android外掛開發——載入外掛
在閱讀本博文的時候,我假設你已經閱讀了我之前寫的幾篇。猛擊此處
通過前面的幾篇部落格,我們解決了如何啟動一個並沒有在ActivityManifest.xml中宣告的activity。但是有很多細心的讀者私信我說,我們所有的例子裡,外掛都是和主工程在一起的呀,我們如何從外部載入一個apk或者dex呢?
本節就是解決這個問題。
在學習本節之前,有一些非常重要的概念需要提一下。比如類載入器的概念。
我們知道在java裡面,有很多種載入器,如果按層次劃分的話,可以分為
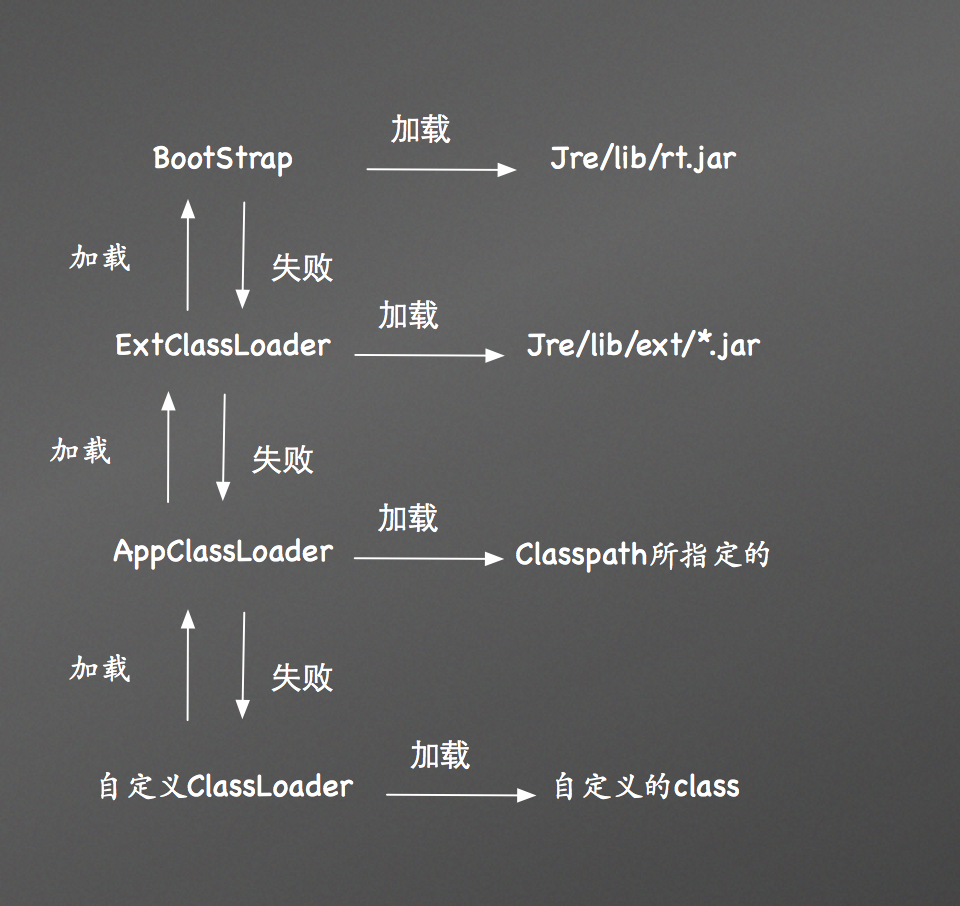
在載入類的時候,他們採用委託機制,比如,我們自定義的ClassLoader要載入一個類,它首先會委託AppClassLoader去載入,AppClassLoader又會委託ExtClassLoader去載入,而ExtClassLoader呢又去委託BootStrap載入,如果BootStrap載入成功了,那就返回,否則會讓ExtClassLoader載入,如果ExtClassLoader也沒載入成功,那就讓AppClassLoader載入,以此類推,如果到自定義ClassLoader都還沒成功載入類,那麼就會丟擲ClassNotFound異常。這種機制可以很大程度的避免重複載入一個類——子載入器首先嚐試讓父載入器載入。因而我們不難得出,在自定義一個類載入器的時候,我們還要為其指定一個父類載入器。當然本文並不是討論這個的。具體的讀者可以參閱姜維前輩的博文:
在android中,系統也提供了兩個類載入器:DexClassLoader和PathClassLoader
PathClassLoader用於載入/data/app中的apk,也就是已經安裝了的apk,所以它就成了系統的預設類載入器。
而對於DexClassLoader呢,他可以用來任意位置的apk/dex/jar檔案。
我們看下原始碼:
/*
* Copyright (C) 2008 The Android Open Source Project
*
* Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
* you may not 由註釋我們看出,第一個引數是,jar/file檔案的位置
第二個引數指定存放dex檔案的位置
第三個引數用於指定存放原生庫的位置(so檔案)
第四個引數就是制定一個父類載入器
很簡單,但是由於篇幅限制,我們不打算做個demo,我們會把DexClassLoader的使用放到下面我們的例子裡。由於不是很複雜,所以這麼做也是合情合理
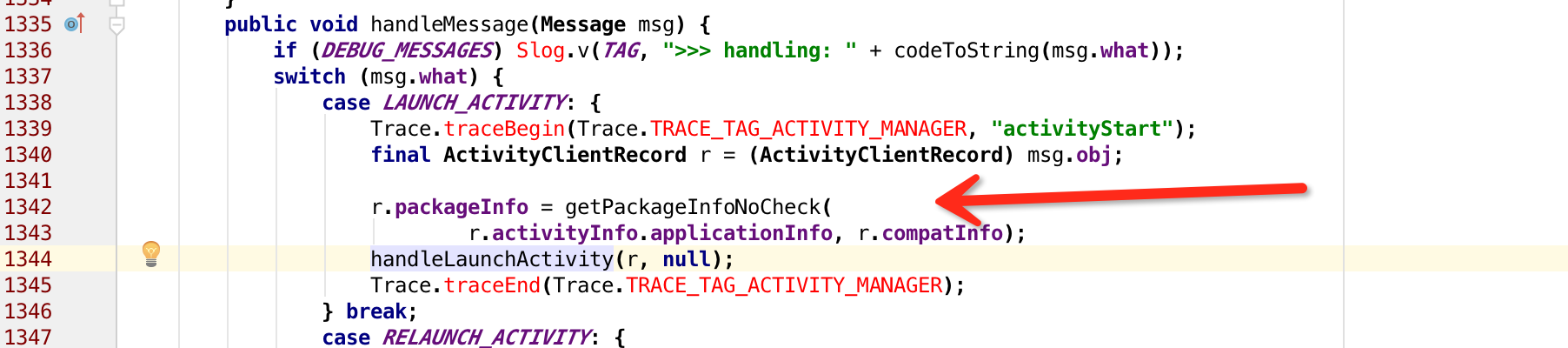
還記得之前的原始碼分析嗎,當AMS做完一切準備工作,讓UI執行緒開始啟動一個新的activity之後,ActivityThread便開始載入一個新的activity
之後再handleLaunchActivity函式中:
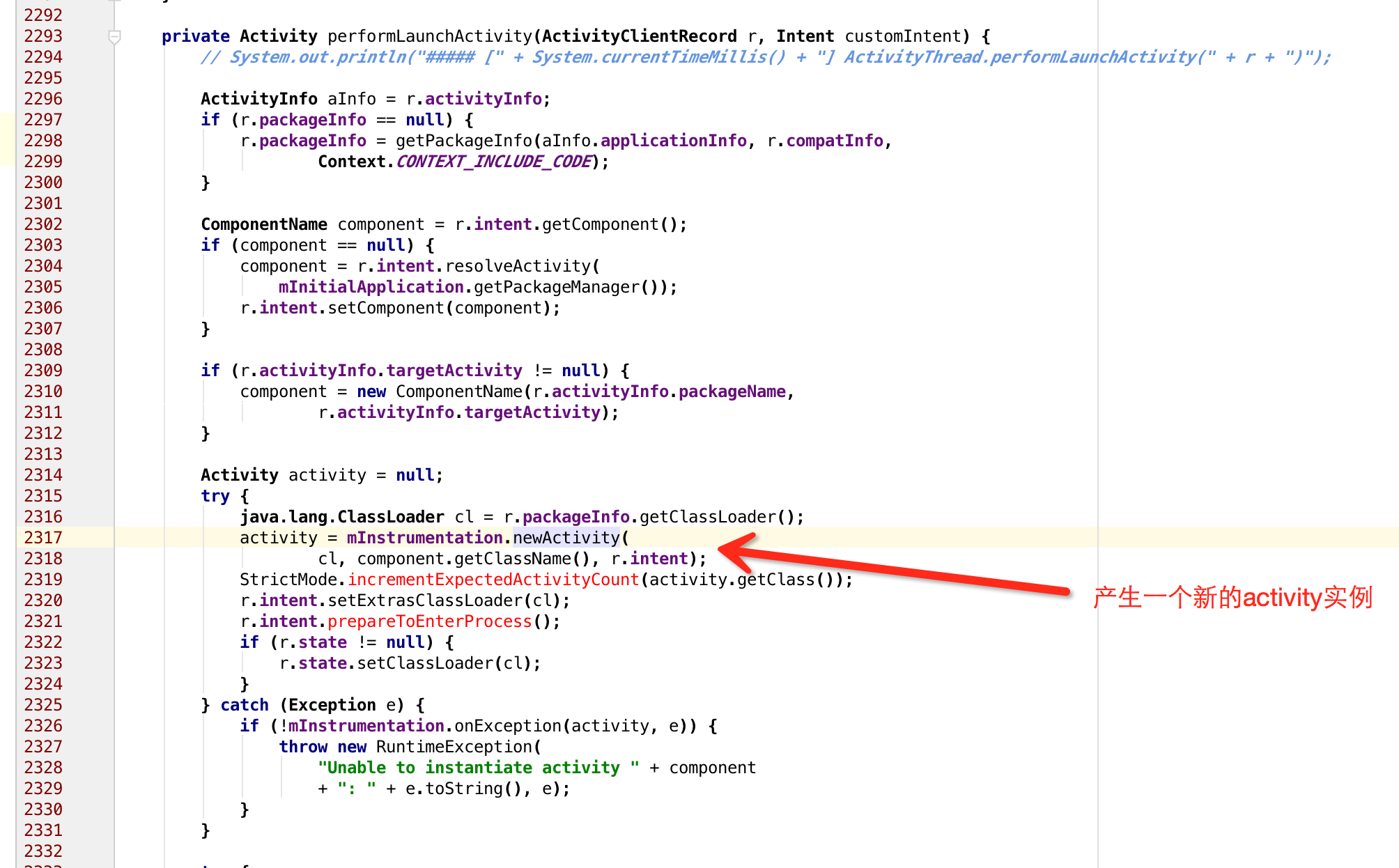
呼叫mInstrumentation.newActivity方法,我們看下函式簽名:
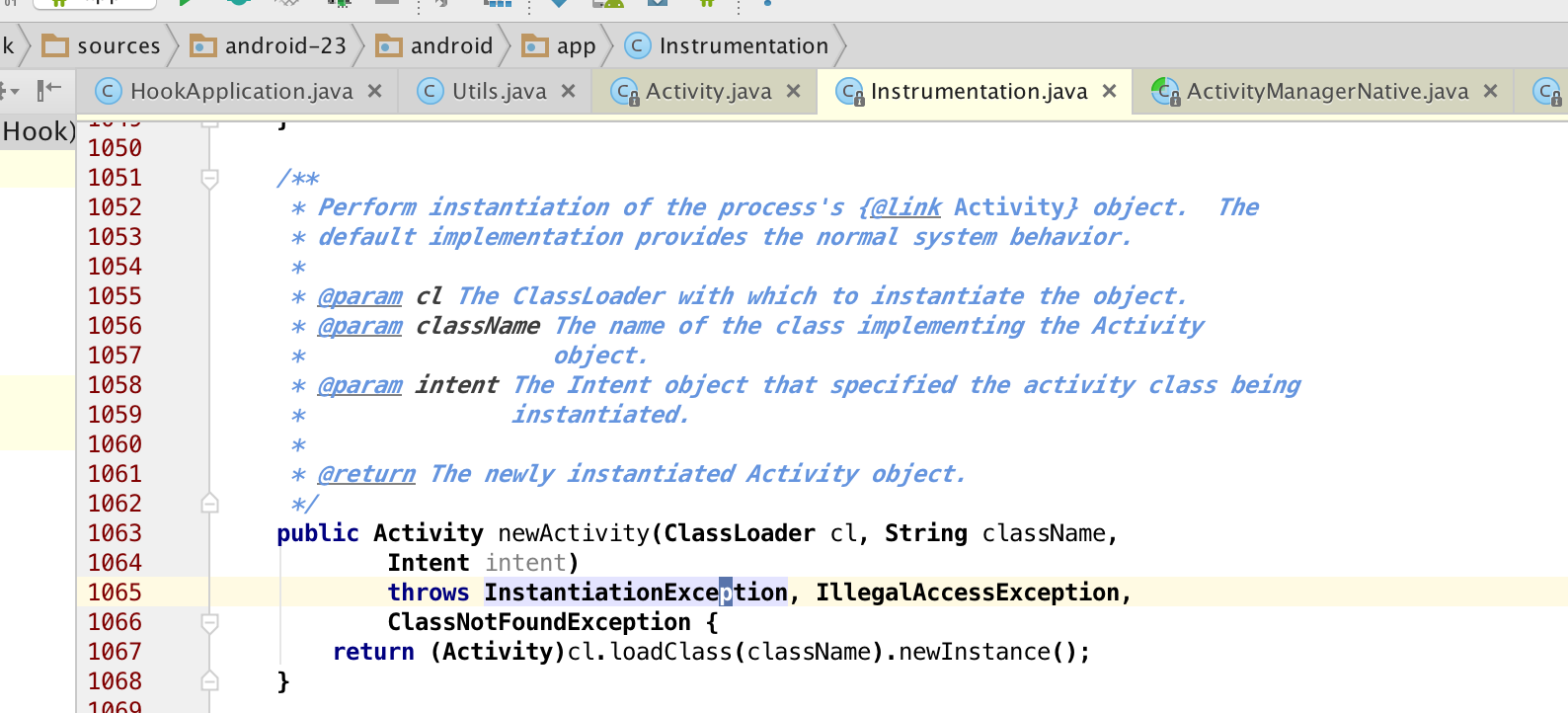
通過class載入一個類,並且例項化。而這個cl是什麼呢,根據上面的程式碼我們可以知道是r.packageInfo.getClassLoader的返回值,而這個r.packageInfo是在H的handleMessage中被賦值的:
我們看下這個field
static final class ActivityClientRecord {
...
LoadedApk packageInfo;
...
}而LoadedApk又是什麼呢:
/**
* Local state maintained about a currently loaded .apk.
* @hide
*/
public final class LoadedApk {
...
}它代表了一個apk所對應的記憶體表示,也就是apk被載入到記憶體後的資訊,比如程式碼,資源等等。
那麼到這裡,我們要知道,如果我們要從外部載入一個apk,首先就要獲得這個LoadApk物件,因為之後activity的例項化,都會用到LoadApk中的類載入器。因而我們首先要解決的事情就是如何產生一個LoadApk
我們要保證一切萬無一失,最好就是模仿android系統的行為,如果我們能和android系統產生一個LoadApk的方式一樣,那就做到了萬無一失。
回溯上文,一個LoadApk的產生是通過:
r.packageInfo = getPackageInfoNoCheck(
r.activityInfo.applicationInfo, r.compatInfo);我們看下函式簽名:
public final LoadedApk getPackageInfoNoCheck(ApplicationInfo ai,
CompatibilityInfo compatInfo) {
return getPackageInfo(ai, compatInfo, null, false, true, false);
}
函式呼叫了getPackageInfo:
private LoadedApk getPackageInfo(ApplicationInfo aInfo, CompatibilityInfo compatInfo,
ClassLoader baseLoader, boolean securityViolation, boolean includeCode,
boolean registerPackage) {
final boolean differentUser = (UserHandle.myUserId() != UserHandle.getUserId(aInfo.uid));
synchronized (mResourcesManager) {
WeakReference<LoadedApk> ref;
if (differentUser) {
// Caching not supported across users
ref = null;
} else if (includeCode) {
//includeCode的值為true 所以必定會呼叫這個函式
//它的作用是,先從快取中獲取LoadApk
ref = mPackages.get(aInfo.packageName);
} else {
ref = mResourcePackages.get(aInfo.packageName);
}
LoadedApk packageInfo = ref != null ? ref.get() : null;
//如果並沒有快取 那就產生一個新的例項
if (packageInfo == null || (packageInfo.mResources != null
&& !packageInfo.mResources.getAssets().isUpToDate())) {
if (localLOGV) Slog.v(TAG, (includeCode ? "Loading code package "
: "Loading resource-only package ") + aInfo.packageName
+ " (in " + (mBoundApplication != null
? mBoundApplication.processName : null)
+ ")");
//產生一個新的例項
packageInfo =
new LoadedApk(this, aInfo, compatInfo, baseLoader,
securityViolation, includeCode &&
(aInfo.flags&ApplicationInfo.FLAG_HAS_CODE) != 0, registerPackage);
if (mSystemThread && "android".equals(aInfo.packageName)) {
packageInfo.installSystemApplicationInfo(aInfo,
getSystemContext().mPackageInfo.getClassLoader());
}
if (differentUser) {
// Caching not supported across users
} else if (includeCode) {
//做下快取
mPackages.put(aInfo.packageName,
new WeakReference<LoadedApk>(packageInfo));
} else {
mResourcePackages.put(aInfo.packageName,
new WeakReference<LoadedApk>(packageInfo));
}
}
return packageInfo;
}
}
這裡呢mPackages的型別為:
final ArrayMap<String, WeakReference<LoadedApk>> mPackages
= new ArrayMap<String, WeakReference<LoadedApk>>();我們不難得出,如果要獲得一個LoadApk物件,要解決兩個問題:1:獲得ApplicationInfo物件。 2:獲得CompatibilityInfo物件
對於ApplicationInfo 官方是這麼解釋的:
/**
* Information you can retrieve about a particular application. This
* corresponds to information collected from the AndroidManifest.xml's
* <application> tag.
*/
public class ApplicationInfo extends PackageItemInfo implements Parcelable {
...
}它是AndroidManifest.xml 標籤下的資訊集合。
而CompatibilityInfo呢,由名字就可以得出,是一些相容性資訊:
/**
* CompatibilityInfo class keeps the information about compatibility mode that the application is
* running under.
*
* {@hide}
*/
public class CompatibilityInfo implements Parcelable {
/** default compatibility info object for compatible applications */
public static final CompatibilityInfo DEFAULT_COMPATIBILITY_INFO = new CompatibilityInfo() {
};
...
}呦,這裡有個靜態域,用於作為預設相容資訊。我們完全可以獲得這個物件啊,那麼問題是不是就只剩下獲得ApplicationInfo物件了
而這個ApplicationInfo物件是通過呼叫r.activityInfo.applicationInfo獲得的。
r.packageInfo = getPackageInfoNoCheck(
r.activityInfo.applicationInfo, r.compatInfo);這個r物件呢,通過我們之前的學習就知道了,是在ActivityStackSupervisor中被建立的
final int startActivityLocked(IApplicationThread caller,
Intent intent, String resolvedType, ActivityInfo aInfo,
IVoiceInteractionSession voiceSession, IVoiceInteractor voiceInteractor,
IBinder resultTo, String resultWho, int requestCode,
int callingPid, int callingUid, String callingPackage,
int realCallingPid, int realCallingUid, int startFlags, Bundle options,
boolean componentSpecified, ActivityRecord[] outActivity, ActivityContainer container,
TaskRecord inTask) {
...
ActivityRecord r = new ActivityRecord(mService, callerApp, callingUid, callingPackage,
intent, resolvedType, aInfo, mService.mConfiguration, resultRecord, resultWho,
requestCode, componentSpecified, this, container, options);
...
return err;
}這裡aInfo是一個很重要的引數。r中很多引數的引用都是來自aInfo中
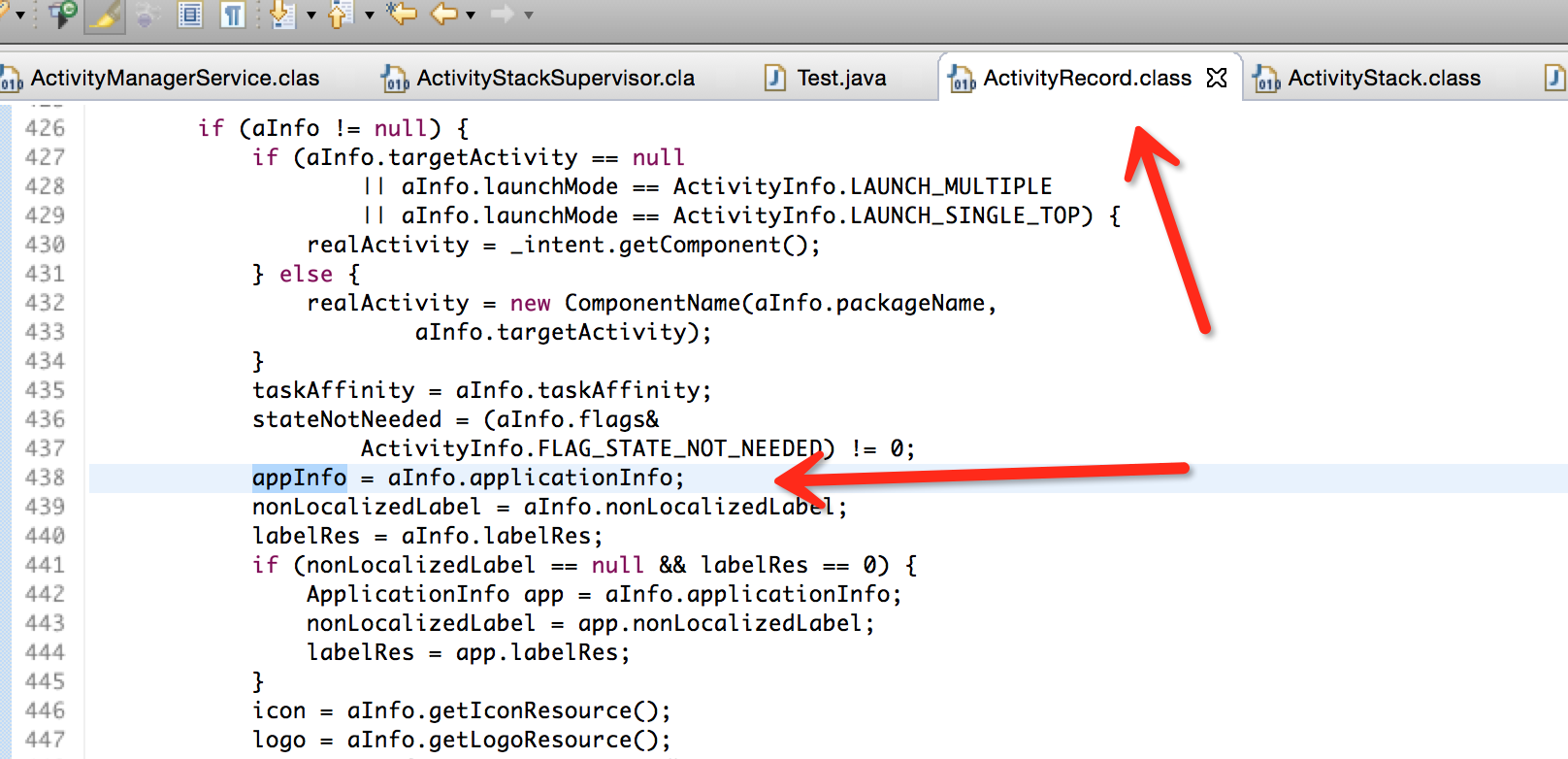
而這個aInfo呢,很簡單是在AMS呼叫ActivityStackSupervisor第一個函式的時候就產生了:
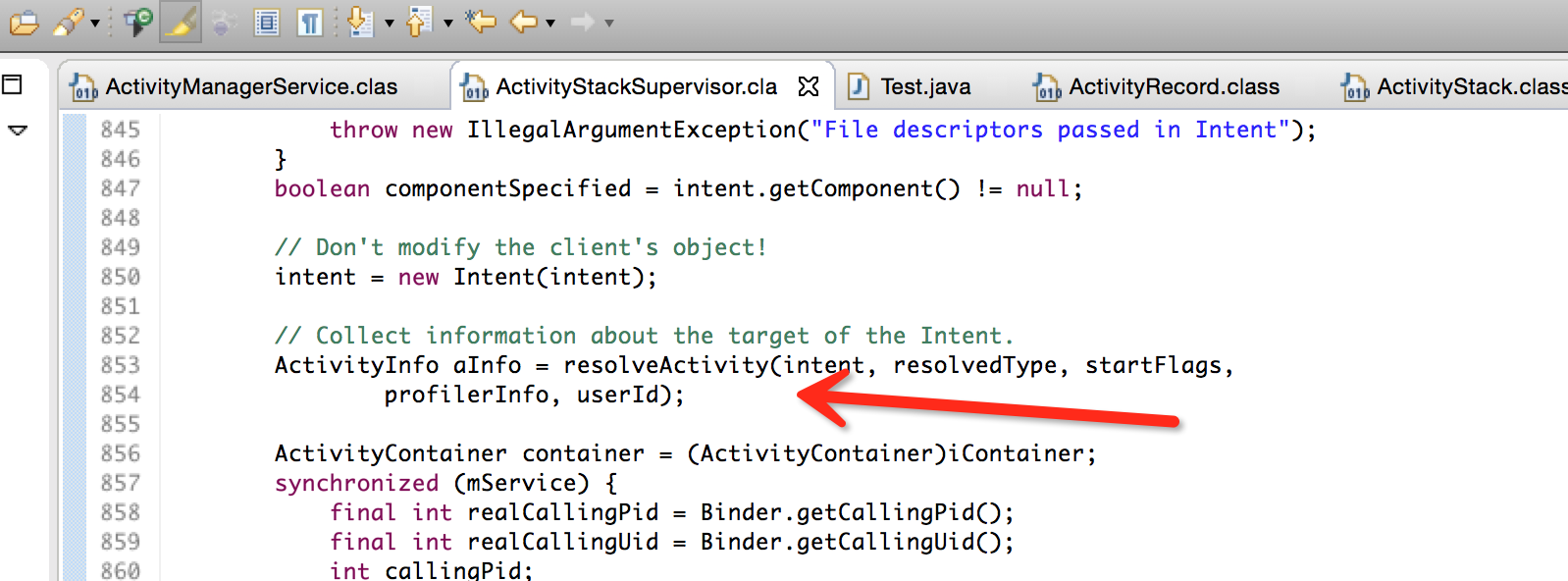
回顧之前的學習,這個函式最終是呼叫PackageManager的getActivityInfo函式來獲得一個activity的資訊:
@Override
public ActivityInfo getActivityInfo(ComponentName component, int flags, int userId) {
...
synchronized (mPackages) {
...
if (mResolveComponentName.equals(component)) {
return PackageParser.generateActivityInfo(mResolveActivity, flags,
new PackageUserState(), userId);
}
}
return null;
}這裡最終呼叫了PackageParser的generateActivityInfo函式:
public static final ActivityInfo generateActivityInfo(Activity a, int flags,
PackageUserState state, int userId) {
...
ai.applicationInfo = generateApplicationInfo(a.owner, flags, state, userId);
return ai;
}這裡產生了applicationInfo物件
那麼我們只要能修改generateApplication返回值是不是就可以了?很不幸,PackageParser是個善變的類,幾乎每次在釋出新版本後這個類都會被修改。我們看下DroidPlugin的原始碼就知道,關於這個類,我們要做非常之多的相容。。。
所以本文都假設你的api是23!
不過還好,generateApplication被過載了很多次,我們可以呼叫它引數最少的一個:
public static ApplicationInfo generateApplicationInfo(Package p, int flags,
PackageUserState state) {
return generateApplicationInfo(p, flags, state, UserHandle.getCallingUserId());
}從函式簽名中我們可以看到,我們如果要獲得ApplicationInfo,首先就要獲得Package物件,還有就是PackageUserState物件
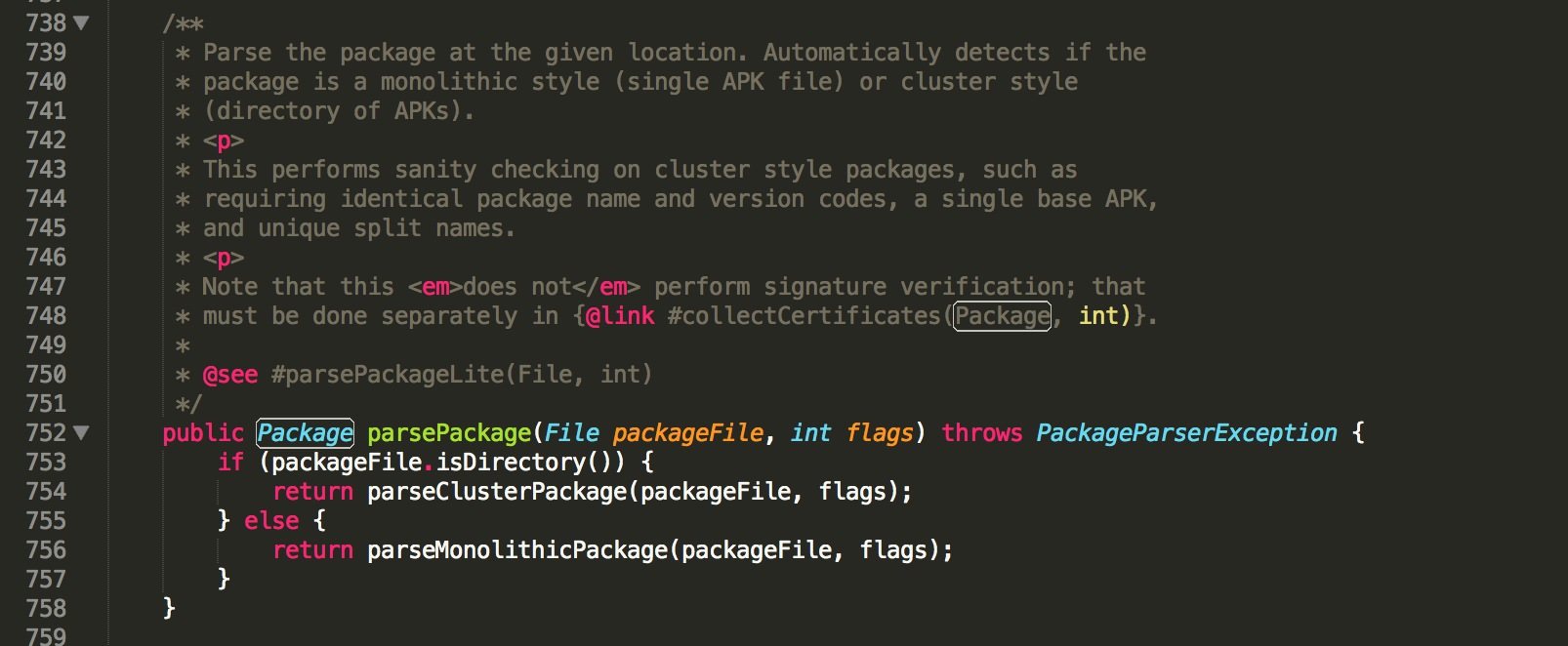
對於Package物件,我們可以通過PackageParse的這個函式獲得:
而PackageUserState直接使用預設的就行了,比如我們之前的例子就是(見上文):
@Override
public ActivityInfo getActivityInfo(ComponentName component, int flags, int userId) {
...
synchronized (mPackages) {
...
if (mResolveComponentName.equals(component)) {
return PackageParser.generateActivityInfo(mResolveActivity, flags,
//這裡就是用的預設的
new PackageUserState(), userId);
}
}
return null;
}我們看下原始碼:
package com.chan.hook.app;
import android.annotation.TargetApi;
import android.app.Application;
import android.content.Context;
import android.content.pm.ApplicationInfo;
import android.os.Build;
import android.os.Handler;
import com.chan.hook.R;
import com.chan.hook.am.AMSHook;
import com.chan.hook.handle.MessageHook;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.lang.ref.WeakReference;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.lang.reflect.Proxy;
import java.util.Map;
import dalvik.system.DexClassLoader;
/**
* Created by chan on 16/4/8.
*/
public class HookApplication extends Application {
private ClassLoader m_classLoader;
private File m_file;
private Object m_pluginLoadApk;
@TargetApi(Build.VERSION_CODES.KITKAT)
@Override
protected void attachBaseContext(Context base) {
super.attachBaseContext(base);
init();
}
private void init() {
try {
setupClassLoader();
//獲得activity thread例項
Class<?> activityThreadClz = Class.forName("android.app.ActivityThread", false, getClassLoader());
Method currentActivityThreadMethod = activityThreadClz.getDeclaredMethod("currentActivityThread");
Object activityThreadObject = currentActivityThreadMethod.invoke(null);
//獲得load apk的快取資訊
Field packagesField = activityThreadClz.getDeclaredField("mPackages");
packagesField.setAccessible(true);
//map 第二個引數是LoadApk的弱引用
Map<String, WeakReference<?>> packages = (Map<String, WeakReference<?>>)
packagesField.get(activityThreadObject);
//下面就只剩下獲得LoadApk了
//根據 public final LoadedApk getPackageInfoNoCheck(ApplicationInfo ai, CompatibilityInfo compatInfo)
//我們要獲得ApplicationInfo 和 CompatibilityInfo
//獲得ApplicationInfo
//通過呼叫PackageParser generateApplicationInfo方法
//public static ApplicationInfo generateApplicationInfo(Package p, int flags, PackageUserState state)
//分別獲取引數的class
Class<?> packageParserClz = Class.forName("android.content.pm.PackageParser", false, getClassLoader());
Class<?> packageParserPackageClz = Class.forName("android.content.pm.PackageParser$Package", false, getClassLoader());
Class<?> packageUserStateClz = Class.forName("android.content.pm.PackageUserState", false, getClassLoader());
//獲取method
Method generateApplicationInfoMethod = packageParserClz.getDeclaredMethod("generateApplicationInfo",
packageParserPackageClz, int.class, packageUserStateClz);
//獲取Package
Method parsePackageMethod = packageParserClz.getDeclaredMethod("parsePackage", File.class, int.class);
//第一個引數是外掛apk位置 第二個引數0代表解析所有內容
Object packageObject = parsePackageMethod.invoke(packageParserClz.newInstance(), m_file, 0);
//已經獲得了application info
ApplicationInfo applicationInfoObject = (ApplicationInfo) generateApplicationInfoMethod.invoke(null, packageObject, 0,
packageUserStateClz.newInstance());
applicationInfoObject.sourceDir = m_file.getAbsolutePath();
applicationInfoObject.publicSourceDir = m_file.getAbsolutePath();
//獲得CompatibilityInfo
Class<?> compatibilityInfoClz = Class.forName("android.content.res.CompatibilityInfo", false, getClassLoader());
Field DEFAULT_COMPATIBILITY_INFO = compatibilityInfoClz.getDeclaredField("DEFAULT_COMPATIBILITY_INFO");
Object compatibilityInfoObject = DEFAULT_COMPATIBILITY_INFO.get(null);
//獲得LoadApk物件
Method getPackageInfoNoCheckMethod = activityThreadClz.getDeclaredMethod("getPackageInfoNoCheck", ApplicationInfo.class, compatibilityInfoClz);
Object pluginLoadApkObject = getPackageInfoNoCheckMethod.invoke(activityThreadObject, applicationInfoObject, compatibilityInfoObject);
//因為load apk放在一個弱引用中 所以 如果被回收了的話 就前功盡棄了 用一個強引用 防止它被回收
m_pluginLoadApk = pluginLoadApkObject;
//替換load apk中的class loader
Field classLoaderField = pluginLoadApkObject.getClass().getDeclaredField("mClassLoader");
classLoaderField.setAccessible(true);
classLoaderField.set(pluginLoadApkObject, m_classLoader);
//新增一個快取 第一個引數是外掛apk的包名
packages.put("com.chan.plugin", new WeakReference<>(pluginLoadApkObject));
//獲得ActivityManagerNative
Class<?> serviceManagerClz = Class.forName("android.app.ActivityManagerNative", false, getClassLoader());
//獲得ActivityManagerNative.getDefault靜態方法
Method getDefaultMethod = serviceManagerClz.getDeclaredMethod("getDefault");
//獲得原始的IActivityManager物件
Object rawIActivityManagerInterface = getDefaultMethod.invoke(null);
//我們自己的Hook的物件
Object hookIActivityManagerInterface = Proxy.newProxyInstance(
getClassLoader(),
new Class[]{Class.forName("android.app.IActivityManager", false, getClassLoader())},
new AMSHook(this, rawIActivityManagerInterface)
);
//反射ActivityManagerNative的gDefault域
Field gDefaultField = serviceManagerClz.getDeclaredField("gDefault");
gDefaultField.setAccessible(true);
Object gDefaultObject = gDefaultField.get(null);
//他的型別是Singleton
Class<?> singletonClz = Class.forName("android.util.Singleton", false, getClassLoader());
//把他的mInstance域替換掉 成為我們自己的Hook物件
Field mInstanceField = singletonClz.getDeclaredField("mInstance");
mInstanceField.setAccessible(true);
mInstanceField.set(gDefaultObject, hookIActivityManagerInterface);
//獲取activity thread的class
//獲得activity thread中的mH域
Field mHField = activityThreadClz.getDeclaredField("mH");
mHField.setAccessible(true);
Object mHObject = mHField.get(activityThreadObject);
//獲得Handler中的mCallback域
Field handlerCallbackField = Handler.class.getDeclaredField("mCallback");
handlerCallbackField.setAccessible(true);
//獲得原來的mCallback物件
Object callbackObject = handlerCallbackField.get(mHObject);
//設定成我們自己的Callback物件
Object hookHObject = new MessageHook(callbackObject, getClassLoader());
handlerCallbackField.set(mHObject, hookHObject);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
private void setupClassLoader() throws IOException {
//我這裡就是簡單的吧raw下的apk讀取出來 然後存放到資料夾下 這已經和真實的業務場景很像了
File dir = getDir("plugin", MODE_PRIVATE);
File file = m_file = new File(dir, "plugin.apk");
InputStream inputStream = getResources().openRawResource(R.raw.plugin);
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = null;
try {
fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream(file);
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];
int length = -1;
while ((length = inputStream.read(bytes)) != -1) {
fileOutputStream.write(bytes, 0, length);
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if (fileOutputStream != null) {
fileOutputStream.flush();
fileOutputStream.close();
}
}
//然後產生一個dex class loader
//第一個引數是外部apk位置
//第二個引數是apk要解壓的位置
//第三個引數是原生庫位置 我們只是一個簡單的外掛 所以並沒有
//第四個引數指定父類載入器
m_classLoader = new DexClassLoader(
file.getAbsolutePath(),
getDir("lib", MODE_PRIVATE).getAbsolutePath(),
null,
getClassLoader());
}
}程式碼有點長 我為了省事並沒有把他們分到多個函式裡。。。 我覺得按照註釋讀程式碼是最好理解的,所以這裡讀者看註釋就行了
之後的程式碼和之前有所不同,比如我們客戶端變成這樣invoke外掛中的activity了:
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
findViewById(R.id.id_start).setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
Utils.invokePluginActivity(MainActivity.this, "com.chan.plugin",
"com.chan.plugin.MainActivity");
}
});
}而utils中則變成:
/**
* Created by chan on 16/4/14.
*/
public class Utils {
public static void invokePluginActivity(Activity activity, String pluginPackage, String pluginClass) {
Intent intent = new Intent();
intent.putExtra(Constant.EXTRA_INVOKE_PLUGIN, true);
intent.setComponent(new ComponentName(pluginPackage, pluginClass));
activity.startActivity(intent);
}
}AMSHook的程式碼:
/**
* Created by chan on 16/4/13.
*/
public class AMSHook implements InvocationHandler {
private Object m_base;
private Context m_context;
public AMSHook(Context context, Object base) {
m_base = base;
m_context = context;
}
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
//攔截startActivity方法
if ("startActivity".equals(method.getName())) {
//查詢原始的intent物件
Intent raw = null;
final int size = (args == null ? 0 : args.length);
int i = 0;
for (; i < size; ++i) {
if (args[i] instanceof Intent) {
raw = (Intent) args[i];
break;
}
}
//看下是否是啟動外掛中的activity
if (raw.getBooleanExtra(Constant.EXTRA_INVOKE_PLUGIN, false)) {
//建立一個新的Intent
Intent intent = new Intent();
//把Component替換為StubActivity的 這樣就不會被系統檢測到 啟動一個沒有在AndroidManifest.xml
//中宣告的activity
intent.setComponent(new ComponentName(m_context.getPackageName(),
StubActivity.class.getCanonicalName()));
//儲存原始的intent
intent.putExtra(Constant.EXTRA_RAW_INTENT, raw);
//替換為新的Intent
args[i] = intent;
}
}
//還是按往常一樣呼叫各種函式
return method.invoke(m_base, args);
}
}變化還是很小的,只不過ctor多了一個引數
而對於MessageHook變化就比較大了:
package com.chan.hook.handle;
import android.content.ComponentName;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.content.pm.ActivityInfo;
import android.os.Handler;
import android.os.Message;
import android.util.Log;
import com.chan.hook.StubActivity;
import com.chan.hook.util.Constant;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
/**
* Created by chan on 16/4/14.
*/
public class MessageHook implements Handler.Callback {
private Handler.Callback m_base;
private static final int LAUNCH_ACTIVITY = 100;
private Field m_intentField;
private Field m_activityInfo;
public MessageHook(Object base, ClassLoader classLoader) throws ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchFieldException {
m_base = (Handler.Callback) base;
//獲取ActivityClientRecord的class
Class<?> activityClientRecordClz = Class.forName("android.app.ActivityThread$ActivityClientRecord", false, classLoader);
//獲得它的intent
m_intentField = activityClientRecordClz.getDeclaredField("intent");
m_intentField.setAccessible(true);
m_activityInfo = activityClientRecordClz.getDeclaredField("activityInfo");
m_activityInfo.setAccessible(true);
}
@Override
public boolean handleMessage(Message msg) {
//檢測到時啟動一個activity
if (msg.what == LAUNCH_ACTIVITY) {
try {
//msg.obj是android.app.ActivityThread$ActivityClientRecord物件,請參考前面的原始碼解析
Intent intent = (Intent) m_intentField.get(msg.obj);
ComponentName componentName = intent.getComponent();
//檢測到是啟動StubActivity
if(componentName != null &&
componentName.getClassName().equals(StubActivity.class.getCanonicalName())) {
//獲得之前啟動外掛的intent
Intent raw = intent.getParcelableExtra(Constant.EXTRA_RAW_INTENT);
//替換成外掛的component
intent.setComponent(raw.getComponent());
//在Activity Thread中,getPackageInfo這個函式根據activity info的application info
// 的包名查詢快取,所以這裡要替換掉,不能用宿主的包名
//否則就會載入不到類
ActivityInfo activityInfo = (ActivityInfo) m_activityInfo.get(msg.obj);
activityInfo.applicationInfo.packageName = raw.getComponent().getPackageName();
}
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
//之後的操作還是和原來一樣
return m_base != null && m_base.handleMessage(msg);
}
}這裡要替換掉r.activityInfo的applicationInfo的packageName,因為getPackageInfo根據他查詢快取
現在開始執行吧:
04-17 04:30:10.186 3686-3686/com.chan.hook E/AndroidRuntime: FATAL EXCEPTION: main
Process: com.chan.hook, PID: 3686
java.lang.RuntimeException: Unable to start activity ComponentInfo{com.chan.plugin/com.chan.plugin.MainActivity}: java.lang.RuntimeException: Unable to instantiate application android.app.Application: java.lang.IllegalStateException: Unable to get package info for com.chan.plugin; is package not installed?
at android.app.ActivityThread.performLaunchActivity(ActivityThread.java:2298)
at android.app.ActivityThread.handleLaunchActivity(ActivityThread.java:2360)
at android.app.ActivityThread.access$800(ActivityThread.java:144)
at android.app.ActivityThread$H.handleMessage(ActivityThread.java:1278)
at android.os.Handler.dispatchMessage(Handler.java:102)
at android.os.Looper.loop(Looper.java:135)
at android.app.ActivityThread.main(ActivityThread.java:5221)
at java.lang.reflect.Method.invoke(Native Method)
at java.lang.reflect.Method.invoke(Method.java:372)
at com.android.internal.os.ZygoteInit$MethodAndArgsCaller.run(ZygoteInit.java:899)
at com.android.internal.os.ZygoteInit.main(ZygoteInit.java:694)
Caused by: java.lang.RuntimeException: Unable to instantiate application android.app.Application: java.lang.IllegalStateException: Unable to get package info for com.chan.plugin; is package not installed?
at android.app.LoadedApk.makeApplication(LoadedApk.java:563)
at android.app.ActivityThread.performLaunchActivity(ActivityThread.java:2216)
at android.app.ActivityThread.handleLaunchActivity(ActivityThread.java:2360)
at android.app.ActivityThread.access$800(ActivityThread.java:144)
at android.app.ActivityThread$H.handleMessage(ActivityThread.java:1278)
at android.os.Handler.dispatchMessage(Handler.java:102)
at android.os.Looper.loop(Looper.java:135)
at android.app.ActivityThread.main(ActivityThread.java:5221)
at java.lang.reflect.Method.invoke(Native Method)
at java.lang.reflect.Method.invoke(Method.java:372)
at com.android.internal.os.ZygoteInit$MethodAndArgsCaller.run(ZygoteInit.java:899)
at com.android.internal.os.ZygoteInit.main(ZygoteInit.java:694)
Caused by: java.lang.IllegalStateException: Unable to get package info for com.chan.plugin; is package not installed?
at android.app.LoadedApk.initializeJavaContextClassLoader(LoadedApk.java:409)
at android.app.LoadedApk.makeApplication(LoadedApk.java:555)
at android.app.ActivityThread.performLaunchActivity(ActivityThread.java:2216)
at android.app.ActivityThread.handleLaunchActivity(ActivityThread.java:2360)
at android.app.ActivityThread.access$800(ActivityThread.java:144)
at android.app.ActivityThread$H.handleMessage(ActivityThread.java:1278)
at android.os.Handler.dispatchMessage(Handler.java:102)
at android.os.Looper.loop(Looper.java:135)
at android.app.ActivityThread.main(ActivityThread.java:5221)
at java.lang.reflect.Method.invoke(Native Method)
at java.lang.reflect.Method.invoke(Method.java:372)
at com.android.internal.os.ZygoteInit$MethodAndArgsCaller.run(ZygoteInit.java:899)
at com.android.internal.os.ZygoteInit.main(ZygoteInit.java:694)
oh,天哪,奔潰了。。。日誌提示是我們並沒有安裝剛剛的外掛apk。。。
我們查詢下錯誤資訊吧:
錯誤提示出現在performLaunchActivity這個函式裡面,並且我們也找到了相關的字串:

我們就從這個try塊的第一行開始看吧:

點進去看下:
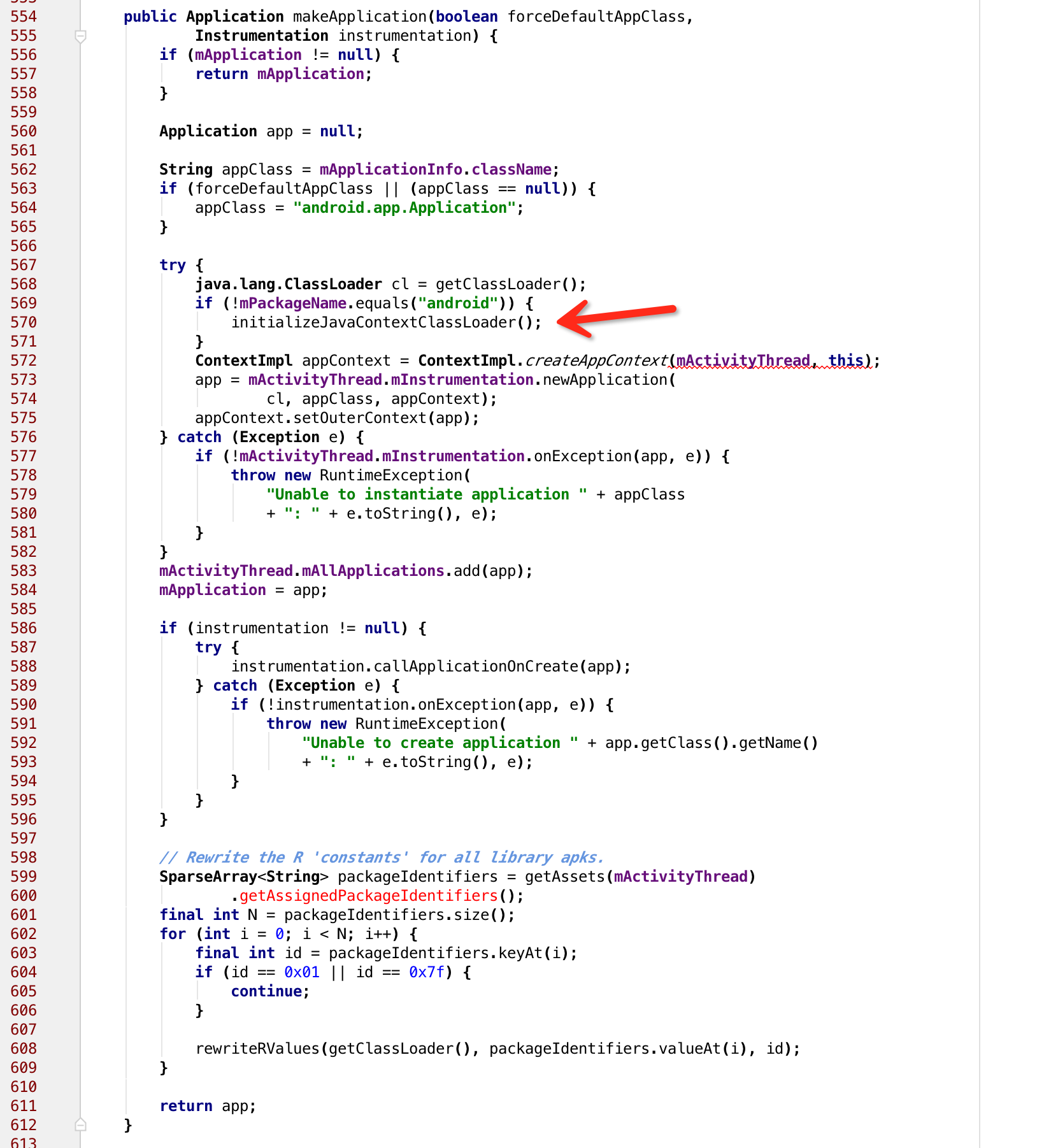
我們看到,如果mApplication不為空,那麼就直接返回,這也對應了平時我們所說的,在一個應用中application只有一個,再往下看。如果當前的包名不是android,那麼久要執行第570行的程式碼,我們進入看下:

我們剛好找到了這裡對應的錯誤資訊,顯然,當執行pm.getPackageInfo後,我們的pi是空的,也就對應了在系統中並沒有安裝,那麼我們就只能hook PM了。
我們找到ActivityThread.getPackageManager去看下

又是 靜態變數,輕車熟路啊,我們之前已經講了太多次這種情況如何hook,所以這裡不加闡述,直接上程式碼,當然,還是在HookApplication中:
// 獲取ActivityThread裡面原始的 sPackageManager
Field sPackageManagerField = m_activityThreadClz.getDeclaredFie