Spring Boot之自動配置原理以及自定義starter
前言:spring boot之所以強大,其核心自動配置起到了關鍵的作用,通過自動配置,摒棄了傳統開發中的一大堆配置檔案xml。如果說spring boot是一把手槍,那starter就是他的子彈。starter簡單來說,就是一堆jar組成的一個功能,而且是可以自動配置jar。
1、自動配置原理
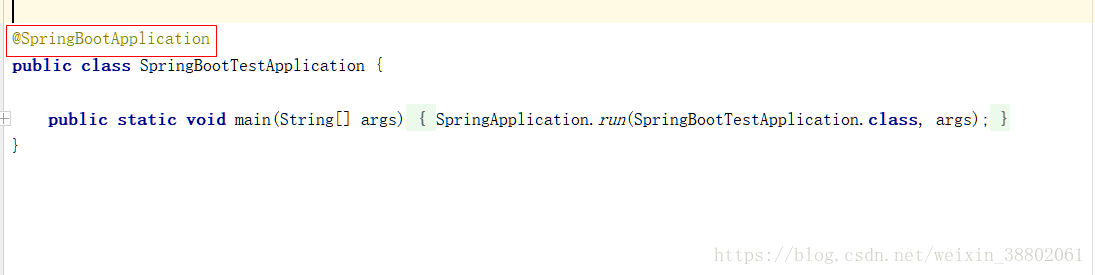
在spring boot應用的主入口
進入到@SpringBootApplication註解中
@SpringBootConfiguration註解說明主程式類也是一個配置類
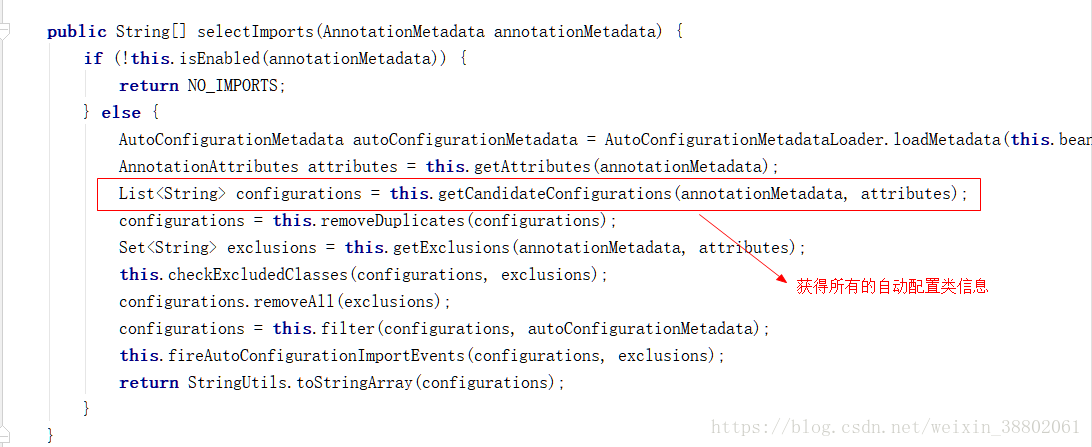
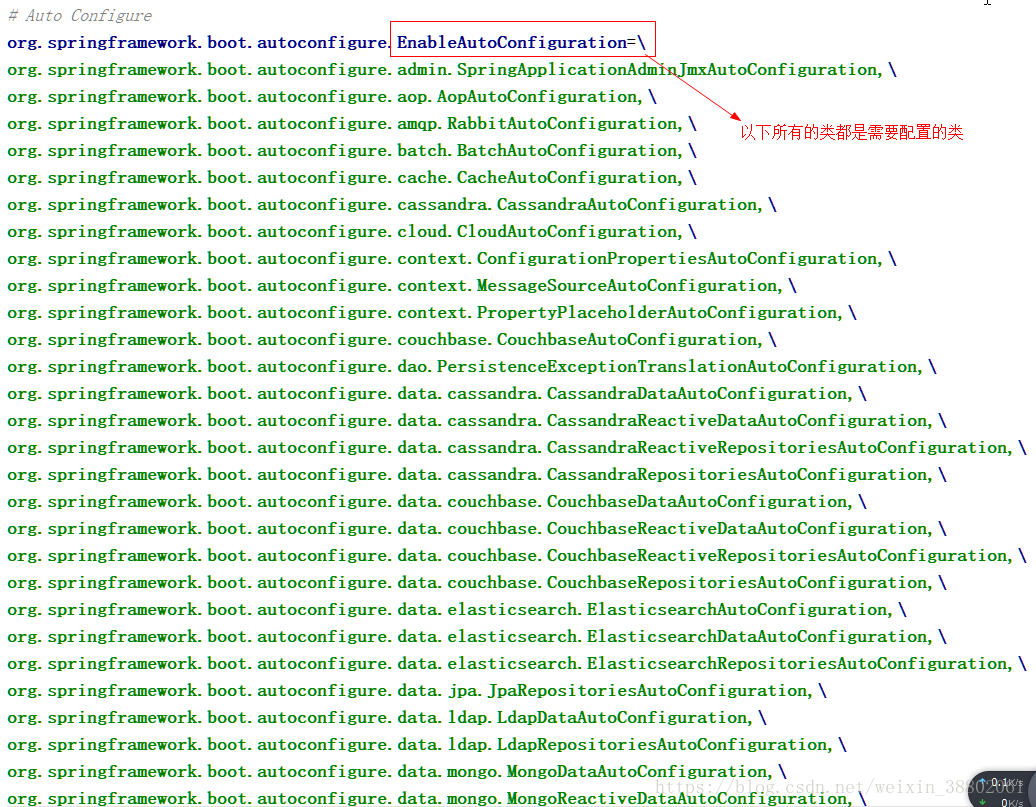
@EnableAutoConfiguration註解中

進入getCandidateConfigurations方法(獲得所有的候選配置資訊)
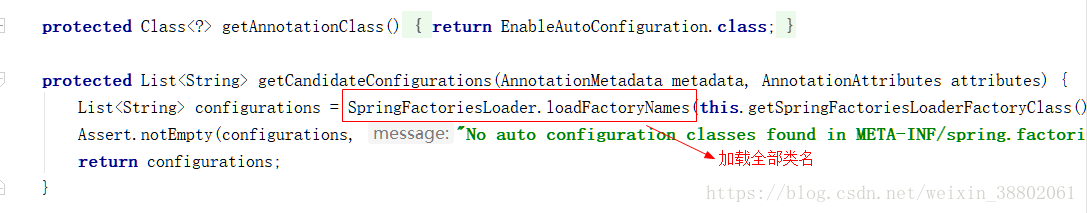
通過SpringFactoriesLoader工廠載入資訊
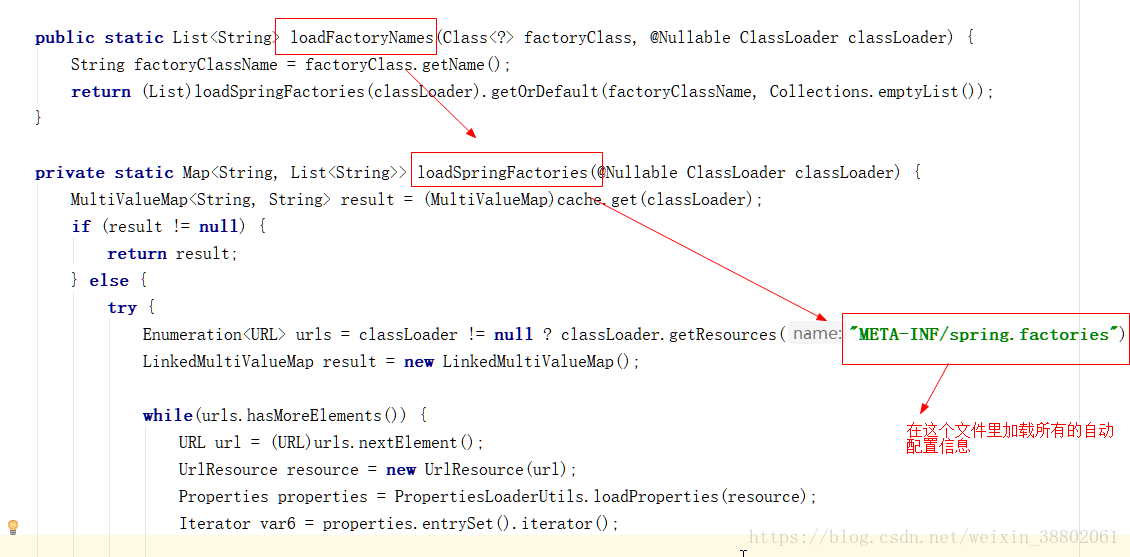
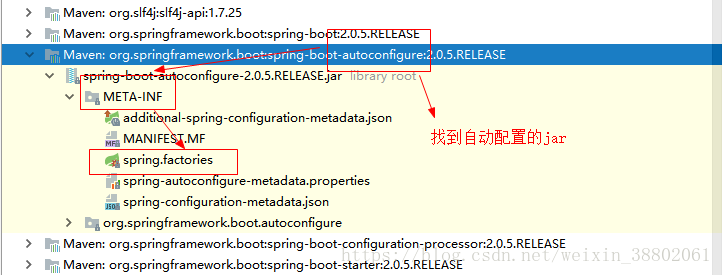
原來載入的是META-INF檔案下的spring.factories檔案配置的資訊
來到自動配置包下的META-INF
進入spring.factories檔案
進入其中的一個自動配置類 ThymeleafAutoConfiguration
@Configuration:配置類
@EnableConfigurationProperties():開啟某屬性類,裡面封裝的是屬性資訊,相當於@ConfigurationProperties載入application.properties裡面的資訊,並用@Component將類交由spring管理
@ConditionalOnClass():當這個類存在時,再進行下面的步驟,否則就不進行下面的步驟了
@AutoConfigureAfter():當自動配置完成後,再執行裡面的類
@ConfigurationOnMissBean():當這個bean不存在時,再新增bean類
@Bean:新增bean類
2、自定義starter
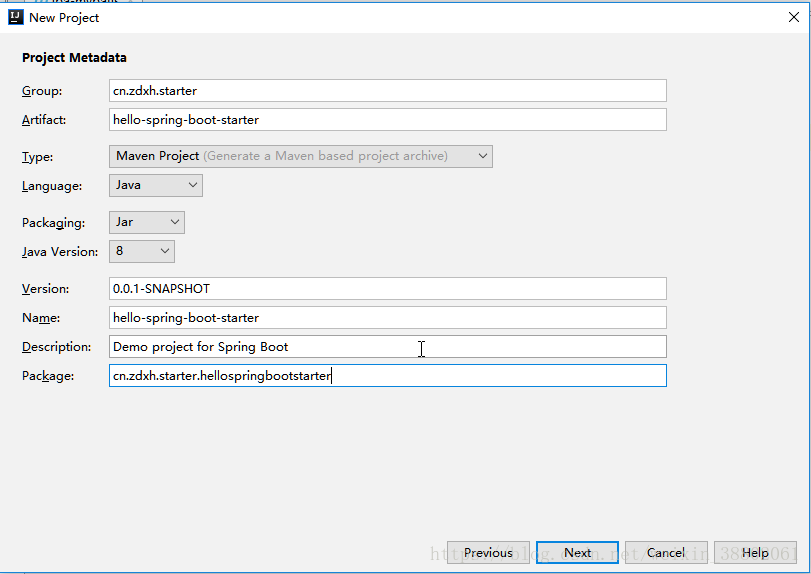
建立專案
Group:本地倉庫的各級目錄
Artifact:{自定義名}-spring-boot-starter
在專案中最好只留spring-boot-starter依賴,這是最基本的starter依賴,其他依賴都可以刪掉,保持專案的簡潔性
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>cn.zdxh.starter</groupId>
<artifactId>hello-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<packaging>jar</packaging>
<name>hello-spring-boot-starter</name>
<description>Demo project for Spring Boot</description>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.0.6.RELEASE</version>
<relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
<properties>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
<project.reporting.outputEncoding>UTF-8</project.reporting.outputEncoding>
<java.version>1.8</java.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</project>
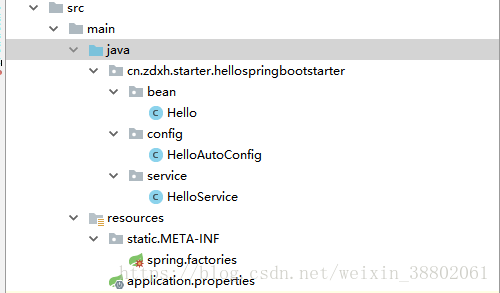
目錄結構:
不要主程式入口!不要主程式入口!不要主程式入口!
bean:讀取properties裡面的資訊
config:實現自動配置的類
service:需要被自動配置的類
static/META-INF/spring.factories:建立該檔案作為存放config類
Hello類
該類交由spring管理,並且繫結application.properties檔案中的init.hello屬性
@Component
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "init.hello")
public class Hello {
private String message="我是初始的message";
public String getMessage() {
return message;
}
public void setMessage(String message) {
this.message = message;
}
}HelloService的目標配置類
注入從檔案中讀出資訊的Hello類
public class HelloService {
@Autowired
private Hello hello;
public void sayHello(){
System.out.println(hello.getMessage());//僅僅作輸出的操作
}
}
HelloAutoConfig自動配置類
核心是@ConditionalOnMissBean(),當容器中沒有這個類時,才進行自動配置操作
@Configuration
public class HelloAutoConfig {
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(HelloService.class)
@Bean
public HelloService helloService(){
return new HelloService();
}
}
spring.factories檔案新增自動配置類
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration=\
cn.zdxh.starter.hellospringbootstarter.config.HelloAutoConfig,
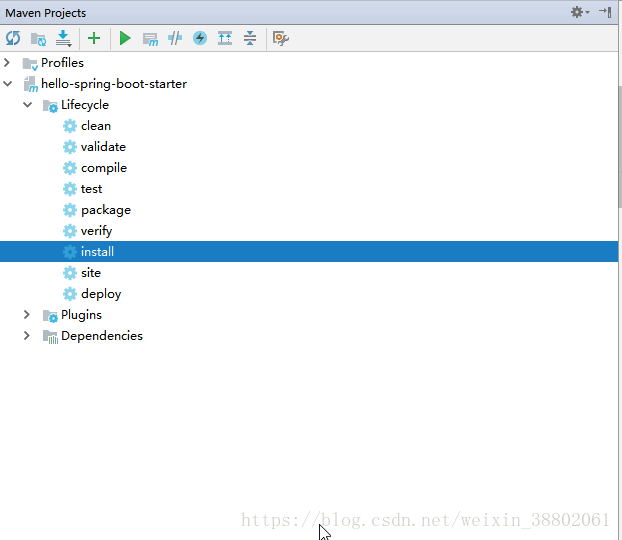
點選右上角的Maven Projects調出以下視窗,並install創庫
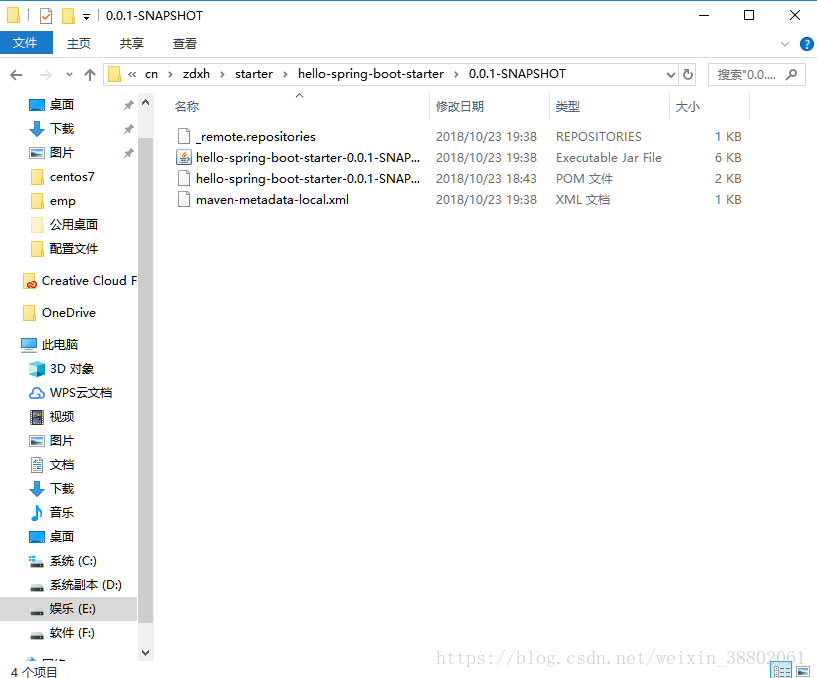
在本地專案中就可以看到建立的starter
驗證自定義starter
在別的專案引入自定義starter
<dependency>
<groupId>cn.zdxh.starter</groupId>
<artifactId>hello-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
</dependency>在application.properties新增需要顯示的資訊
init.hello.message=我是配置的message資訊在測試類中注入HelloService類
@Autowired
HelloService helloService;
@Test
public void testHelloService(){
helloService.sayHello();
}在控制檯看到如下資訊,則自動配置資訊成功
當別人引用這個自定義starter時,HelloService類就會被自動配置,就不需要手動添加了,這就是spring boot的魅力所在!