線段樹模板題5題
題目描述
如題,已知一個數列,你需要進行下面兩種操作:
1.將某區間每一個數加上x
2.求出某區間每一個數的和
輸入輸出格式
輸入格式:
第一行包含兩個整數N、M,分別表示該數列數字的個數和操作的總個數。
第二行包含N個用空格分隔的整數,其中第i個數字表示數列第i項的初始值。
接下來M行每行包含3或4個整數,表示一個操作,具體如下:
操作1: 格式:1 x y k 含義:將區間[x,y]內每個數加上k
操作2: 格式:2 x y 含義:輸出區間[x,y]內每個數的和
輸出格式:
輸出包含若干行整數,即為所有操作2的結果。
輸入輸出樣例
輸入樣例#1: 複製
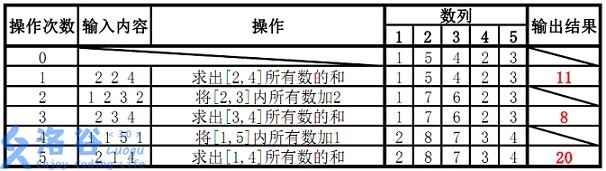
5 5 1 5 4 2 3 2 2 4 1 2 3 2 2 3 4 1 1 5 1 2 1 4
輸出樣例#1: 複製
11 8 20
說明
時空限制:1000ms,128M
資料規模:
對於30%的資料:N<=8,M<=10
對於70%的資料:N<=1000,M<=10000
對於100%的資料:N<=100000,M<=100000
(資料已經過加強^_^,保證在int64/long long資料範圍內)
樣例說明:
#include<iostream> using namespace std; const int maxn = 100010; int n, m, p, x, a, b; long long ans; struct Node { long long l, r, w, f; }node[4 * maxn + 10]; void build(int l, int r, int k) { node[k].r = r; node[k].l = l; if (l == r) { cin >> node[k].w; return; } int mid = (r + l) / 2; build(l, mid, k * 2); build(mid + 1, r, k * 2 + 1); node[k].w = node[k * 2].w + node[k * 2 + 1].w; } void down(int k) { node[k * 2].f += node[k].f; node[k * 2 + 1].f += node[k].f; node[k * 2].w += (node[k * 2].r - node[k * 2].l + 1) * node[k].f; node[k * 2 + 1].w += (node[k * 2 + 1].r - node[k * 2 + 1].l + 1) * node[k].f; node[k].f = 0; } void add(int k) { if (node[k].l >= a && node[k].r <= b) { node[k].w += (node[k].r -node[k].l + 1) * x; node[k].f += x; return; } if (node[k].f) down(k); int mid = (node[k].l + node[k].r) / 2; if (a <= mid) { add(k * 2); } if (b > mid) { add(k * 2 + 1); } node[k].w = node[k * 2].w + node[k * 2 + 1].w; } void sum(int k) { if (node[k].l >= a && node[k].r <= b) { ans += node[k].w; return; } if (node[k].f) down(k); int mid = (node[k].l + node[k].r) / 2; if (a <= mid) { sum(k * 2); } if (b > mid) { sum(k * 2 + 1); } } int main () { cin >> n >> m; build(1, n, 1); for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++) { cin >> p; ans = 0; if (p == 1) { cin >> a >> b >> x; add(1); } else { cin >> a >> b; sum(1); cout << ans << endl; } } return 0; }
題目描述
如題,已知一個數列,你需要進行下面三種操作:
1.將某區間每一個數乘上x
2.將某區間每一個數加上x
3.求出某區間每一個數的和
輸入輸出格式
輸入格式:
第一行包含三個整數N、M、P,分別表示該數列數字的個數、操作的總個數和模數。
第二行包含N個用空格分隔的整數,其中第i個數字表示數列第i項的初始值。
接下來M行每行包含3或4個整數,表示一個操作,具體如下:
操作1: 格式:1 x y k 含義:將區間[x,y]內每個數乘上k
操作2: 格式:2 x y k 含義:將區間[x,y]內每個數加上k
操作3: 格式:3 x y 含義:輸出區間[x,y]內每個數的和對P取模所得的結果
輸出格式:
輸出包含若干行整數,即為所有操作3的結果。
輸入輸出樣例
輸入樣例#1: 複製
5 5 38 1 5 4 2 3 2 1 4 1 3 2 5 1 2 4 2 2 3 5 5 3 1 4
輸出樣例#1: 複製
17 2
說明
時空限制:1000ms,128M
資料規模:
對於30%的資料:N<=8,M<=10
對於70%的資料:N<=1000,M<=10000
對於100%的資料:N<=100000,M<=100000
(資料已經過加強^_^)
樣例說明:
故輸出應為17、2(40 mod 38=2)
思路:該題比較複雜,因為存在倆個不同的改變區域的方案,因此我設計了倆個懶標籤,同時因為要取模,所以有倆種方案的優先順序可以選擇,一種是先加後乘,另外一種是先乘後加,都是用在更新結點上,如果我們採取前者的方案可能存在精度損失,所以我們選擇後者,其他的具體看程式碼,注意down裡面的程式碼和一個懶標記很不一樣,其他也有一些部分需要稍微改改,總的來說這個題目真的是一個很不錯的模板題
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
const int maxn = 100010;
struct Node{
long long l, r, w, add, mul;
}node[4 * maxn + 10];
long long a, b, x, n, m, z, p, ans;
void build(int l, int r, int k) {
node[k].r = r;
node[k].l = l;
node[k].mul = 1;
if (l == r) {
cin >> node[k].w;
return;
}
int mid = (l + r) / 2;
build(l, mid, k * 2);
build(mid + 1, r, k * 2 + 1);
node[k].w = (node[k * 2].w + node[k * 2 + 1].w) % p;
}
void down(int k) {
node[k * 2].w = (node[k].mul * node[k * 2].w + node[k].add * (node[k * 2].r - node[k * 2].l + 1)) % p;
node[k * 2 + 1].w = (node[k].mul * node[k * 2 + 1].w + node[k].add * (node[k * 2 + 1].r - node[k * 2 + 1].l + 1)) % p;
node[k * 2].mul = (node[k].mul * node[k * 2].mul) % p;
node[k * 2 + 1].mul = (node[k].mul * node[k * 2 + 1].mul) % p;
node[k * 2].add = (node[k].mul * node[k * 2].add + node[k].add) % p;
node[k * 2 + 1].add = (node[k].mul * node[k * 2 + 1].add + node[k].add) % p;
node[k].mul = 1;
node[k].add = 0;
}
void add(int k) {
if (a <= node[k].l && b >= node[k].r) {
node[k].w = (node[k].w + (node[k].r - node[k].l + 1) * x) % p;
node[k].add = (node[k].add + x) % p;
return;
}
if(node[k].add || node[k].mul != 1) down(k);
int mid = (node[k].l + node[k].r) / 2;
if (a <= mid) {
add(k * 2);
}
if (b > mid) {
add(k * 2 + 1);
}
node[k].w = (node[k * 2].w + node[k * 2 + 1].w) % p;
}
void mul(int k) {
if (a <= node[k].l && b >= node[k].r) {
node[k].w = (node[k].w * x) % p;
node[k].mul = (node[k].mul * x) % p;
node[k].add = (x * node[k].add) % p;
return;
}
if(node[k].add || node[k].mul != 1) down(k);
int mid = (node[k].l + node[k].r) / 2;
if (a <= mid) {
mul(k * 2);
}
if (b > mid) {
mul(k * 2 + 1);
}
node[k].w = (node[k * 2].w + node[k * 2 + 1].w) % p;
}
void sum(int k) {
if (a <= node[k].l && b >= node[k].r) {
ans = (node[k].w + ans) % p;
return;
}
if(node[k].add || node[k].mul != 1) down(k);
int mid = (node[k].l + node[k].r) / 2;
if (a <= mid) {
sum(k * 2);
}
if (b > mid) {
sum(k * 2 + 1);
}
}
int main() {
cin >> n >> m >> p;
build(1, n, 1);
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++) {
cin >> z;
if (z == 1) {
cin >> a >> b >> x;
mul(1);
} else if (z == 2) {
cin >> a >> b >> x;
add(1);
} else {
cin >> a >> b;
ans = 0;
sum(1);
cout << ans << endl;
}
}
return 0;
}
一行N個方格,開始每個格子裡都有一個整數。現在動態地提出一些問題和修改:提問的形式是求某一個特定的子區間[a,b]中所有元素的和;修改的規則是指定某一個格子x,加上或者減去一個特定的值A。現在要求你能對每個提問作出正確的回答。1≤N<100000,,提問和修改的總數m<10000條。
輸入描述 Input Description
輸入檔案第一行為一個整數N,接下來是n行n個整數,表示格子中原來的整數。接下一個正整數m,再接下來有m行,表示m個詢問,第一個整數表示詢問代號,詢問代號1表示增加,後面的兩個數x和A表示給位置X上的數值增加A,詢問代號2表示區間求和,後面兩個整數表示a和b,表示要求[a,b]之間的區間和。
輸出描述 Output Description
共m行,每個整數
樣例輸入 Sample Input
6
4
5
6
2
1
3
4
1 3 5
2 1 4
1 1 9
2 2 6
樣例輸出 Sample Output
22
22
資料範圍及提示 Data Size & Hint
1≤N≤100000, m≤10000 。
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
const int maxn = 100000;
int n, x, y, p, ans, m;
struct node {
int l, r, w;
}tree[4 * maxn + 10];
void build(int l, int r, int k) {
tree[k].l = l;
tree[k].r = r;
if (l == r) {
cin >> tree[k].w;
return;
}
int mid = (l + r) / 2;
build(l, mid, k * 2);
build(mid + 1, r, k * 2 + 1);
tree[k].w = tree[k * 2].w + tree[k * 2 + 1].w;
}
void add(int k) {
if (tree[k].l == tree[k].r) {
tree[k].w += y;
return;
}
int mid = (tree[k].l + tree[k].r) / 2;
if (x <= mid) add(k * 2);
else add(k * 2 + 1);
tree[k].w = tree[k * 2].w + tree[k * 2 + 1].w;
}
void sum(int k) {
if (tree[k].l >= x && tree[k].r <= y) {
ans += tree[k].w;
return;
}
int mid = (tree[k].l + tree[k].r) / 2;
if (x <= mid) sum(k * 2);
if (y > mid) sum(k * 2 + 1);
}
int main() {
cin >> n;
build(1, n, 1);
cin >> m;
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++) {
cin >> p >> x >> y;
ans = 0;
if (p == 1) {
add(1);
} else {
sum(1);
cout << ans << endl;
}
}
return 0;
}
題目描述 Description
給你N個數,有兩種操作
1:給區間[a,b]的所有數都增加X
2:詢問第i個數是什麼?
輸入描述 Input Description
第一行一個正整數n,接下來n行n個整數,再接下來一個正整數Q,表示操作的個數. 接下來Q行每行若干個整數。如果第一個數是1,後接3個正整數a,b,X,表示在區間[a,b]內每個數增加X,如果是2,後面跟1個整數i, 表示詢問第i個位置的數是多少。
輸出描述 Output Description
對於每個詢問輸出一行一個答案
樣例輸入 Sample Input
3
1
2
3
2
1 2 3 2
2 3
樣例輸出 Sample Output
5
資料範圍及提示 Data Size & Hint
資料範圍
1<=n<=100000
1<=q<=100000
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
const int maxn = 100010;
int n, m, p, x, a, b, ans;
struct node {
int l, r, w, f;
}tree[4 * maxn + 10];
void build(int l, int r, int k) {
tree[k].l = l;
tree[k].r = r;
if (l == r) {
cin >> tree[k].w;
return;
}
int mid = (l + r) / 2;
build(l, mid, k * 2);
build(mid + 1, r, k * 2 + 1);
tree[k].w = tree[k * 2].w + tree[k * 2 + 1].w;
}
void down(int k) {
tree[k * 2].f += tree[k].f;
tree[k * 2 + 1].f += tree[k].f;
tree[2 * k].w += tree[k].f * (tree[k * 2].r - tree[k * 2].l + 1);
tree[2 * k + 1].w += tree[k].f * (tree[k * 2 + 1].r - tree[k * 2 + 1].l + 1);
tree[k].f = 0;
}
void add(int k) {
if (tree[k].l >= a && tree[k].r <= b) {
tree[k].w += (tree[k].r - tree[k].l + 1) * x;
tree[k].f += x;
return;
}
if (tree[k].f) down(k);
int mid = (tree[k].l + tree[k].r) / 2;
if (a <= mid) add(k * 2);
if (b > mid) add(k * 2 + 1);
tree[k].w = tree[k * 2].w + tree[k * 2 + 1].w;
}
void ask(int k) {
if (tree[k].l == tree[k].r) {
ans = tree[k].w;
return;
}
if (tree[k].f) down(k);
int mid = (tree[k].l + tree[k].r) / 2;
if (x <= mid) ask(k * 2);
else ask(k * 2 + 1);
}
int main () {
cin >> n;
build(1, n, 1);
cin >> m;
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
cin >> p;
if (p == 1) {
cin >> a >> b >> x;
add(1);
} else {
cin >> x;
ask(1);
cout << ans << endl;
}
}
return 0;
}
題目描述 Description
給你N個數,有兩種操作:
1:給區間[a,b]的所有數增加X
2:詢問區間[a,b]的數的和。
輸入描述 Input Description
第一行一個正整數n,接下來n行n個整數,
再接下來一個正整數Q,每行表示操作的個數,
如果第一個數是1,後接3個正整數,
表示在區間[a,b]內每個數增加X,如果是2,
表示操作2詢問區間[a,b]的和是多少。
pascal選手請不要使用readln讀入
輸出描述 Output Description
對於每個詢問輸出一行一個答案
樣例輸入 Sample Input
3
1
2
3
2
1 2 3 2
2 2 3
樣例輸出 Sample Output
9
資料範圍及提示 Data Size & Hint
資料範圍
1<=n<=200000
1<=q<=200000
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
const int maxn = 200010;
int n, m, p, x, a, b;
long long ans;
struct Node {
long long l, r, w, f;
}node[4 * maxn + 10];
void build (int l, int r, int k) {
node[k].l = l;
node[k].r = r;
if (l == r) {
cin >> node[k].w;
return;
}
int mid = (l + r) / 2;
build(l, mid, k * 2);
build(mid + 1, r, k * 2 + 1);
node[k].w = node[k * 2].w + node[k * 2 + 1].w;
}
void down(int k) {
node[2 * k].f += node[k].f;
node[2 * k + 1].f += node[k].f;
node[2 * k].w += (node[2 * k].r - node[2 * k].l + 1) * node[k].f;
node[2 * k + 1].w += (node[2 * k + 1].r - node[2 * k + 1].l + 1) * node[k].f;
node[k].f = 0;
}
void add(int k) {
if (node[k].l >= a && b >= node[k].r) {
node[k].w += (node[k].r - node[k].l + 1) * x;
node[k].f += x;
return;
}
if (node[k].f) down(k);
int mid = (node[k].l + node[k].r) / 2;
if (a <= mid) {
add(k * 2);
}
if (b > mid) {
add(k * 2 + 1);
}
node[k].w = node[k * 2].w + node[k * 2 + 1].w;
}
void sum(int k) {
if (node[k].l >= a && node[k].r <= b) {
ans += node[k].w;
return;
}
if (node[k].f) down(k);
int mid = (node[k].l + node[k].r) / 2;
if (a <= mid) {
sum(k * 2);
}
if (b > mid) {
sum(k * 2 + 1);
}
}
int main() {
cin >> n;
build(1, n, 1);
cin >> m;
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
cin >> p;
ans = 0;
if (p == 1) {
cin >> a >> b >> x;
add(1);
} else {
cin >> a >> b;
sum(1);
cout << ans << endl;
}
}
return 0;
}
總結:其實這類的模板題寫多了就熟練了,可以進行更近一步的題目的針對訓練了,題目來源自洛古語codevs,有興趣的可以登入這倆個平臺然後將這幾個題做一做