Codeforces Round #528 (Div. 2, based on Technocup 2019 Elimination Round 4) C. Connect Three 【模擬】
傳送門:http://codeforces.com/contest/1087/problem/C
C. Connect Three
time limit per test 1 second memory limit per test 256 megabytes input standard input output standard outputThe Squareland national forest is divided into equal
Three friends, Alice, Bob, and Charlie are going to buy three distinct plots of land A,B,C
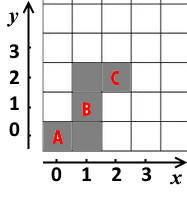 For example, A=(0,0)A=(0,0), B=(1,1)B=(1,1), C=(2,2)C=(2,2). The minimal number of plots to be cleared is 55. One of the ways to do it is shown with the gray color.
For example, A=(0,0)A=(0,0), B=(1,1)B=(1,1), C=(2,2)C=(2,2). The minimal number of plots to be cleared is 55. One of the ways to do it is shown with the gray color.
Of course, the friends don't want to strain too much. Help them find out the smallest number of plots they need to clean from trees.
InputThe first line contains two integers xAxA and yAyA — coordinates of the plot AA (0≤xA,yA≤10000≤xA,yA≤1000). The following two lines describe coordinates (xB,yB)(xB,yB) and (xC,yC)(xC,yC) of plots BB and CC respectively in the same format (0≤xB,yB,xC,yC≤10000≤xB,yB,xC,yC≤1000). It is guaranteed that all three plots are distinct.
OutputOn the first line print a single integer kk — the smallest number of plots needed to be cleaned from trees. The following kk lines should contain coordinates of all plots needed to be cleaned. All kk plots should be distinct. You can output the plots in any order.
If there are multiple solutions, print any of them.
Examples input Copy0 0 1 1 2 2output Copy
5 0 0 1 0 1 1 1 2 2 2input Copy
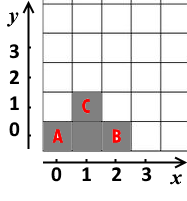
0 0 2 0 1 1output Copy
4 0 0 1 0 1 1 2 0Note
The first example is shown on the picture in the legend.
The second example is illustrated with the following image:
題意概括:
給三個格子的座標,要求用最少的格子把這三個格子連起來,要求相鄰格子相連需要是要有公共邊。
解題思路:
所需要的總步數就是 X軸方向最大差值 加 Y軸方向最大差值 加 1.
輸出的方格:
先按 X 小 Y 大的優先順序對三個座標排序。
從第一個點出發到第二個點,採取先沿著 X 軸 方向走,後沿著 Y軸 方向走,同時記錄離第三個點的曼哈頓距離最近的一個轉折點。
從轉折點走到第三個點,採取先沿著Y軸方向走,後沿著 X軸方向走。
tip:如果擔心會走重複的格子,加個標記就可以了。
AC code:
1 #include <queue> 2 #include <cmath> 3 #include <cstdio> 4 #include <vector> 5 #include <cstring> 6 #include <iostream> 7 #include <algorithm> 8 #define LL long long 9 using namespace std; 10 11 const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f; 12 const int MAXN = 1e3+10; 13 int N; 14 15 struct date 16 { 17 int x, y; 18 }index[4]; 19 20 bool cmp(date a, date b) 21 { 22 if(a.x != b.x) return a.x < b.x; 23 else return a.y > b.y; 24 } 25 26 bool mmp[MAXN][MAXN]; 27 28 int main() 29 { 30 date kk, nxt; 31 int maxx = 0, maxy = 0, minx = INF, miny = INF; 32 for(int i = 1; i <= 3; i++){ 33 scanf("%d %d", &index[i].x, &index[i].y); 34 maxx = max(maxx, index[i].x); 35 maxy = max(maxy, index[i].y); 36 minx = min(minx, index[i].x); 37 miny = min(miny, index[i].y); 38 } 39 sort(index+1, index+4, cmp); 40 memset(mmp, 1, sizeof(mmp)); 41 int ans = (maxx-minx)+(maxy-miny)+1; 42 printf("%d\n", ans); 43 printf("%d %d\n", index[1].x, index[1].y); 44 kk.x = index[1].x; 45 kk.y = index[1].y; 46 nxt.x = index[2].x; 47 nxt.y = index[2].y; 48 mmp[kk.x][kk.y] = false; 49 50 int len = abs(index[2].x - index[1].x); 51 for(int i = 1; i <= len; i++){ 52 kk.x++; 53 if(mmp[kk.x][kk.y]) printf("%d %d\n", kk.x, kk.y); 54 if(kk.x == index[3].x){ 55 nxt.x = kk.x; 56 nxt.y = kk.y; 57 } 58 mmp[kk.x][kk.y] = false; 59 } 60 61 len = abs(index[1].y - index[2].y); 62 for(int i = 1; i <= len; i++){ 63 if(index[1].y < index[2].y) kk.y++; 64 else kk.y--; 65 if(mmp[kk.x][kk.y]) printf("%d %d\n", kk.x, kk.y); 66 if(kk.y == index[3].y){ 67 nxt.x = kk.x; 68 nxt.y = kk.y; 69 } 70 mmp[kk.x][kk.y] = false; 71 } 72 73 // printf("nxtx:%d nxty:%d\n", nxt.x, nxt.y); 74 75 len = abs(index[3].y - nxt.y); 76 for(int i = 1; i <= len; i++){ 77 if(nxt.y < index[3].y) nxt.y++; 78 else nxt.y--; 79 if(mmp[nxt.x][nxt.y]) printf("%d %d\n", nxt.x, nxt.y); 80 mmp[nxt.x][nxt.y] = false; 81 } 82 83 len = abs(index[3].x - nxt.x); 84 for(int i = 1; i <= len; i++){ 85 nxt.x++; 86 if(mmp[nxt.x][nxt.y]) printf("%d %d\n", nxt.x, nxt.y); 87 mmp[nxt.x][nxt.y] = false; 88 } 89 90 return 0; 91 }
