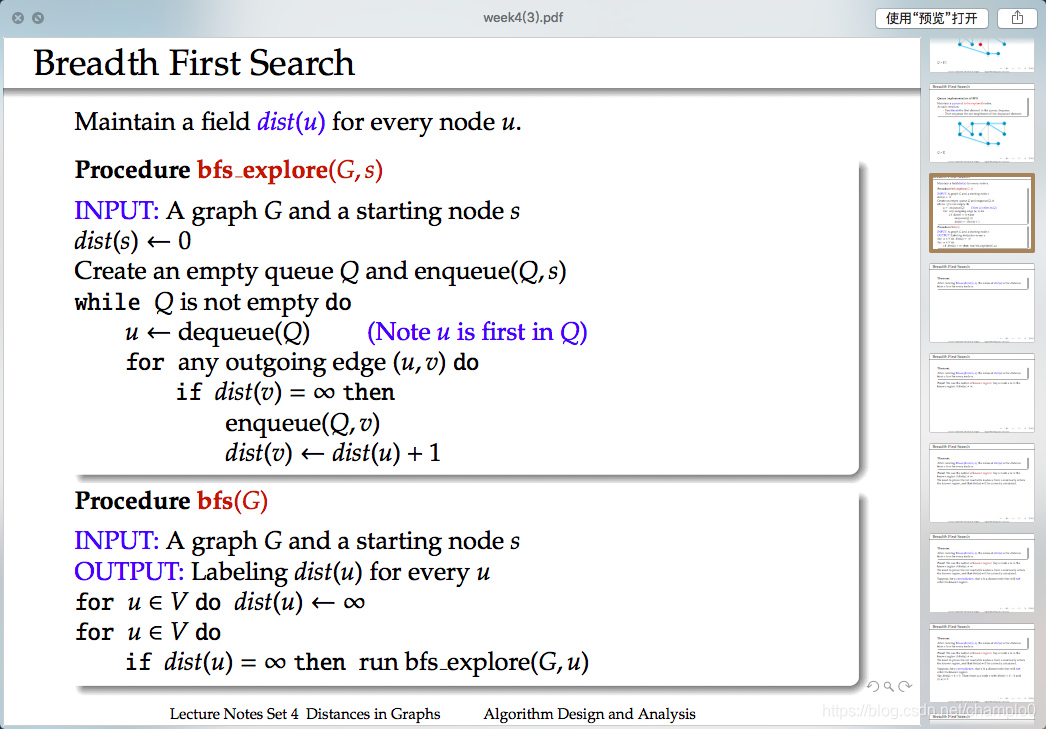
The running time of the BFS algorithm is O(m + n).
5. DFS VS BFS
DFS:線性,scc,reachability,O(m + n)
BFS:最短路徑,O(m + n)
6. Dijkstra’s Algorithm
7.Spanning Trees
A spanning tree of G is a connected subgraph that contains all nodes in V and no cycles.
A minimal spanning tree of a weighted graph is a spanning tree whose total weight is minimal.(可能不唯一)
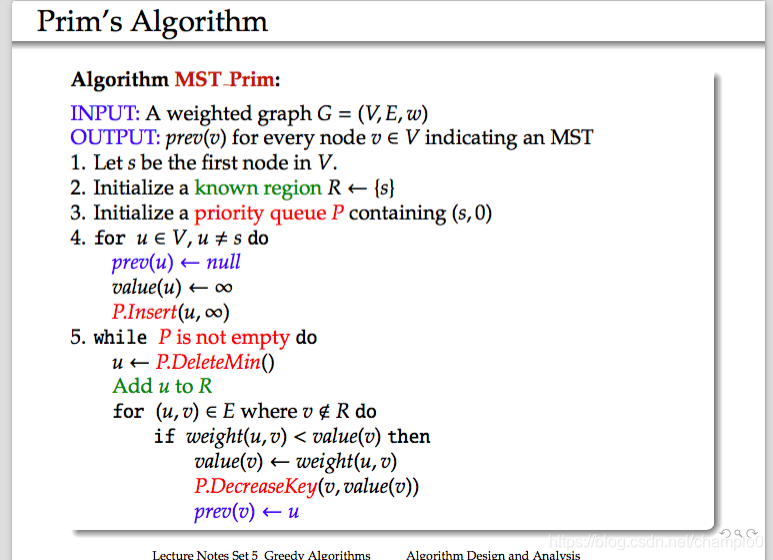
8.Prim’s Algorithm
To Find MST(similar way as Dijkstra’s algorithm.)
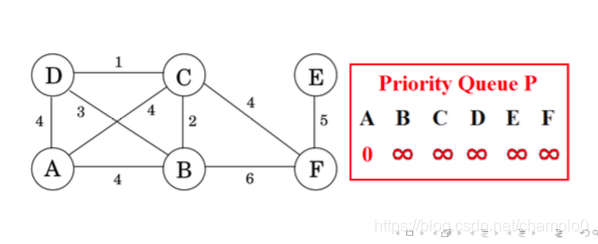

1.訪問dis.最短的節點
2.推出佇列,更新到其他點的距離
3.連結節點,更新MST

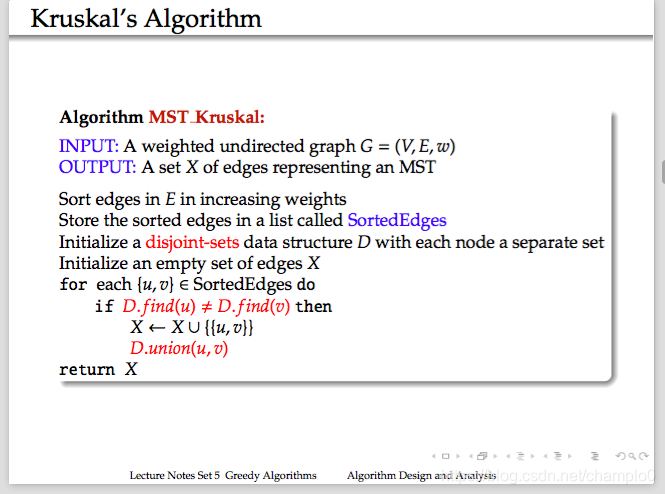
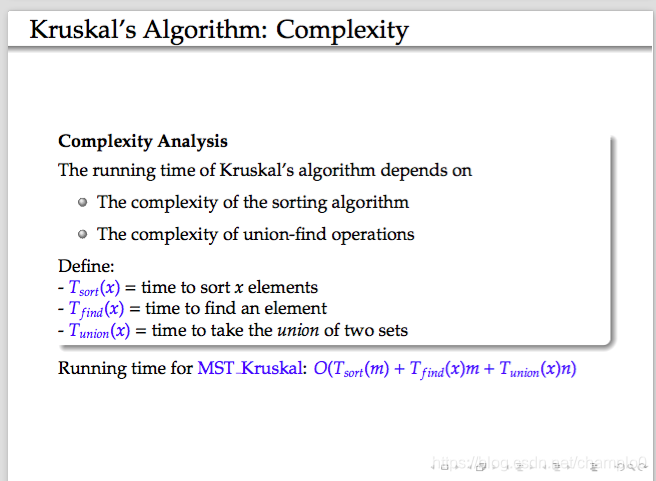
9.Kruskal’s Algorithm
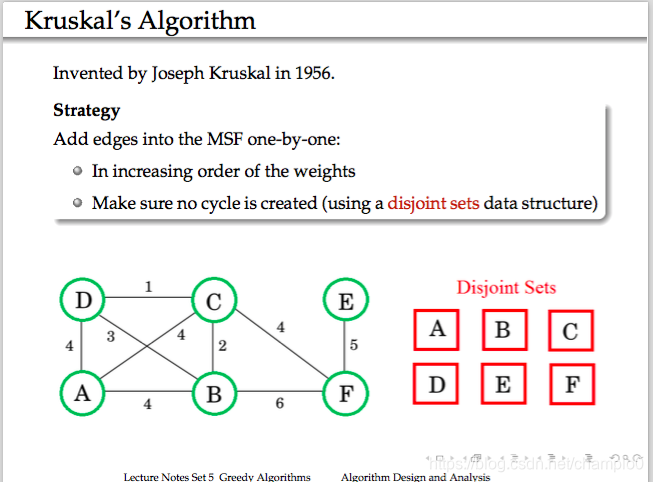
選擇圖中最短的edge合併
10.Greedy Algorithms
Dijkstra’s: 選擇到起點距離最短的節點
Prim’s: 選擇連線到已知節點的edge中最短的
Kruskal’s: 選擇最短的edge連線(不構成環)

11. Example : 小偷問題
描述:

思路:
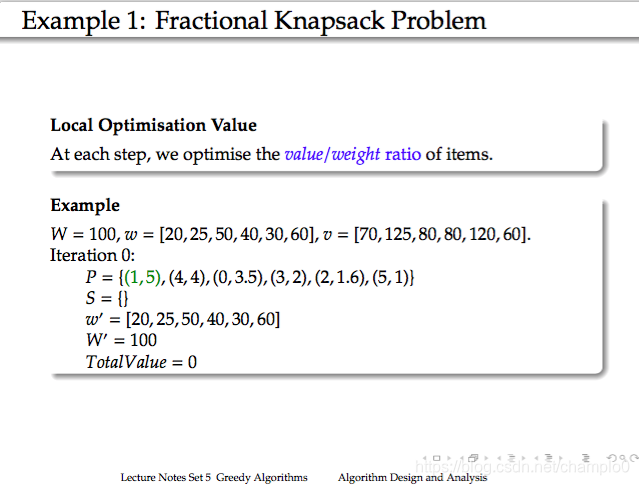
W:總可容納重量
w:各物品的重量
v:各物品的價值
P:優先佇列,(1,5)表示index為1,價值/重量比為5
(比值最高的在佇列最前)
S:輸出的方案,(1,25)表示index為1,重量為25
w’:w的餘,0代表被取出
W’:剩餘的總重量
TotalValue:取得的物品總價值
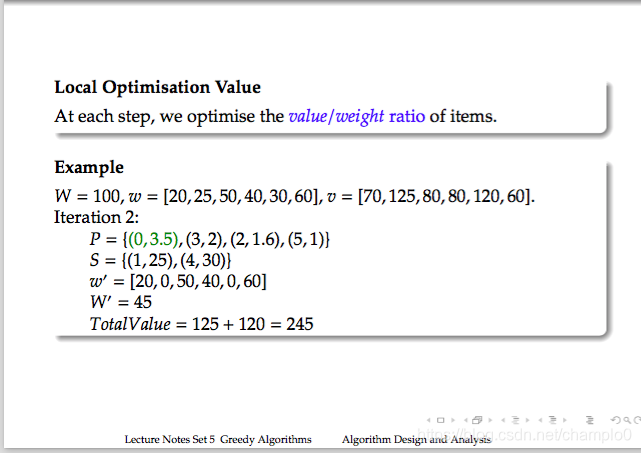
答案:S = {(1, 25), (4, 30), (0, 20), (3, 25)}
TotalValue = 315 + 50 = 365
偽碼描述:

12.Bellman-Ford Algorithm
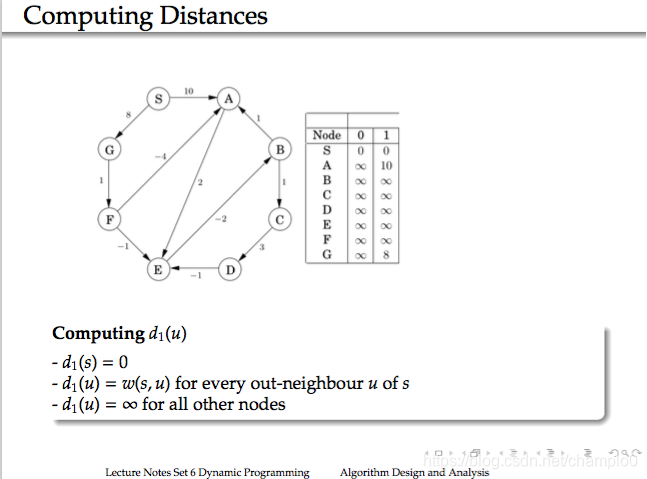
Node1,2,3…代表能使用的節點

example:
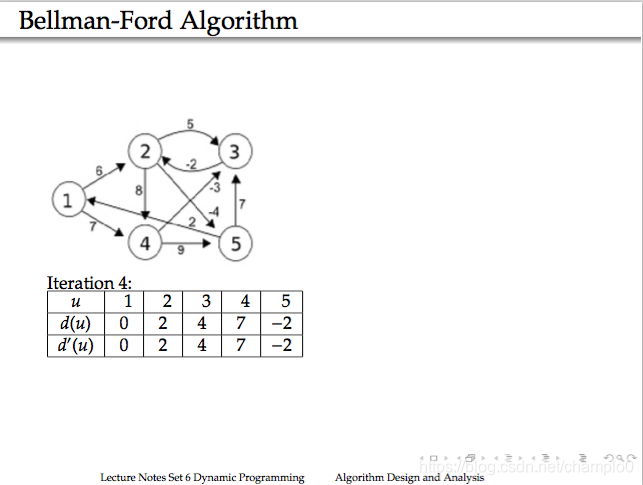
time :Θ(mn).
Dijkstra’s and Bell-Ford algorithm both solves Single-Source Shortest Path Problem.
13. Floyd-Warshall Algorithm
fk(i, j) 是經過 v1,…,vk 節點的vi, vj間的最短路徑。

Time Complexity : O(n3)
最短路徑問題總結
Single-Source Weights:
- Positive :
- Dijkstra’s algorithm :
- List O(n2)
- Binary /Binomial Heap O((n + m) log n)
- Fibonacci Heap O(m + n log n)
- Dijkstra’s algorithm :
- Positive/Negative:
- Bellman-Ford(動態): algorithm: O(nm)
All-Pair Weights:
- Floyd-Warshall(動態): algorithm:O(n3)
14. Example: Longest Increasing Subsequence

訪問每個新節點時,在以下情況中選擇最大的:
1.延續上一個節點的值不變
2.相連的前個節點加1
答案:11222344

分析:

15. Edit Distance

一行一行更新,訪問新的點時,在以下情況中選擇最小的:
- 左邊的點 +1
- 上面的點 +1
- 左上角的點
- 假如相同 +0
- 假如不同 +1

distance 為3


