plot_learning_curve 繪製學習曲線
sklearn.model_selection.learning_curve
sklearn.model_selection.learning_curve(estimator, X, y, groups=None,
train_sizes=array([0.1, 0.33, 0.55, 0.78, 1. ]),
cv=’warn’, scoring=None,
exploit_incremental_learning=False,
n_jobs=None, pre_dispatch=’all’, verbose=0,
shuffle= Returns:
train_sizes_abs : array, shape (n_unique_ticks,), dtype int
Numbers of training examples that has been used to generate the learning curve. Note that the number of ticks might be less than n_ticks because duplicate entries will be removed.
train_scores: array, shape (n_ticks, n_cv_folds)
Scores on training sets.
test_scores : array, shape (n_ticks, n_cv_folds)
Scores on test set.
train_sizes指定訓練樣本數量的變化規則,比如np.linspace(.1, 1.0, 5)表示把訓練樣本數量從0.1~1分成五等分,從[0.1, 0.33, 0.55, 0.78, 1. ]的序列中取出訓練樣本數量百分比,逐個計算在當前訓練樣本數量情況下訓練出來的模型準確性。
在畫訓練集的曲線時:橫軸為 train_sizes,縱軸為 train_scores_mean;
畫測試集的曲線時:橫軸為train_sizes,縱軸為test_scores_mean。
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.naive_bayes import GaussianNB
from sklearn.svm import SVC
from sklearn.datasets import load_digits
from sklearn.model_selection import learning_curve
from sklearn.model_selection import ShuffleSplit
def plot_learning_curve(estimator, title, X, y,
ylim=None, cv=None,n_jobs=None,
train_sizes=np.linspace(.1, 1.0, 5)):
plt.figure()
plt.title(title)
if ylim is not None:
plt.ylim(*ylim)
plt.xlabel("Training examples")
plt.ylabel("Score")
train_sizes, train_scores, test_scores = learning_curve(estimator, X, y,
cv=cv, n_jobs=n_jobs,
train_sizes=train_sizes)
train_scores_mean = np.mean(train_scores, axis=1)
train_scores_std = np.std(train_scores, axis=1)
test_scores_mean = np.mean(test_scores, axis=1)
test_scores_std = np.std(test_scores, axis=1)
plt.grid()
plt.fill_between(train_sizes, train_scores_mean - train_scores_std,
train_scores_mean + train_scores_std,
alpha=0.1, color="r")
plt.fill_between(train_sizes, test_scores_mean - test_scores_std,
test_scores_mean + test_scores_std,
alpha=0.1, color="g")
plt.plot(train_sizes, train_scores_mean, 'o-', color="r",
label="Training score")
plt.plot(train_sizes, test_scores_mean, 'o-', color="g",
label="Cross-validation score")
plt.legend(loc="best")
return plt
digits = load_digits()
X, y = digits.data, digits.target
if __name__=='__main__':
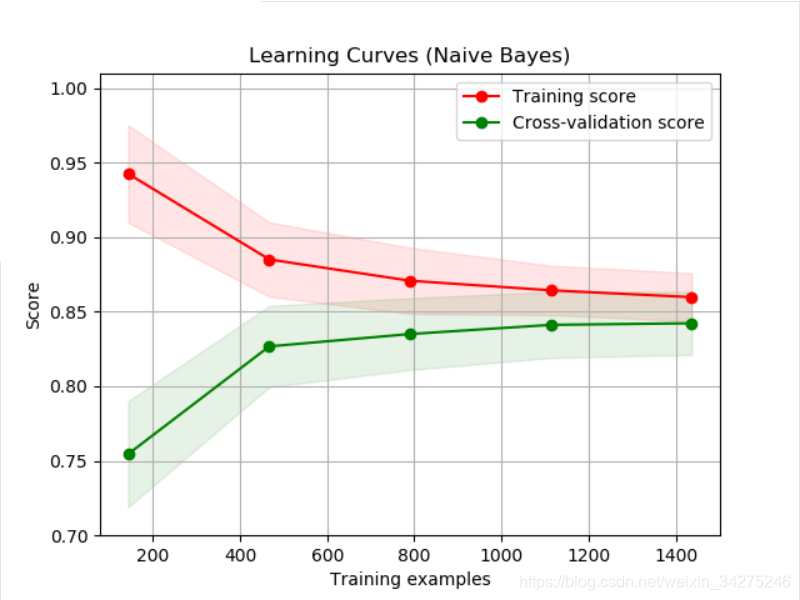
title = "Learning Curves (Naive Bayes)"
# Cross validation with 100 iterations to get smoother mean test and train
# score curves, each time with 20% data randomly selected as a validation set.
cv = ShuffleSplit(n_splits=100, test_size=0.2, random_state=0)
estimator = GaussianNB()
plot_learning_curve(estimator, title, X, y, ylim=(0.7, 1.01), cv=cv, n_jobs=4)
title = "Learning Curves (SVM, RBF kernel, $\gamma=0.001$)"
# SVC is more expensive so we do a lower number of CV iterations:
cv = ShuffleSplit(n_splits=10, test_size=0.2, random_state=0)
estimator = SVC(gamma=0.001)
plot_learning_curve(estimator, title, X, y, (0.7, 1.01), cv=cv, n_jobs=4)
plt.show()
ImportError: [joblib] Attempting to do parallel computing without protecting your import on a system that does not support forking.
只需在主程式碼前加if name==‘main’:即可。
title:影象的名字。
cv : 整數, 交叉驗證生成器或可迭代的可選項,確定交叉驗證拆分策略。
Determines the cross-validation splitting strategy. Possible inputs for cv are:
- 無,使用預設的3倍交叉驗證,
- 整數,指定摺疊數。
- 要用作交叉驗證生成器的物件。
- 可迭代的yielding訓練/測試分裂。
ShuffleSplit:我們這裡設定cv,交叉驗證使用ShuffleSplit方法,一共取得100組訓練集與測試集,每次的測試集為20%,它返回的是每組訓練集與測試集的下標索引,由此可以知道哪些是train,那些是test。
ylim:tuple, shape (ymin, ymax), 可選的。定義繪製的最小和最大y值,這裡是(0.7,1.01)。
n_jobs : 整數,可選並行執行的作業數(預設值為1)。windows開多執行緒需要在if “name” == “main”: 中執行。

參考地址:
sklearn.model_selection.ShuffleSplit
ShuffleSplit(n_splits=10, test_size=’default’, train_size=None, random_state=None)
用於將樣本集合隨機“打散”後劃分為訓練集、測試集。
matplotlib.pyplot.fill_between
基於matplotlib的資料視覺化(圖形填充fill、fill_between)


