常惠琢 201771010102《面向物件程式設計(java)》第十七週學習總結
實驗十七 執行緒同步控制
實驗時間 2018-12-10
1、實驗目的與要求
(1) 掌握執行緒同步的概念及實現技術;
(2) 執行緒綜合程式設計練習
2、實驗內容和步驟
實驗1:測試程式並進行程式碼註釋。
測試程式1:
l 在Elipse環境下除錯教材651頁程式14-7,結合程式執行結果理解程式;
l 掌握利用鎖物件和條件物件實現的多執行緒同步技術。

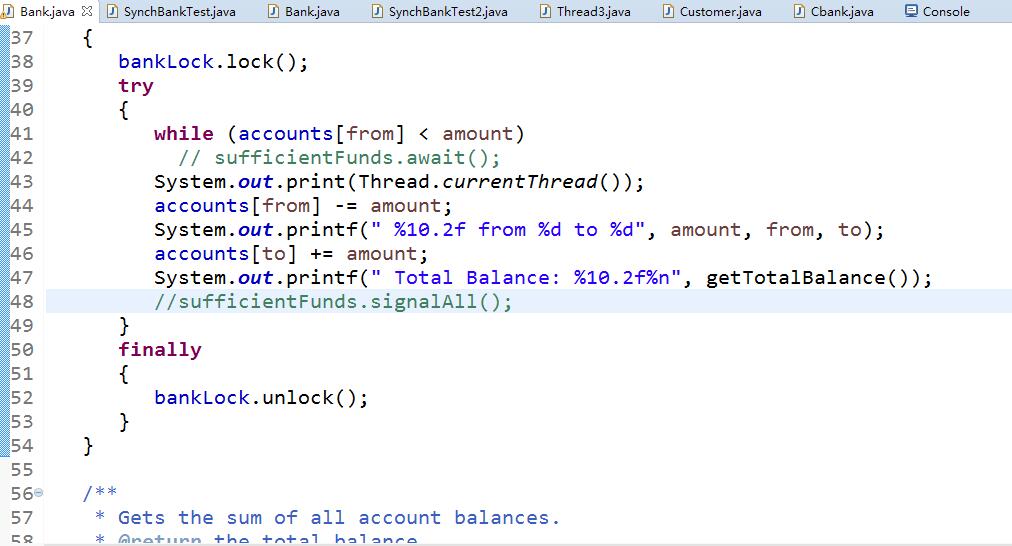
1 package synch; 2 3 import java.util.*; 4 import java.util.concurrent.locks.*;//View Code匯入locks包 5 6 /** 7 * 具有多個銀行帳戶的銀行,使用鎖序列化訪問 8 * @version 1.30 2004-08-01 9 * @author Cay Horstmann 10 */ 11 public class Bank 12 { 13 private final double[] accounts;//使銀行運轉的基礎資料 14 private Lock bankLock; 15 private Condition sufficientFunds;//擴張的兩個私有屬性lock and Condition的一個鎖物件一個條件物件 16 17 /**18 * 建設銀行。 19 * @param 賬號 20 * @param 每個賬戶的初始餘額 21 */ 22 public Bank(int n, double initialBalance) 23 { 24 accounts = new double[n];//n個賬戶 25 Arrays.fill(accounts, initialBalance);//每個賬戶初始資金為1000元 26 bankLock = new ReentrantLock();//建立鎖物件(避免執行緒共享的bank物件內容發生混亂) 27 sufficientFunds = bankLock.newCondition();//建立條件物件(便於得到鎖物件的執行緒在不能做有用的工作時對該執行緒進行處理) 28 } 29 30 /** 31 * 把錢從一個賬戶轉到另一個賬戶 32 * @param 從賬戶轉賬 33 * @param 轉到要轉賬的賬戶 34 * @param 轉賬金額 35 */ 36 public void transfer(int from, int to, double amount) throws InterruptedException 37 { 38 bankLock.lock();//在鄰接區加鎖(執行緒進入的條件) 39 try 40 {//臨界區 41 while (accounts[from] < amount)//賬戶餘額不滿足支出時 42 sufficientFunds.await(); 43 System.out.print(Thread.currentThread());//列印當前執行緒資訊 44 accounts[from] -= amount;//該賬戶支出一筆錢 45 System.out.printf(" %10.2f from %d to %d", amount, from, to); 46 accounts[to] += amount;//一個隨機賬戶得到這筆錢 47 System.out.printf(" Total Balance: %10.2f%n", getTotalBalance()); 48 sufficientFunds.signalAll();//喚醒所有等待的執行緒 49 } 50 finally 51 { 52 bankLock.unlock();//unlock()解鎖 lock上鎖 53 } 54 } 55 56 /** 57 * 獲取所有帳戶餘額的總和。 58 * @return 總餘額 59 */ 60 public double getTotalBalance()//加鎖行為 61 { 62 bankLock.lock(); 63 try 64 { 65 double sum = 0; 66 67 for (double a : accounts) 68 sum += a; 69 70 return sum; 71 } 72 finally 73 { 74 bankLock.unlock();//釋放鎖 75 } 76 } 77 78 /** 79 * 獲取銀行中的帳戶數量。 80 * @return 賬號 81 */ 82 public int size() 83 { 84 return accounts.length; 85 } 86 }

1 package synch; 2 3 /** 4 * 這個程式顯示了多個執行緒如何安全地訪問資料結構 5 * @version 1.31 2015-06-21 6 * @author Cay Horstmann 7 */ 8 public class SynchBankTest 9 { 10 public static final int NACCOUNTS = 100;//帳目 11 public static final double INITIAL_BALANCE = 1000;//期初餘額 12 public static final double MAX_AMOUNT = 1000;//最大金額 13 public static final int DELAY = 10;//延遲時間 14 15 public static void main(String[] args) 16 { 17 Bank bank = new Bank(NACCOUNTS, INITIAL_BALANCE);//建立一個銀行物件,這個銀行有一百個使用者,一百個使用者使用這個銀行 18 for (int i = 0; i < NACCOUNTS; i++) 19 { 20 int fromAccount = i; 21 Runnable r = () -> { 22 try 23 { 24 while (true) 25 { 26 int toAccount = (int) (bank.size() * Math.random());//拿出一個隨機賬戶 27 double amount = MAX_AMOUNT * Math.random();//設定隨機一筆錢(支出/得到) 28 bank.transfer(fromAccount, toAccount, amount);//轉賬操作 29 Thread.sleep((int) (DELAY * Math.random()));//隨機的休眠時間 30 } 31 } 32 catch (InterruptedException e) 33 { 34 } 35 }; 36 Thread t = new Thread(r);//呼叫了Thread(Runnable target)方法。且父類物件變數指向子類物件。 37 t.start();//使執行緒處於可執行狀態 38 } 39 } 40 }View Code
 測試程式2:
測試程式2:
l 在Elipse環境下除錯教材655頁程式14-8,結合程式執行結果理解程式;
l 掌握synchronized在多執行緒同步中的應用。

1 package synch2; 2 3 import java.util.*; 4 5 /** 6 * A bank with a number of bank accounts that uses synchronization primitives. 7 * @version 1.30 2004-08-01 8 * @author Cay Horstmann 9 */ 10 public class Bank 11 { 12 private final double[] accounts; 13 14 /** 15 * Constructs the bank. 16 * @param n the number of accounts 17 * @param initialBalance the initial balance for each account 18 */ 19 public Bank(int n, double initialBalance) 20 { 21 accounts = new double[n]; 22 Arrays.fill(accounts, initialBalance); 23 } 24 25 /** 26 * Transfers money from one account to another. 27 * @param from the account to transfer from 28 * @param to the account to transfer to 29 * @param amount the amount to transfer 30 */ 31 public synchronized void transfer(int from, int to, double amount) throws InterruptedException 32 { 33 while (accounts[from] < amount) 34 wait(); 35 System.out.print(Thread.currentThread()); 36 accounts[from] -= amount; 37 System.out.printf(" %10.2f from %d to %d", amount, from, to); 38 accounts[to] += amount; 39 System.out.printf(" Total Balance: %10.2f%n", getTotalBalance()); 40 notifyAll(); 41 } 42 43 /** 44 * Gets the sum of all account balances. 45 * @return the total balance 46 */ 47 public synchronized double getTotalBalance() 48 { 49 double sum = 0; 50 51 for (double a : accounts) 52 sum += a; 53 54 return sum; 55 } 56 57 /** 58 * Gets the number of accounts in the bank. 59 * @return the number of accounts 60 */ 61 public int size() 62 { 63 return accounts.length; 64 } 65 }View Code

1 package synch2; 2 3 /** 4 * This program shows how multiple threads can safely access a data structure, 5 * using synchronized methods. 6 * @version 1.31 2015-06-21 7 * @author Cay Horstmann 8 */ 9 public class SynchBankTest2 10 { 11 public static final int NACCOUNTS = 100; 12 public static final double INITIAL_BALANCE = 1000; 13 public static final double MAX_AMOUNT = 1000; 14 public static final int DELAY = 10; 15 16 public static void main(String[] args) 17 { 18 Bank bank = new Bank(NACCOUNTS, INITIAL_BALANCE); 19 for (int i = 0; i < NACCOUNTS; i++) 20 { 21 int fromAccount = i; 22 Runnable r = () -> { 23 try 24 { 25 while (true) 26 { 27 int toAccount = (int) (bank.size() * Math.random()); 28 double amount = MAX_AMOUNT * Math.random(); 29 bank.transfer(fromAccount, toAccount, amount); 30 Thread.sleep((int) (DELAY * Math.random())); 31 } 32 } 33 catch (InterruptedException e) 34 { 35 } 36 }; 37 Thread t = new Thread(r); 38 t.start(); 39 } 40 } 41 }View Code

測試程式3:
l 在Elipse環境下執行以下程式,結合程式執行結果分析程式存在問題;
l 嘗試解決程式中存在問題。
| class Cbank { private static int s=2000; public static void sub(int m) { int temp=s; temp=temp-m; try { Thread.sleep((int)(1000*Math.random())); } catch (InterruptedException e) { } s=temp; System.out.println("s="+s); } }
class Customer extends Thread { public void run() { for( int i=1; i<=4; i++) Cbank.sub(100); } } public class Thread3 { public static void main(String args[]) { Customer customer1 = new Customer(); Customer customer2 = new Customer(); customer1.start(); customer2.start(); } } |

1 public class Thread3 2 { 3 public static void main(String args[]) 4 { 5 Customer customer1 = new Customer(); 6 Customer customer2 = new Customer(); 7 customer1.start(); 8 customer2.start(); 9 } 10 }Thread3

1 class Customer extends Thread 2 { 3 public void run() 4 { 5 for( int i=1; i<=4; i++) 6 Cbank.sub(100); 7 } 8 }Customer

1 class Cbank 2 { 3 private static int s=2000; 4 public static void sub(int m) 5 { 6 int temp=s; 7 temp=temp-m; 8 try { 9 Thread.sleep((int)(1000*Math.random())); 10 } 11 catch (InterruptedException e) { } 12 s=temp; 13 System.out.println("s="+s); 14 } 15 }Cbank

實驗2 程式設計練習
利用多執行緒及同步方法,編寫一個程式模擬火車票售票系統,共3個視窗,賣10張票,程式輸出結果類似(程式輸出不唯一,可以是其他類似結果)。
Thread-0視窗售:第1張票
Thread-0視窗售:第2張票
Thread-1視窗售:第3張票
Thread-2視窗售:第4張票
Thread-2視窗售:第5張票
Thread-1視窗售:第6張票
Thread-0視窗售:第7張票
Thread-2視窗售:第8張票
Thread-1視窗售:第9張票
Thread-0視窗售:第10張票

1 import java.awt.geom.FlatteningPathIterator; 2 3 public class Demo { 4 5 public static void main(String[] args) { 6 Myrhread myrhread=new Myrhread(); 7 Thread t1 = new Thread(myrhread); 8 Thread t2 = new Thread(myrhread); 9 Thread t3 = new Thread(myrhread); 10 t1.start(); 11 t2.start(); 12 t3.start(); 13 } 14 15 } 16 class Myrhread implements Runnable{ 17 int t=1; 18 boolean flag =true; 19 @Override 20 public void run() { 21 while (flag) { 22 try { 23 Thread.sleep(500); 24 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 25 // TODO Auto-generated catch block 26 e.printStackTrace(); 27 } 28 synchronized (this) { 29 if(t<=10) { 30 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"視窗售:第"+t+"張票"); 31 t++; 32 } 33 if(t>10) { 34 flag=false; 35 } 36 37 } 38 39 } 40 41 } 42 43 }Demo

實驗總結:
這次實驗很少,最後一個程式的程式設計也學到了很多東西,比如unlock()解鎖 , lock上鎖等。

