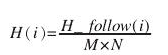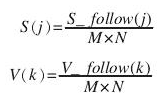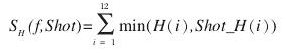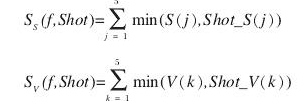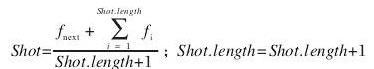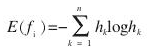[OpenCV] 基於聚類的視訊關鍵幀提取
阿新 • • 發佈:2018-12-25
參考論文:
1.《用非監督式聚類進行視訊鏡頭分割》
2.《一種基於視訊聚類的關鍵幀提取方法》
右邊為提取出來的關鍵幀
聚類的基本思想是,先把視訊聚成n個類,這n個類內的視訊幀是相似的,而類與類之間的視訊幀是不相似的。第二步是從每個類內提取一個代表作為關鍵幀,另外,如果一個類的幀數太少,那麼這個類不具有代表性,可以直接與相鄰幀合併。
因為HSV空間相比起RGB空間對顏色特性有著更好的支援,所以第一步我們先把顏色對映到HSV空間上。
首先,把分佈在0~255的RGB顏色直接對映到0~255
完成對映後,接下來需要構建HSV的顏色空間。我們設影象的大小為為MXN。然後分別統計H,S,V分量中,值為i的佔的百分比為多少。
計算兩張影象的相似度,需要我們先分別計算三個顏色直方圖的相似性,具體的計算方法是累加兩張影象直方圖相同索引處對應的最小值。
又因為人眼對H分量的敏感程度大於對S分量,而對
接下來,開始具體的計算。
1.對於每個類,維護一個質心:
2.對於每一幀,計算它聚類質心的相似度(根據前面提到的相似度公式)
如果相似度小於某一閾值,那麼把它歸到一個新建的類中,否則加入之前的類中。
3.合併一部分過小的聚類。
4.計算每個聚類中熵最大的影象,將其作為關鍵幀,計算方法:
#include <opencv2/opencv.hpp> #include<string> #include<io.h> #include<list> #include<array> using namespace std; using namespace cv; #define NUM_FRAME 300 #define SIZE 7 char path[100];//輸入檔案路徑 struct shot { list<array<float, 22> >content; list<int> id; array<float, 22> center; }; float similarity(array<float, 22> x1, array<float, 22> x2) { float s1 = 0, s2 = 0, s3 = 0; float alpha1 = 0.5, alpha2 = 0.3, alpha3 = 0.2; for (int i = 0; i < 12; i++) { s1 += min(x1[i], x2[i]); } for (int i = 12; i < 17; i++) { s2 += min(x1[i], x2[i]); } for (int i = 17; i < 22; i++) { s3 += min(x1[i], x2[i]); } return s1*alpha1 + s2*alpha2 + s3*alpha3; } int findMaxEntropyId(list<array<float, 22> >x,list<int> y) { float s1,s2,s3,max; list<array<float, 22> >::iterator it; list<int>::iterator i = y.begin(); int id = 0; for (it = x.begin(); it != x.end(); it++,i++) { s1 = 0.0f, s2 = 0.0f, s3 = 0.0f, max = 0.0f; for (int j = 0; j < 12; j++) { if ((*it)[j] != 0)s1 += -(*it)[j] * log((*it)[j])/log(2); } for (int j = 12; j < 17; j++) { if ((*it)[j] != 0)s2 += -(*it)[j] * log((*it)[j])/log(2); } for (int j = 17; j < 22; j++) { if ((*it)[j] != 0)s3 += -(*it)[j] * log((*it)[j])/log(2); } float s = 0.5f*s1 + 0.3f*s2 + 0.2f*s3; //printf("s = %f\n", s); if (s>max) { max = s; id = *i; } } return id; } const array<float, 22> operator +(const array<float, 22> &x, const array<float, 22> &y) { array<float, 22>ans; for (int i = 0; i < 22; i++) { ans[i] = x[i] + y[i]; } return ans; } const array<float, 22> operator /(const array<float, 22> &x, int s) { array<float, 22>ans; for (int i = 0; i < 22; i++) { ans[i] = x[i] / s; } return ans; } void combine(vector<shot>& Shot, int i, int j) { list<array<float, 22> >::iterator it; list<int>::iterator k = Shot[j].id.begin(); vector<shot>::iterator v = Shot.begin() + j; for (it = Shot[j].content.begin(); it != Shot[j].content.end(); it++,k++) { Shot[i].content.push_back(*it); Shot[i].center = *it + Shot[i].center; Shot[i].id.push_back(*k); } Shot.erase(v); } array<float, 22> sum(list<array<float, 22> >& arr) { array<float, 22> ans = { 0 }; list<array<float, 22> >::iterator it; for (it = arr.begin(); it != arr.end(); it++) { for (int i = 0; i < 22; i++) { ans[i] += (*it)[i]; } } return ans; } //將圖片序列轉換為視訊 void handleVideo() { int i = 0; IplImage* img = 0;//讀入影象 IplImage* outimg = 0;//修改影象尺寸 char image_name[100];//影象名字 char videoname[100]; strcpy(videoname, "1.avi"); //從檔案讀入視訊 CvCapture* capture = cvCaptureFromAVI(videoname); //讀取和顯示 IplImage* frameimg;//從視訊中提取的幀影象 int fps = (int)cvGetCaptureProperty(capture, CV_CAP_PROP_FPS);//視訊的fps int frameH = (int)cvGetCaptureProperty(capture, CV_CAP_PROP_FRAME_HEIGHT);//視訊的高度 int frameW = (int)cvGetCaptureProperty(capture, CV_CAP_PROP_FRAME_WIDTH);//視訊的寬度 printf("\tvideo height : %d\n\tvideo width : %d\n\tfps : %d\n", frameH, frameW, fps); list<array<float, 22> >colorbar; //建立視窗 cvNamedWindow("mainWin", CV_WINDOW_AUTOSIZE); //讀入圖片,並製作幻燈片 while (1) { frameimg = cvQueryFrame(capture); //獲取一幀圖片 if (!frameimg)break;//讀到盡頭,退出 cvCvtColor(frameimg, frameimg, CV_BGR2HSV); array<float, 22> color = { 0 }; uchar* data = (uchar *)frameimg->imageData; int step = frameimg->widthStep / sizeof(uchar); int channels = frameimg->nChannels; uchar* h = new uchar[frameimg->height*frameimg->width]; uchar* s = new uchar[frameimg->height*frameimg->width]; uchar* v = new uchar[frameimg->height*frameimg->width]; for (int i = 0; i < frameimg->height; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < frameimg->width; j++) { h[i*frameimg->height + j] = data[i*step + j*channels + 0] / 21; if (h[i*frameimg->height + j] > 11)h[i*frameimg->height + j] = 11; s[i*frameimg->height + j] = data[i*step + j*channels + 1] / 51; if (s[i*frameimg->height + j] > 4)s[i*frameimg->height + j] = 4; v[i*frameimg->height + j] = data[i*step + j*channels + 2] / 51; if (v[i*frameimg->height + j] > 4)v[i*frameimg->height + j] = 4; color[h[i*frameimg->height + j]]++; color[12 + s[i*frameimg->height + j]]++; color[17 + v[i*frameimg->height + j]]++; } } for (int i = 0; i < 22; i++) { color[i] /= frameimg->height*frameimg->width; } colorbar.push_back(color); } float threshold = 0.8f; list<array<float, 22> >::iterator it = colorbar.begin(); it++; vector<shot>Shot; //放入第一幀 shot first; first.content.push_back(*colorbar.begin()); first.center = *colorbar.begin(); first.id.push_back(0); Shot.push_back(first); int count = 0; int num = 1; int index = 0; float max = 0; for (; it != colorbar.end(); it++) { max = 0; index = 0; //計算相似度最大的 for (int i = 0; i < num; i++) { float ratio = similarity(*it, Shot[i].center); if (ratio > max) { max = ratio; index = i; } } //如果最大的小於某個閾值,則新建一個聚類 if (max < threshold) { num++; shot newshot; newshot.center = *it; newshot.content.push_back(*it); newshot.id.push_back(count); Shot.push_back(newshot); } else { Shot[index].center = (*it + sum(Shot[index].content)) / (Shot[index].content.size() + 1); Shot[index].content.push_back(*it); Shot[index].id.push_back(count); } count++; } for (int i = 0; i < Shot.size(); i++) { if (Shot[i].content.size() <10 && i>0) { combine(Shot, i - 1, i); i--; } } float maxE = 0.0f; int indexE = 0; for (int i = 0; i < Shot.size(); i++) { int id = findMaxEntropyId(Shot[i].content, Shot[i].id); printf("%d\n", id); } printf("%d", Shot.size()); cvDestroyWindow("mainWin"); } int main(int argc, char* argv[]) { handleVideo(); waitKey(); system("pause"); return 0; }