淺談tcp cubic擁塞演算法以及優化建議
1. tcp cubic數學模型
CUBIC在設計上簡化了BIC-TCP的視窗調整演算法,在BIC-TCP的視窗調整中會出現一個凹和凸(這裡的凹和凸指的是數學意義上的凹和凸,凹函式/凸函式)的增長曲線,CUBIC使用了一個三次函式(即一個立方函式),在三次函式曲線中同樣存在一個凹和凸的部分,該曲線形狀和BIC-TCP的曲線圖十分相似,於是該部分取代BIC-TCP的增長曲線。另外,CUBIC中最關鍵的點在於它的視窗增長函式僅僅取決於連續的兩次擁塞事件的時間間隔值,從而視窗增長完全獨立於網路的時延RTT,之前講述過的HSTCP存在嚴重的RTT不公平性,而CUBIC的RTT獨立性質使得CUBIC能夠在多條共享瓶頸鍊路的TCP連線之間保持良好的RRTT公平性。
來看下具體細節:當某次擁塞事件發生時,Wmax設定為此時發生擁塞時的視窗值,然後把視窗進行乘法減小,乘法減小因子設為β,當從快速恢復階段退出然後進入到擁塞避免階段,此時CUBIC的視窗增長開始按照“凹”式增長曲線進行增長,該過程一直持續直到視窗再次增長到Wmax,緊接著,該函式轉入“凸”式增長階段。該方式的增長可以使得視窗一直維持在Wmax附近,從而可以達到網路頻寬的高利用率和協議本身的穩定性。
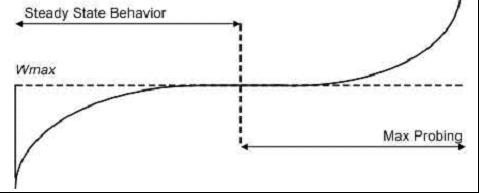
視窗的增長函式如下:
W(t) = C * (t-K)3 + Wmax, 其中C和β為常量。
t為當前時間距上一次視窗減小的時間差,而K就代表該函式從W增長到Wmax的時間週期,![]() 。
。
當收到ACK後,CUBIC計算利用該演算法計算下一個RTT內的視窗增長速度,即計算W(t+RTT),該值將作為cwnd的目標值,根據cwnd的大小,CUBIC將進入三種不同模式,如果cwnd會小於在標準TCP下經過上次擁塞之後的時刻t視窗將會達到的值(該值是通過標準TCP的視窗增長函式計算出來的),那麼CUBIC就處於標準TCP模式,如果小於Wmax,那麼位於凹階段的,如果大於Wmax,那麼處於凸階段。
2. tcp cubic 核心原始碼呼叫邏輯
CUBIC整體架構呼叫的邏輯如下:
1. 連線每收到一個ack,則呼叫tcp_ack
2. tcp_ack會呼叫bictcp_acked,用來更新cnt和delayed_ack(用來消除delay包的影響)
3. tcp_ack會呼叫bictcp_cong_avoid,這是分兩種情況:
(1)snd_cwnd小於慢啟動閾值,處於慢啟動階段,則呼叫tcp_slow_start
(2)snd_cwnd大於慢啟動閾值,處於擁塞避免階段,則呼叫bictcp_update來更新bictcp,再呼叫tcp_cong_avoid_ai
4. tcp_ack中如果檢測到丟包,進入擁塞處理階段
5. tcp_ack中完成丟包重傳後,退出擁塞處理階段,則呼叫bictcp_undo_cwnd來更新snd_cwnd
快速重傳:tcp_ack中的丟包檢測,即檢測到連續3個重複ACK。
快速恢復:bictcp_undo_cwnd,直接把snd_cwnd更新為max(snd_cwnd,last_max_cwnd),和掉包前相差不大。
3:程式碼解讀
/*
* TCP CUBIC: Binary Increase Congestion control for TCP v2.3
* Home page:
* http://netsrv.csc.ncsu.edu/twiki/bin/view/Main/BIC
* This is from the implementation of CUBIC TCP in
* Sangtae Ha, Injong Rhee and Lisong Xu,
* "CUBIC: A New TCP-Friendly High-Speed TCP Variant"
* in ACM SIGOPS Operating System Review, July 2008.
* Available from:
* http://netsrv.csc.ncsu.edu/export/cubic_a_new_tcp_2008.pdf
*
* CUBIC integrates a new slow start algorithm, called HyStart.
* The details of HyStart are presented in
* Sangtae Ha and Injong Rhee,
* "Taming the Elephants: New TCP Slow Start", NCSU TechReport 2008.
* Available from:
* http://netsrv.csc.ncsu.edu/export/hystart_techreport_2008.pdf
*
* All testing results are available from:
* http://netsrv.csc.ncsu.edu/wiki/index.php/TCP_Testing
*
* Unless CUBIC is enabled and congestion window is large
* this behaves the same as the original Reno.
*/
#include <linux/mm.h>
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/math64.h>
#include <net/tcp.h>
#define BICTCP_BETA_SCALE 1024 /* Scale factor beta calculation
* max_cwnd = snd_cwnd * beta
*/
#define BICTCP_HZ 10 /* BIC HZ 2^10 = 1024 */
/* Two methods of hybrid slow start */
#define HYSTART_ACK_TRAIN 0x1
#define HYSTART_DELAY 0x2
/* Number of delay samples for detecting the increase of delay */
#define HYSTART_MIN_SAMPLES 8
#define HYSTART_DELAY_MIN (2U<<3)
#define HYSTART_DELAY_MAX (16U<<3)
#define HYSTART_DELAY_THRESH(x) clamp(x, HYSTART_DELAY_MIN, HYSTART_DELAY_MAX)
static int fast_convergence __read_mostly = 1;
static int beta __read_mostly = 717; /* = 717/1024 (BICTCP_BETA_SCALE) */
static int initial_ssthresh __read_mostly;
//bic_scale就是paper中三次方係數C的1024倍縮放值
//MODULE_PARM_DESC(bic_scale, "scale (scaled by 1024) value for bic function (bic_scale/1024)");
static int bic_scale __read_mostly = 41;
static int tcp_friendliness __read_mostly = 1;
static int hystart __read_mostly = 1;
static int hystart_detect __read_mostly = HYSTART_ACK_TRAIN | HYSTART_DELAY;
static int hystart_low_window __read_mostly = 16;
static u32 cube_rtt_scale __read_mostly;
static u32 beta_scale __read_mostly;
static u64 cube_factor __read_mostly;
/* Note parameters that are used for precomputing scale factors are read-only */
module_param(fast_convergence, int, 0644);
MODULE_PARM_DESC(fast_convergence, "turn on/off fast convergence");
module_param(beta, int, 0644);
MODULE_PARM_DESC(beta, "beta for multiplicative increase");
module_param(initial_ssthresh, int, 0644);
MODULE_PARM_DESC(initial_ssthresh, "initial value of slow start threshold");
module_param(bic_scale, int, 0444);
MODULE_PARM_DESC(bic_scale, "scale (scaled by 1024) value for bic function (bic_scale/1024)");
module_param(tcp_friendliness, int, 0644);
MODULE_PARM_DESC(tcp_friendliness, "turn on/off tcp friendliness");
module_param(hystart, int, 0644);
MODULE_PARM_DESC(hystart, "turn on/off hybrid slow start algorithm");
module_param(hystart_detect, int, 0644);
MODULE_PARM_DESC(hystart_detect, "hyrbrid slow start detection mechanisms"
" 1: packet-train 2: delay 3: both packet-train and delay");
module_param(hystart_low_window, int, 0644);
MODULE_PARM_DESC(hystart_low_window, "lower bound cwnd for hybrid slow start");
/* BIC TCP Parameters */
struct bictcp {
u32 cnt; /* increase cwnd by 1 after ACKs */
u32 last_max_cwnd; /* last maximum snd_cwnd */
//兩個重要的count值:
//第一個是tcp_sock->snd_cwnd_cnt,表示在當前的擁塞視窗中已經
//傳送(經過對方ack包確認)的資料段的個數,
//而第二個是bictcp->cnt,它是cubic擁塞演算法的核心,
//主要用來控制在擁塞避免狀態的時候,什麼時候才能增大擁塞視窗,
//具體實現是通過比較cnt和snd_cwnd_cnt,來決定是否增大擁塞視窗,
u32 loss_cwnd; /* congestion window at last loss */
u32 last_cwnd; /* the last snd_cwnd */
u32 last_time; /* time when updated last_cwnd */
u32 bic_origin_point;/* origin point of bic function */
u32 bic_K; /* time to origin point from the beginning of the current epoch */
u32 delay_min; /* min delay */
u32 epoch_start; /* beginning of an epoch */
u32 ack_cnt; /* number of acks */
u32 tcp_cwnd; /* estimated tcp cwnd */
#define ACK_RATIO_SHIFT 4
u16 delayed_ack; /* estimate the ratio of Packets/ACKs << 4 */
u8 sample_cnt; /* number of samples to decide curr_rtt */
u8 found; /* the exit point is found? */
u32 round_start; /* beginning of each round */
u32 end_seq; /* end_seq of the round */
u32 last_jiffies; /* last time when the ACK spacing is close */
u32 curr_rtt; /* the minimum rtt of current round */
};
static inline void bictcp_reset(struct bictcp *ca)
{
ca->cnt = 0;
ca->last_max_cwnd = 0;
ca->loss_cwnd = 0;
ca->last_cwnd = 0;
ca->last_time = 0;
ca->bic_origin_point = 0;
ca->bic_K = 0;
ca->delay_min = 0;
ca->epoch_start = 0;
ca->delayed_ack = 2 << ACK_RATIO_SHIFT;
ca->ack_cnt = 0;
ca->tcp_cwnd = 0;
ca->found = 0;
}
static inline void bictcp_hystart_reset(struct sock *sk)
{
struct tcp_sock *tp = tcp_sk(sk);
struct bictcp *ca = inet_csk_ca(sk);
ca->round_start = ca->last_jiffies = jiffies;
ca->end_seq = tp->snd_nxt;
ca->curr_rtt = 0;
ca->sample_cnt = 0;
}
static void bictcp_init(struct sock *sk)
{
bictcp_reset(inet_csk_ca(sk));
if (hystart)
bictcp_hystart_reset(sk);
if (!hystart && initial_ssthresh)
tcp_sk(sk)->snd_ssthresh = initial_ssthresh;
}
/* calculate the cubic root of x using a table lookup followed by one
* Newton-Raphson iteration.
* Avg err ~= 0.195%
*/
static u32 cubic_root(u64 a)
{
u32 x, b, shift;
/*
* cbrt(x) MSB values for x MSB values in [0..63].
* Precomputed then refined by hand - Willy Tarreau
*
* For x in [0..63],
* v = cbrt(x << 18) - 1
* cbrt(x) = (v[x] + 10) >> 6
*/
static const u8 v[] = {
/* 0x00 */ 0, 54, 54, 54, 118, 118, 118, 118,
/* 0x08 */ 123, 129, 134, 138, 143, 147, 151, 156,
/* 0x10 */ 157, 161, 164, 168, 170, 173, 176, 179,
/* 0x18 */ 181, 185, 187, 190, 192, 194, 197, 199,
/* 0x20 */ 200, 202, 204, 206, 209, 211, 213, 215,
/* 0x28 */ 217, 219, 221, 222, 224, 225, 227, 229,
/* 0x30 */ 231, 232, 234, 236, 237, 239, 240, 242,
/* 0x38 */ 244, 245, 246, 248, 250, 251, 252, 254,
};
b = fls64(a);
if (b < 7) {
/* a in [0..63] */
return ((u32)v[(u32)a] + 35) >> 6;
}
b = ((b * 84) >> 8) - 1;
shift = (a >> (b * 3));
x = ((u32)(((u32)v[shift] + 10) << b)) >> 6;
/*
* Newton-Raphson iteration
* 2
* x = ( 2 * x + a / x ) / 3
* k+1 k k
*/
x = (2 * x + (u32)div64_u64(a, (u64)x * (u64)(x - 1)));
x = ((x * 341) >> 10);
return x;
}
/*
函式關鍵點
1. 我們最終要得到的是ca->cnt,用來控制snd_cwnd的增長。
2. ca->cnt的值,是根據cwnd和w( t + after ) 的大小來判斷的。w( t + after )即bic_target,它表示我們預期的
在經過after時間後的snd_cwnd。如果此時cwnd < w( t + after ),那麼我們就快速增加視窗,達到預期目標。
如果cwnd > w( t + after ),那說明我們已經增加過快了,需要降速了,這樣才能達到預期目標。
cwnd / (bic_target - cwnd ) // bic_target > cwnd
cnt =
100 * cwnd // bic_target < cwnd
3. cwnd是傳入的引數,已知。現在我們只需要計算bic_target。
而根據Cubic的視窗增長函式:W(t) = C(t - K)^3 + Wmax,
我們要計算時間( 當前 + after ),以及時間K。時間K即bic_K,表示函式值為Wmax所對應的時間。
通過程式碼可以發現,after為min RTT,即連線的傳播時延。
*/
/*
* Compute congestion window to use.
*/
static inline void bictcp_update(struct bictcp *ca, u32 cwnd)
{
u64 offs;/* 時間差,| t - K | */
u32 delta, t, bic_target, max_cnt;/* delta是cwnd差,bic_target是預測值,t為預測時間 */
ca->ack_cnt++; /* count the number of ACKs */
if (ca->last_cwnd == cwnd &&
(s32)(tcp_time_stamp - ca->last_time) <= HZ / 32)
return;
ca->last_cwnd = cwnd;
ca->last_time = tcp_time_stamp;
if (ca->epoch_start == 0) {
ca->epoch_start = tcp_time_stamp; /* record the beginning of an epoch */
ca->ack_cnt = 1; /* start counting */
ca->tcp_cwnd = cwnd; /* syn with cubic */
/* 取max(last_max_cwnd , cwnd)作為當前Wmax */
if (ca->last_max_cwnd <= cwnd) {
ca->bic_K = 0;
ca->bic_origin_point = cwnd;
} else {
/* Compute new K based on
* (wmax-cwnd) * (srtt>>3 / HZ) / c * 2^(3*bictcp_HZ)
*/
ca->bic_K = cubic_root(cube_factor
* (ca->last_max_cwnd - cwnd));
ca->bic_origin_point = ca->last_max_cwnd;
}
}
/* cubic function - calc*/
/* calculate c * time^3 / rtt,
* while considering overflow in calculation of time^3
* (so time^3 is done by using 64 bit)
* and without the support of division of 64bit numbers
* (so all divisions are done by using 32 bit)
* also NOTE the unit of those veriables
* time = (t - K) / 2^bictcp_HZ
* c = bic_scale >> 10
* rtt = (srtt >> 3) / HZ
* !!! The following code does not have overflow problems,
* if the cwnd < 1 million packets !!!
*/
/* change the unit from HZ to bictcp_HZ */
t = ((tcp_time_stamp + (ca->delay_min>>3) - ca->epoch_start)
<< BICTCP_HZ) / HZ;
/* 求| t - bic_K | */
if (t < ca->bic_K) /* 還未達到Wmax */
offs = ca->bic_K - t;
else
offs = t - ca->bic_K; //此時已經超過Wmax
/* c/rtt * (t-K)^3 */
/* 計算delta =| W(t) - W(bic_K) |
* cube_rtt_scale = (bic_scale * 10) = c / srtt * 2^10,c/srtt = 0.4
*/
delta = (cube_rtt_scale * offs * offs * offs) >> (10+3*BICTCP_HZ);
if (t < ca->bic_K) /* below origin*/
bic_target = ca->bic_origin_point - delta;
else /* above origin*/
bic_target = ca->bic_origin_point + delta;
/* cubic function - calc bictcp_cnt /* 計算bic_target,即預測cwnd */
if (bic_target > cwnd) {
/* 相差越多,增長越快,這就是函式形狀由來 */
ca->cnt = cwnd / (bic_target - cwnd);
} else {
ca->cnt = 100 * cwnd; /* very small increment 目前cwnd已經超出預期了,應該降速*/
}
/* TCP Friendly /* TCP Friendly —如果cubic比RENO慢,則提升cwnd增長速度,即減小cnt
* 以上次丟包以後的時間t算起,每次RTT增長 3B / ( 2 - B),那麼可以得到
* 採用RENO演算法的cwnd。
* cwnd (RENO) = cwnd + 3B / (2 - B) * ack_cnt / cwnd
* B為乘性減少因子,在此演算法中為0.3
*/
if (tcp_friendliness) {
u32 scale = beta_scale;
delta = (cwnd * scale) >> 3;
while (ca->ack_cnt > delta) { /* update tcp cwnd */
ca->ack_cnt -= delta;
ca->tcp_cwnd++;
}
if (ca->tcp_cwnd > cwnd){ /* if bic is slower than tcp */
delta = ca->tcp_cwnd - cwnd;
max_cnt = cwnd / delta;
if (ca->cnt > max_cnt)
ca->cnt = max_cnt;
}
}
ca->cnt = (ca->cnt << ACK_RATIO_SHIFT) / ca->delayed_ack;//做了一個比較直接的delay_ack的控制
//ratio = (15*ratio + sample) / 16 這裡ca-delayed_ack由
if (ca->cnt == 0) /* cannot be zero */
ca->cnt = 1;/* 此時代表cwnd遠小於bic_target,增長速度最大 */
}
static void bictcp_cong_avoid(struct sock *sk, u32 ack, u32 in_flight)
{
struct tcp_sock *tp = tcp_sk(sk);
struct bictcp *ca = inet_csk_ca(sk);
//判斷髮送擁塞視窗是否到達限制,如果到達限制則直接返回
if (!tcp_is_cwnd_limited(sk, in_flight))
return;
if (tp->snd_cwnd <= tp->snd_ssthresh) {
if (hystart && after(ack, ca->end_seq))
bictcp_hystart_reset(sk);
tcp_slow_start(tp);//進入slow start狀態
} else {
bictcp_update(ca, tp->snd_cwnd);
tcp_cong_avoid_ai(tp, ca->cnt);//然後進入擁塞避免,更新tcp_sock->snd_cwnd_cnt
}
}
//做了兩件事:重賦值last_max_cwnd、返回新的慢啟動閾值
static u32 bictcp_recalc_ssthresh(struct sock *sk)
{
const struct tcp_sock *tp = tcp_sk(sk);
struct bictcp *ca = inet_csk_ca(sk);
ca->epoch_start = 0; /* end of epoch */
/* Wmax and fast convergence */
//當一個新的TCP流加入到網路,
//網路中已有TCP流需要放棄自己頻寬,
//給新的TCP流提供一定的上升空間。
//為提高已有TCP流所釋放的頻寬而引入快速收斂機制。
if (tp->snd_cwnd < ca->last_max_cwnd && fast_convergence)
//表示已有TCP流所經歷的飽和點因為可用頻寬改變而正在降低。
//然後,通過進一步降低Wmax讓已有流釋放更多頻寬。
//這種行為有效地延長已有流增大其視窗的時間,
//因為降低後的Wmax強制已有流更早進入平穩狀態。
//這允許新流有更多的時間來趕上其視窗尺寸。
ca->last_max_cwnd = (tp->snd_cwnd * (BICTCP_BETA_SCALE + beta))
/ (2 * BICTCP_BETA_SCALE);//last_max_cwnd = 0.9 * snd_cwnd
else
ca->last_max_cwnd = tp->snd_cwnd;
ca->loss_cwnd = tp->snd_cwnd;
//修改snd_ssthresh,即max(0.7*snd_cwnd,2)
return max((tp->snd_cwnd * beta) / BICTCP_BETA_SCALE, 2U);
}
//快速恢復:直接把snd_cwnd更新為max(snd_cwnd,last_max_cwnd),和掉包前相差不大
static u32 bictcp_undo_cwnd(struct sock *sk)
{
struct bictcp *ca = inet_csk_ca(sk);
return max(tcp_sk(sk)->snd_cwnd, ca->last_max_cwnd);
}
static void bictcp_state(struct sock *sk, u8 new_state)
{
if (new_state == TCP_CA_Loss) {
bictcp_reset(inet_csk_ca(sk));
bictcp_hystart_reset(sk);
}
}
static void hystart_update(struct sock *sk, u32 delay)
{
struct tcp_sock *tp = tcp_sk(sk);
struct bictcp *ca = inet_csk_ca(sk);
if (!(ca->found & hystart_detect)) {
u32 curr_jiffies = jiffies;
/* first detection parameter - ack-train detection */
if (curr_jiffies - ca->last_jiffies <= msecs_to_jiffies(2)) {
ca->last_jiffies = curr_jiffies;
if (curr_jiffies - ca->round_start >= ca->delay_min>>4)
ca->found |= HYSTART_ACK_TRAIN;
}
/* obtain the minimum delay of more than sampling packets */
if (ca->sample_cnt < HYSTART_MIN_SAMPLES) {
if (ca->curr_rtt == 0 || ca->curr_rtt > delay)
ca->curr_rtt = delay;
ca->sample_cnt++;
} else {
if (ca->curr_rtt > ca->delay_min +
HYSTART_DELAY_THRESH(ca->delay_min>>4))
ca->found |= HYSTART_DELAY;
}
/*
* Either one of two conditions are met,
* we exit from slow start immediately.
*/
if (ca->found & hystart_detect)
tp->snd_ssthresh = tp->snd_cwnd;
}
}
/* Track delayed acknowledgment ratio using sliding window
* ratio = (15*ratio + sample) / 16
*/
//跟蹤延遲確認在滑動視窗的比例,主要考慮正常和丟包的時候,是一個參考值
//根據下面這個函式。化簡得 delayed_ack = 15/16*delayed_ack + cnt;
//由於 ratio = delayed_ack/ 16; 16*ration = 15*ration+cnt
//所以 ratio = 15/16 * ratio + cnt / 16;
static void bictcp_acked(struct sock *sk, u32 cnt, s32 rtt_us)
{
const struct inet_connection_sock *icsk = inet_csk(sk);
const struct tcp_sock *tp = tcp_sk(sk);
struct bictcp *ca = inet_csk_ca(sk);
u32 delay;
if (icsk->icsk_ca_state == TCP_CA_Open) {
cnt -= ca->delayed_ack >> ACK_RATIO_SHIFT;
ca->delayed_ack += cnt;
}
/* Some calls are for duplicates without timetamps */
if (rtt_us < 0)
return;
/* Discard delay samples right after fast recovery */
if ((s32)(tcp_time_stamp - ca->epoch_start) < HZ)
return;
delay = usecs_to_jiffies(rtt_us) << 3;
if (delay == 0)
delay = 1;
/* first time call or link delay decreases */
if (ca->delay_min == 0 || ca->delay_min > delay)
ca->delay_min = delay;
/* hystart triggers when cwnd is larger than some threshold */
if (hystart && tp->snd_cwnd <= tp->snd_ssthresh &&
tp->snd_cwnd >= hystart_low_window)
hystart_update(sk, delay);
}
static struct tcp_congestion_ops cubictcp = {
.init = bictcp_init,
.ssthresh = bictcp_recalc_ssthresh,
.cong_avoid = bictcp_cong_avoid,
.set_state = bictcp_state,
.undo_cwnd = bictcp_undo_cwnd,
.pkts_acked = bictcp_acked,
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.name = "cubic",
};
static int __init cubictcp_register(void)
{
BUILD_BUG_ON(sizeof(struct bictcp) > ICSK_CA_PRIV_SIZE);
/* Precompute a bunch of the scaling factors that are used per-packet
* based on SRTT of 100ms
*/
//beta_scale == 8*(1024 + 717) / 3 / (1024 -717 ),大約為15
beta_scale = 8*(BICTCP_BETA_SCALE+beta)/ 3 / (BICTCP_BETA_SCALE - beta);
//cube_rtt_scale cube_rtt_scale是bic_scale/RTT, 這裡rtt=100ms=0.1s
cube_rtt_scale = (bic_scale * 10); /* 1024*c/rtt */
/* calculate the "K" for (wmax-cwnd) = c/rtt * K^3
* so K = cubic_root( (wmax-cwnd)*rtt/c )
* the unit of K is bictcp_HZ=2^10, not HZ
*
* c = bic_scale >> 10
* rtt = 100ms
*
* the following code has been designed and tested for
* cwnd < 1 million packets
* RTT < 100 seconds
* HZ < 1,000,00 (corresponding to 10 nano-second)
*/
/* 1/c * 2^2*bictcp_HZ * srtt */
//通過bic_K和paper中的公式對比,可以知道cube_factor就是1/(C/RTT)
//具體需要參考演算法實現,以及這裡的30是開根號
cube_factor = 1ull << (10+3*BICTCP_HZ); /* 2^40 */
/* divide by bic_scale and by constant Srtt (100ms) */
do_div(cube_factor, bic_scale * 10);
return tcp_register_congestion_control(&cubictcp);
}
static void __exit cubictcp_unregister(void)
{
tcp_unregister_congestion_control(&cubictcp);
}
module_init(cubictcp_register);
module_exit(cubictcp_unregister);
MODULE_AUTHOR("Sangtae Ha, Stephen Hemminger");
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
MODULE_DESCRIPTION("CUBIC TCP");
MODULE_VERSION("2.3");
4:調整tcp引數說明
所有的引數是全域性從symbol讀取,可以設定。
fast_convergence = 0 開啟後快速收斂,丟包後略小的W-max,可以關閉。
tcp_friendliness = 1 預設引數,始終開啟, 開啟後實際上保證了per RTT內的增長率。
我們知道RENO採用AIMD,其中a=1,B=0.5。在某些條件下,在同一時間點,
cwnd( Cubic ) < cwnd( Reno ),這說明Cubic此時比Reno慢。友好性函式在這種情況下被呼叫,用來加快
連線的cwnd的增長速度,即減小cnt。
那麼怎麼算採用Reno時的cwnd呢?以上次丟包以後的時間t算起,每次RTT增長3B / ( 2 - B),那麼就和採用
Reno有著相同的平均cwnd,即從效果上等同於採用Reno。
beta=717 可以設定的更大(beta/1024)控制丟包後的視窗大小,早期值為819
BICTCP_HZ=10 對於HZ>=1000可以適當調整這個值,來讓K有高的精度, 影響不大
hystart = 1 保持預設開啟,快速退出慢啟動,使用三次方增長曲線
bic_scale = 41 係數C的1024倍,C越大K越小,可以適當增大這個數值
其他:
程式碼中cube_rtt_scale和cube_factor使用了RTT=100ms來計算,可以適當減小這個數值
更小的RTT意味著
- cube_rtt_scale更大,更高的增長率係數C
- cube_factor更小, 更小的K值
