java 集合類之LinkedList
阿新 • • 發佈:2018-12-25
本文將結合原始碼簡單介紹一下java 中LinkedList的實現。
繼承結構
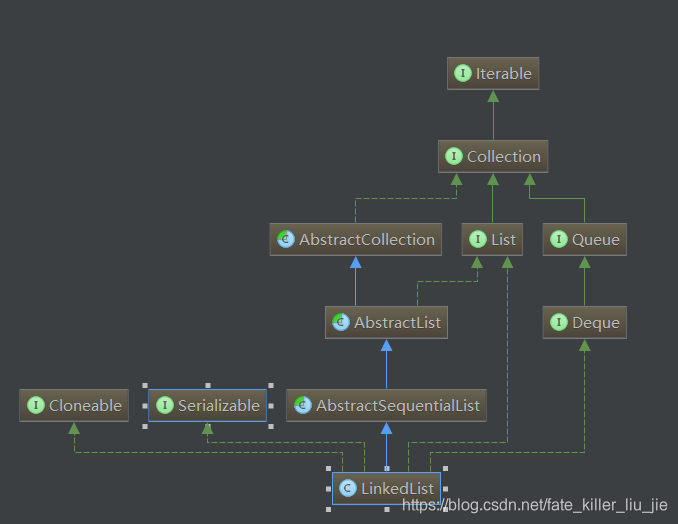
相比ArrayList,LinkedList的繼承結構要複雜一些,可以看出,LinkedList還是雙向佇列的實現。也意味著LinkedList可以作為棧使用。
重要的欄位
transient int size = 0;
/**
* Pointer to first node.
* Invariant: (first == null && last == null) ||
* (first.prev == null && first.item != null)
* 不變約束:頭為空且尾為空或頭的前置為空且頭的內容不為空
*/ 其實LinkedList中一共只聲明瞭3個欄位,非常簡潔,分別是表示長度的size,頭節點和尾節點。
節點的定義
private static class Node<E> {
E item;
Node<E> next;
Node<E> prev;
Node(Node<E> prev, E element, Node<E> next) {
this.item = element;
this.next = next;
this.prev = prev;
}
}
可以看到是一個非常簡單的定義,只有一個建構函式,是一個經典的雙端連結串列的節點的定義。
重要方法的實現
- add(E)
這個方法向連結串列中插入一個元素,注意使用的方法是尾插法,具體實現如下:
/**
* Appends the specified element to the end of this list.
*
* <p>This method is equivalent to {@link #addLast}.
*
* @param e element to be appended to this list
* @return {@code true} (as specified by {@link Collection#add})
*/
public boolean add(E e) {
linkLast(e);
return true;
}
/**
* Links e as last element.
* 將元素插入連結串列尾部,並更新連結串列的尾指標
*/
void linkLast(E e) {
final Node<E> l = last;
final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(l, e, null);
last = newNode;
if (l == null)
first = newNode;
else
l.next = newNode;
size++;
modCount++;
}
2 addFirst(E)
向連結串列的頭部插入一個數據
/**
* Inserts the specified element at the beginning of this list.
*
* @param e the element to add
*/
public void addFirst(E e) {
linkFirst(e);
}
/**
* Links e as first element.
*/
private void linkFirst(E e) {
final Node<E> f = first;
final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(null, e, f);
first = newNode;
if (f == null)
last = newNode;
else
f.prev = newNode;
size++;
modCount++;
}
簡單的頭插法插入實現。
3 node(index)
返回位於index處的節點,這個是LinkedList查詢的實現函式,所有帶查詢操作的函式均以此實現。
/**
* Returns the (non-null) Node at the specified element index.
*/
Node<E> node(int index) {
if (index < (size >> 1)) {
Node<E> x = first;
for (int i = 0; i < index; i++)
x = x.next;
return x;
} else {
Node<E> x = last;
for (int i = size - 1; i > index; i--)
x = x.prev;
return x;
}
}
從原始碼中可以看出,查詢的操作根據查詢的位置進行了優化,要是查詢小於size/2的就從頭開始,反之則從尾指標開始。
作為佇列和棧使用
作為佇列使用
向隊尾加入offer(E)
查詢隊頭並移除poll()
查詢隊頭但不移除peek()
作為棧使用
壓棧 push(E)
出棧 pop()
