sklearn中SVM簡單使用
阿新 • • 發佈:2018-12-30
在看周志華老師的機器學習書時,利用sklearn中的SVM解決第六章的一些課後習題。
*************************************************************************************************************
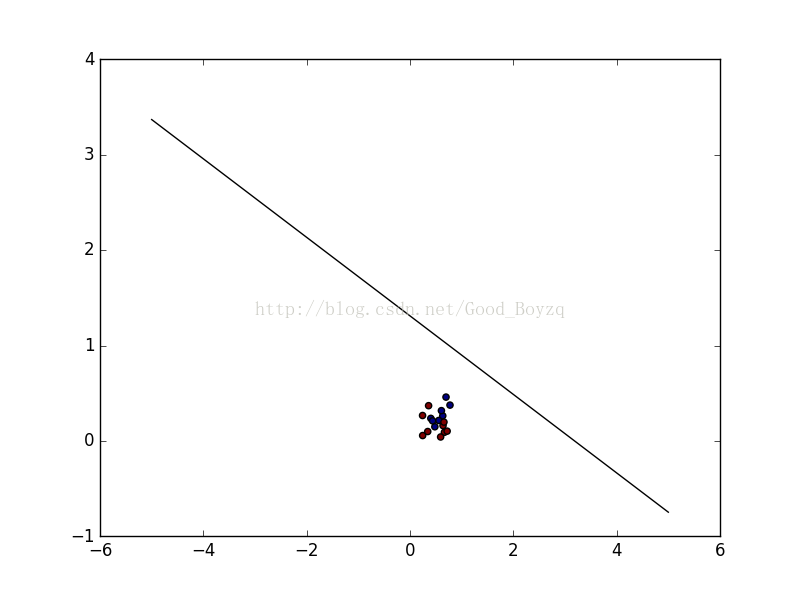
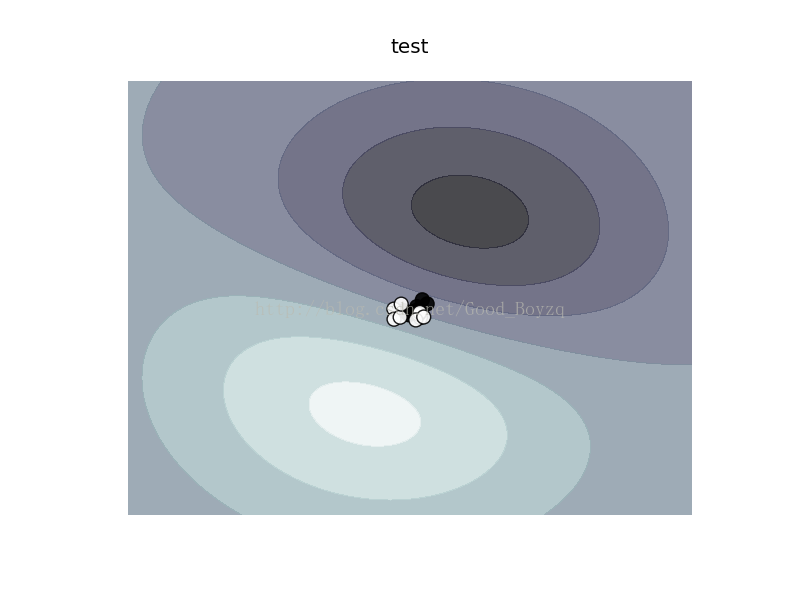
1、在西瓜資料集3.0alpha上分別用線性和高斯核訓練一個SVM,並比較其支援向量的差別。
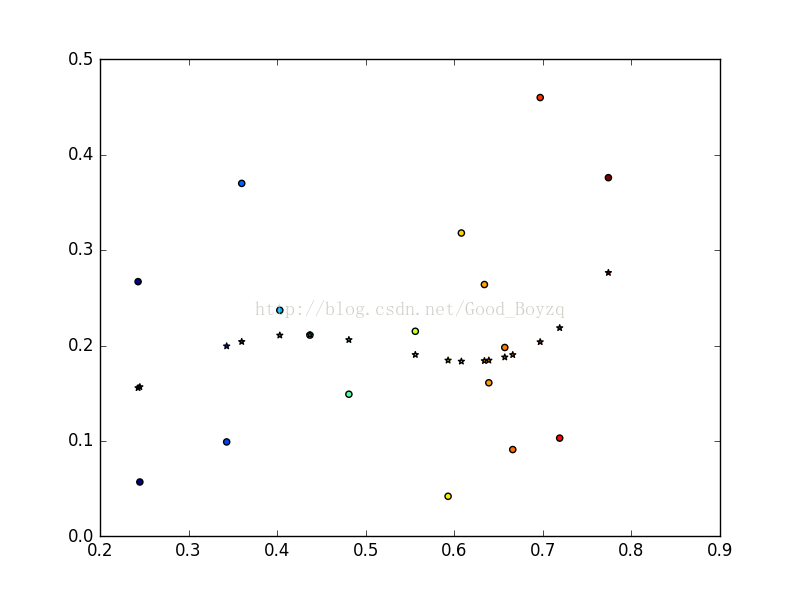
2、以“密度”為輸入,“含糖量”為輸出,訓練一個SVR。
資料如下:
程式碼:編號 密度 含糖率 好瓜 1 0.697 0.46 是 2 0.774 0.376 是 3 0.634 0.264 是 4 0.608 0.318 是 5 0.556 0.215 是 6 0.403 0.237 是 7 0.481 0.149 是 8 0.437 0.211 是 9 0.666 0.091 否 10 0.243 0.267 否 11 0.245 0.057 否 12 0.343 0.099 否 13 0.639 0.161 否 14 0.657 0.198 否 15 0.36 0.37 否 16 0.593 0.042 否 17 0.719 0.103 否
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*- """ Created on Thu Dec 29 21:14:16 2016 @author: ZQ """ import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from sklearn.svm import SVC from sklearn.svm import SVR def plot_decision_function(X,classifier,sample_weight,axis,title): xx,yy = np.meshgrid(np.linspace(-4,5,500),np.linspace(-4,5,500)) Z = classifier.decision_function(np.c_[xx.ravel(),yy.ravel()]) Z = Z.reshape(xx.shape) axis.contourf(xx,yy,Z,alpha = 0.75,cmap = plt.cm.bone) axis.scatter(X[:,0],X[:,1],c=y,s=100*sample_weight,alpha = 0.9, cmap = plt.cm.bone) axis.axis('off') axis.set_title(title) def loadData(filename): data = [] with open(filename) as f: for line in f.readlines(): data.append(line.strip().split('\t')[1:]) return np.array(data[1:]) def initData(data): m,n = np.shape(data) retDat = np.zeros((m,n)) for i in range(m): for j in range(n): if data[i][j] == '是': retDat[i][j] = 0 elif data[i][j] == '否': retDat[i][j] = 1 else: retDat[i][j] = float(data[i][j]) return retDat if __name__ == '__main__': data = loadData('watermelon3.0Alpha.txt') num_data = initData(data) x = num_data[:,:2] y = num_data[:,-1] """ #線性畫圖 lclf = SVC(C = 1.0,gamma=0.1,kernel='linear') bclf = SVC(C = 1.0,gamma = 0.1) plt.scatter(x[:,0],x[:,1],c = y) xx = np.linspace(-5,5) lclf.fit(x,y) lw = lclf.coef_[0] la = -lw[0]/lw[1] ly = la*xx - lclf.intercept_[0]/lw[1] h0 = plt.plot(xx,ly,'k-',label = 'linear') """ """ #高斯畫圖 bclf.fit(x,y) weight = np.ones(len(x)) fig,axis = plt.subplots(1,1) plot_decision_function(x,bclf,weight,axis,'test') """ #訓練的SVR
svr_rbf = SVR(kernel = 'rbf',C = 1e3,gamma = 3)
X = x[:,0].reshape((17,1))
y = x[:,1].reshape((17,1))
y_rbf = svr_rbf.fit(X,y.ravel()).predict(X)
plt.scatter(x[:,0],x[:,1],c = x[:,0])
plt.scatter(x[:,0],y_rbf,c = x[:,0],marker = '*')
plt.show()結果如下:
對於線性和高斯核的SVC的支援向量都是相同的,如下:
更為直觀的畫圖顯示,第一個為線性核,第二個為高斯核。
不知道是程式碼原因還是資料原因導致結果不是很好。希望大家能多多指正。
SVR的結果如下: