Activity啟動流程原始碼分析(應用中)
在移動應用開發中,Android四大元件之一Activity是最常用的。很多介面,如:閃屏、主介面、次功能介面等都需要Activity來作為主要的載體;介面與介面之間,即不同的Activity之間也都存在跳轉切換,弄懂這其中跳轉切換原理,將有助於我們更好的理解Android中Activity之間的互動邏輯,從而更好的開發Android應用。本篇博文將會重點介紹Android應用中的Activity的啟動流程。
在開始介紹之前,我們需要了解一些概念,如:
- ActivityThread: 應用的啟動入口類,當應用啟動,會首先執行其main方法,開啟主執行緒訊息迴圈機制。
- ApplicationThread:ActivityThread的內部類,主要與系統程序AMS通訊,從而對應用程序的具體Activity操作進行管理。
- Instrumentation: ActivityThread的屬性變數,主要輔助ActivityThread類呼叫Activity的生命週期相關方法。
- ActivityManagerService(AMS): Activity管理系統服務類,主要是對所有的Activity進行管理。
- ActivityStack: Activity任務棧,AMS的屬性變數,AMS中Activtiy的實際管理者。
一、Activity啟動流程
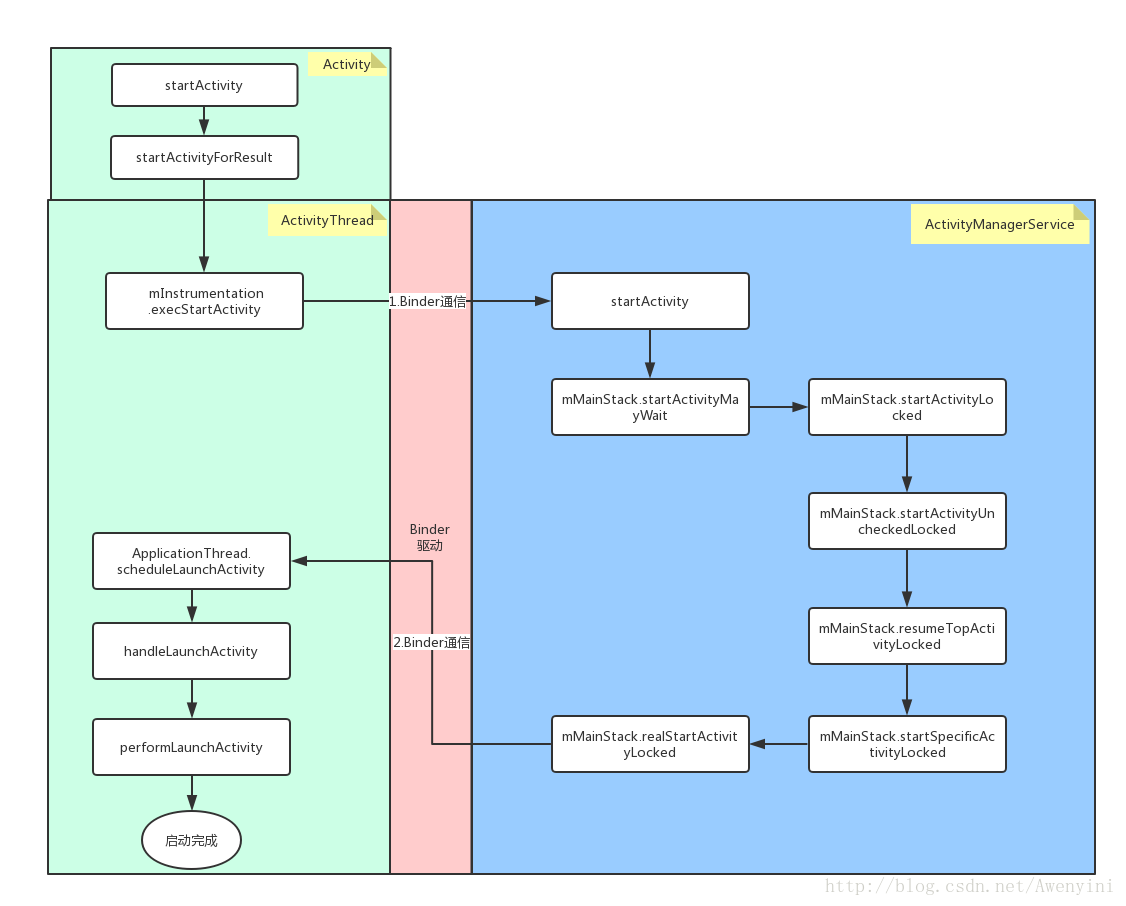
Activity啟動流程圖:
此流程圖,主要是根據Android原始碼中程式碼執行順序來梳理的。淺綠色部分為應用程序,淺藍色部分為系統服務程序,兩個程序間通過Binder驅動來進行通訊,第一次Binder通訊主要的類有:ActivityManagerService(AMS),ActivityManagerNative(AMN),ActivityManagerProxy(AMP);第二次Binder通訊主要的類有:ApplicationThread(AT),ApplicationThreadNative(ATN),ApplicationThreadProxy(ATP)。
二、Activity啟動流程原始碼分析
根據上面流程圖,下面讓我們一起來看看原始碼,首先從Activity的startActivity開始:
@Override
public void startActivity(Intent intent) {
startActivity(intent, null);
}
@Override
public void startActivity(Intent intent, Bundle options) {
if (options != null) {
startActivityForResult(intent, -1 在Activity原始碼中,startActivity之後都會呼叫startActivityForResult;在註釋1處,當mParent為空時,會直接呼叫Instrumentation中的execStartActivity方法,當mParent不為空時,呼叫mParent.startActivityFromChild方法。通過跟蹤查詢發現,mParent也是Activity,在Activity attach的時候會初始化,從ActivityRecord中獲得值。我們繼續來看看startActivityFromChild方法
public void startActivityFromChild(Activity child, Intent intent,
int requestCode) {
startActivityFromChild(child, intent, requestCode, null);
}
public void startActivityFromChild(Activity child, Intent intent,
int requestCode, Bundle options) {
Instrumentation.ActivityResult ar =
mInstrumentation.execStartActivity(
this, mMainThread.getApplicationThread(), mToken, child,
intent, requestCode, options);
if (ar != null) {
mMainThread.sendActivityResult(
mToken, child.mEmbeddedID, requestCode,
ar.getResultCode(), ar.getResultData());
}
}由此發現,startActivityForResult之後都呼叫了Instrumentation中的execStartActivity方法。我們繼續來看看execStartActivity方法:
public ActivityResult execStartActivity(
Context who, IBinder contextThread, IBinder token, Activity target,
Intent intent, int requestCode, Bundle options) {
IApplicationThread whoThread = (IApplicationThread) contextThread;
......
try {
intent.setAllowFds(false);
intent.migrateExtraStreamToClipData();
//核心程式碼
int result = ActivityManagerNative.getDefault()
.startActivity(whoThread, intent,
intent.resolveTypeIfNeeded(who.getContentResolver()),
token, target != null ? target.mEmbeddedID : null,
requestCode, 0, null, null, options);
checkStartActivityResult(result, intent);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
}
return null;
}這裡主要是呼叫了ActivityManagerNative.getDefault()中的startActivity(…)方法,這裡就涉及到Binder的一次跨程序通訊,通過跨程序通訊呼叫了ActivityManagerService中的startActivity方法。具體Binder怎麼跨程序通訊的,我已寫過文章 Android跨程序通訊方式(IPC)解析,想了解的同學,可以點選看看。下面我們繼續來看看AMS中的startActivity方法:
public final int startActivity(IApplicationThread caller,
Intent intent, String resolvedType, IBinder resultTo,
String resultWho, int requestCode, int startFlags,
String profileFile, ParcelFileDescriptor profileFd, Bundle options) {
enforceNotIsolatedCaller("startActivity");
......
return mMainStack.startActivityMayWait(caller, -1, intent, resolvedType,
resultTo, resultWho, requestCode, startFlags, profileFile, profileFd,
null, null, options, userId);
}在AMS的startActivity方法中,又呼叫ActivityStack中的startActivityMayWait()方法,我們再來看看ActivityStack的原始碼:
final int startActivityMayWait(IApplicationThread caller, int callingUid,
Intent intent, String resolvedType, IBinder resultTo,
String resultWho, int requestCode, int startFlags, String profileFile,
ParcelFileDescriptor profileFd, WaitResult outResult, Configuration config,
Bundle options, int userId) {
......
//核心程式碼
int res = startActivityLocked(caller, intent, resolvedType,
aInfo, resultTo, resultWho, requestCode, callingPid, callingUid,
startFlags, options, componentSpecified, null);
......
return res;
}
}我們這裡主要分析啟動流程,所以省略掉部分細節。讓我們繼續看ActivityStack中的startActivityLocked()方法
final int startActivityLocked(IApplicationThread caller,
Intent intent, String resolvedType, ActivityInfo aInfo, IBinder resultTo,
String resultWho, int requestCode,
int callingPid, int callingUid, int startFlags, Bundle options,
boolean componentSpecified, ActivityRecord[] outActivity) {
......
//建立一個新的ActivityRecord
ActivityRecord r = new ActivityRecord(mService, this, callerApp, callingUid,
intent, resolvedType, aInfo, mService.mConfiguration,
resultRecord, resultWho, requestCode, componentSpecified);
......
err = startActivityUncheckedLocked(r, sourceRecord,
startFlags, true, options);
......
return err;
}同上,也省略的部分細節。我們繼續
final int startActivityUncheckedLocked(ActivityRecord r,
ActivityRecord sourceRecord, int startFlags, boolean doResume,
Bundle options) {
......
if (sourceRecord == null) {
if ((launchFlags&Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_NEW_TASK) == 0) {
launchFlags |= Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_NEW_TASK;
}
} else if (sourceRecord.launchMode == ActivityInfo.LAUNCH_SINGLE_INSTANCE) {
launchFlags |= Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_NEW_TASK;
} else if (r.launchMode == ActivityInfo.LAUNCH_SINGLE_INSTANCE
|| r.launchMode == ActivityInfo.LAUNCH_SINGLE_TASK) {
launchFlags |= Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_NEW_TASK;
}
......//省略程式碼:Activity四種啟動模式standard,singleTop,singleTask,singleInstance的判斷
if (sourceRecord != null) {
.......
if (!addingToTask &&(launchFlags&Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_REORDER_TO_FRONT) != 0) {
// In this case, we are launching an activity in our own task
// that may already be running somewhere in the history, and
// we want to shuffle it to the front of the stack if so.
int where = findActivityInHistoryLocked(r, sourceRecord.task.taskId);
if (where >= 0) {
ActivityRecord top = moveActivityToFrontLocked(where);
logStartActivity(EventLogTags.AM_NEW_INTENT, r, top.task);
top.updateOptionsLocked(options);
top.deliverNewIntentLocked(callingUid, r.intent);
if (doResume) {
resumeTopActivityLocked(null);//核心程式碼
}
return ActivityManager.START_DELIVERED_TO_TOP;
}
}
// An existing activity is starting this new activity, so we want
// to keep the new one in the same task as the one that is starting
// it.
r.setTask(sourceRecord.task, sourceRecord.thumbHolder, false);
if (DEBUG_TASKS) Slog.v(TAG, "Starting new activity " + r
+ " in existing task " + r.task);
} else {
......
}
......
return ActivityManager.START_SUCCESS;
}
在startActivityUncheckedLocked()方法中,主要針對Activity的啟動模式進行了檢測判斷,從而啟動Activity。我們知道,Activity有四種啟動模式,分別為standard,singleTop,singleTask和singleInstance,但這裡我們主要是分析Activity的啟動流程,所以具體啟動模式的判斷邏輯細節,這裡就不展開分析了。我們主要來看一下,把Activity啟動放到棧頂的方法resumeTopActivityLocked()
final boolean resumeTopActivityLocked(ActivityRecord prev) {
return resumeTopActivityLocked(prev, null);
}
final boolean resumeTopActivityLocked(ActivityRecord prev, Bundle options) {
//找到一個棧頂的未finish的Activity的ActivityRecord
ActivityRecord next = topRunningActivityLocked(null);
......
if (next == null) {//棧頂無Activity,直接啟動Launcher
if (mMainStack) {
ActivityOptions.abort(options);
return mService.startHomeActivityLocked(0);
}
}
......
//如果Activity所在的程序已經存在
if (next.app != null && next.app.thread != null) {
......
try {
.......
//重新顯示Activity
if (next.newIntents != null) {
next.app.thread.scheduleNewIntent(next.newIntents, next.appToken);
}
EventLog.writeEvent(EventLogTags.AM_RESUME_ACTIVITY,
System.identityHashCode(next),
next.task.taskId, next.shortComponentName);
next.sleeping = false;
showAskCompatModeDialogLocked(next);
next.app.pendingUiClean = true;
//執行Activity onResume方法
next.app.thread.scheduleResumeActivity(next.appToken,
mService.isNextTransitionForward());
checkReadyForSleepLocked();
} catch (Exception e) {
//如果啟動異常,就重啟Activity
if (DEBUG_STATES) Slog.v(TAG, "Resume failed; resetting state to "
+ lastState + ": " + next);
next.state = lastState;
mResumedActivity = lastResumedActivity;
Slog.i(TAG, "Restarting because process died: " + next);
if (!next.hasBeenLaunched) {
next.hasBeenLaunched = true;
} else {
if (SHOW_APP_STARTING_PREVIEW && mMainStack) {
mService.mWindowManager.setAppStartingWindow(
next.appToken, next.packageName, next.theme,
mService.compatibilityInfoForPackageLocked(
next.info.applicationInfo),
next.nonLocalizedLabel,
next.labelRes, next.icon, next.windowFlags,
null, true);
}
}
startSpecificActivityLocked(next, true, false);//核心程式碼,重啟Activity
return true;
}
// From this point on, if something goes wrong there is no way
// to recover the activity.
try {
next.visible = true;
completeResumeLocked(next);
} catch (Exception e) {
// If any exception gets thrown, toss away this
// activity and try the next one.
Slog.w(TAG, "Exception thrown during resume of " + next, e);
requestFinishActivityLocked(next.appToken, Activity.RESULT_CANCELED, null,
"resume-exception");
return true;
}
// Didn't need to use the icicle, and it is now out of date.
if (DEBUG_SAVED_STATE) Slog.i(TAG, "Resumed activity; didn't need icicle of: " + next);
next.icicle = null;
next.haveState = false;
next.stopped = false;
} else {
//Activity所在的程序不存在,啟動Activity
if (!next.hasBeenLaunched) {
next.hasBeenLaunched = true;
} else {
if (SHOW_APP_STARTING_PREVIEW) {
mService.mWindowManager.setAppStartingWindow(
next.appToken, next.packageName, next.theme,
mService.compatibilityInfoForPackageLocked(
next.info.applicationInfo),
next.nonLocalizedLabel,
next.labelRes, next.icon, next.windowFlags,
null, true);
}
if (DEBUG_SWITCH) Slog.v(TAG, "Restarting: " + next);
}
startSpecificActivityLocked(next, true, true);//啟動Activity
}
return true;
}通過上面註釋中的分析,在判斷Activity程序之後,就會通過startSpecificActivityLocked()方法來啟動Activity,我們繼續看
private final void startSpecificActivityLocked(ActivityRecord r,
boolean andResume, boolean checkConfig) {
// Is this activity's application already running?
ProcessRecord app = mService.getProcessRecordLocked(r.processName,
r.info.applicationInfo.uid);
if (r.launchTime == 0) {
r.launchTime = SystemClock.uptimeMillis();
if (mInitialStartTime == 0) {
mInitialStartTime = r.launchTime;
}
} else if (mInitialStartTime == 0) {
mInitialStartTime = SystemClock.uptimeMillis();
}
if (app != null && app.thread != null) {//Activity所在程序判斷,程序存在時,直接啟動Activity
try {
app.addPackage(r.info.packageName);
realStartActivityLocked(r, app, andResume, checkConfig);//核心程式碼
return;
} catch (RemoteException e) {
Slog.w(TAG, "Exception when starting activity "
+ r.intent.getComponent().flattenToShortString(), e);
}
// If a dead object exception was thrown -- fall through to
// restart the application.
}
mService.startProcessLocked(r.processName, r.info.applicationInfo, true, 0,
"activity", r.intent.getComponent(), false, false);
}在startSpecificActivityLocked()方法中也對Activity的程序是否存在做了判斷,當程序存在時直接呼叫realStartActivityLocked()方法啟動Activity;當Activity的程序不存在時,就會呼叫AMS的startProcessLocked()方法建立程序,這裡其實是Activity的另一種啟動流程,從Laucher啟動,只有從Launcher啟動才會沒有程序,這裡先不做深度分析,後續我們針對Activity的Launcher啟動再寫一篇博文。下面讓我們繼續看realStartActivityLocked()方法:
final boolean realStartActivityLocked(ActivityRecord r,
ProcessRecord app, boolean andResume, boolean checkConfig)
throws RemoteException {
.......
app.thread.scheduleLaunchActivity(new Intent(r.intent), r.appToken,
System.identityHashCode(r), r.info,
new Configuration(mService.mConfiguration),
r.compat, r.icicle, results, newIntents, !andResume,
mService.isNextTransitionForward(), profileFile, profileFd,
profileAutoStop);
......
return true;
}這裡主要通過呼叫app.thread.scheduleLaunchActivity(…)方法實現了跨程序通訊,這裡主要實現了流程圖中的第二次Binder跨程序通訊。通過Binder跨程序通訊呼叫了ApplicationThread中的scheduleLaunchActivity(…)方法,具體Binder怎麼跨程序通訊的,我已寫過文章 Android跨程序通訊方式(IPC)解析,想了解的同學,可以點選看看。下面我們繼續來看看ApplicationThread中的scheduleLaunchActivity方法:
public final void scheduleLaunchActivity(Intent intent, IBinder token, int ident,
ActivityInfo info, Configuration curConfig, CompatibilityInfo compatInfo,
Bundle state, List<ResultInfo> pendingResults,
List<Intent> pendingNewIntents, boolean notResumed, boolean isForward,
String profileName, ParcelFileDescriptor profileFd, boolean autoStopProfiler) {
ActivityClientRecord r = new ActivityClientRecord();
......
queueOrSendMessage(H.LAUNCH_ACTIVITY, r);
}
public void handleMessage(Message msg) {
if (DEBUG_MESSAGES) Slog.v(TAG, ">>> handling: " + codeToString(msg.what));
switch (msg.what) {
case LAUNCH_ACTIVITY: {
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER, "activityStart");
ActivityClientRecord r = (ActivityClientRecord)msg.obj;
r.packageInfo = getPackageInfoNoCheck(
r.activityInfo.applicationInfo, r.compatInfo);
handleLaunchActivity(r, null);//核心程式碼
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER);
} break;
.......
}
}由上易知,通過Handler訊息迴圈機制,從而執行handleLaunchActivity()方法,我們繼續來看此方法
private void handleLaunchActivity(ActivityClientRecord r, Intent customIntent) {
.......
Activity a = performLaunchActivity(r, customIntent);
......
}
private Activity performLaunchActivity(ActivityClientRecord r, Intent customIntent) {
// System.out.println("##### [" + System.currentTimeMillis() + "] ActivityThread.performLaunchActivity(" + r + ")");
ActivityInfo aInfo = r.activityInfo;
if (r.packageInfo == null) {
r.packageInfo = getPackageInfo(aInfo.applicationInfo, r.compatInfo,
Context.CONTEXT_INCLUDE_CODE);
}
ComponentName component = r.intent.getComponent();
if (component == null) {
component = r.intent.resolveActivity(
mInitialApplication.getPackageManager());
r.intent.setComponent(component);
}
if (r.activityInfo.targetActivity != null) {
component = new ComponentName(r.activityInfo.packageName,
r.activityInfo.targetActivity);
}
Activity activity = null;
try {
//1.核心程式碼
java.lang.ClassLoader cl = r.packageInfo.getClassLoader();
activity = mInstrumentation.newActivity(
cl, component.getClassName(), r.intent);
StrictMode.incrementExpectedActivityCount(activity.getClass());
r.intent.setExtrasClassLoader(cl);
if (r.state != null) {
r.state.setClassLoader(cl);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
if (!mInstrumentation.onException(activity, e)) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"Unable to instantiate activity " + component
+ ": " + e.toString(), e);
}
}
try {
Application app = r.packageInfo.makeApplication(false, mInstrumentation);
if (localLOGV) Slog.v(TAG, "Performing launch of " + r);
if (localLOGV) Slog.v(
TAG, r + ": app=" + app
+ ", appName=" + app.getPackageName()
+ ", pkg=" + r.packageInfo.getPackageName()
+ ", comp=" + r.intent.getComponent().toShortString()
+ ", dir=" + r.packageInfo.getAppDir());
if (activity != null) {
ContextImpl appContext = new ContextImpl();
appContext.init(r.packageInfo, r.token, this);
appContext.setOuterContext(activity);
CharSequence title = r.activityInfo.loadLabel(appContext.getPackageManager());
Configuration config = new Configuration(mCompatConfiguration);
if (DEBUG_CONFIGURATION) Slog.v(TAG, "Launching activity "
+ r.activityInfo.name + " with config " + config);
//2.核心程式碼
activity.attach(appContext, this, getInstrumentation(), r.token,
r.ident, app, r.intent, r.activityInfo, title, r.parent,
r.embeddedID, r.lastNonConfigurationInstances, config);
if (customIntent != null) {
activity.mIntent = customIntent;
}
r.lastNonConfigurationInstances = null;
activity.mStartedActivity = false;
int theme = r.activityInfo.getThemeResource();
if (theme != 0) {
activity.setTheme(theme);
}
activity.mCalled = false;
//3.核心程式碼
mInstrumentation.callActivityOnCreate(activity, r.state);
if (!activity.mCalled) {
throw new SuperNotCalledException(
"Activity " + r.intent.getComponent().toShortString() +
" did not call through to super.onCreate()");
}
r.activity = activity;
r.stopped = true;
if (!r.activity.mFinished) {
activity.performStart();
r.stopped = false;
}
if (!r.activity.mFinished) {
if (r.state != null) {
mInstrumentation.callActivityOnRestoreInstanceState(activity, r.state);
}
}
if (!r.activity.mFinished) {
activity.mCalled = false;
mInstrumentation.callActivityOnPostCreate(activity, r.state);
if (!activity.mCalled) {
throw new SuperNotCalledException(
"Activity " + r.intent.getComponent().toShortString() +
" did not call through to super.onPostCreate()");
}
}
}
r.paused = true;
mActivities.put(r.token, r);
} catch (SuperNotCalledException e) {
throw e;
} catch (Exception e) {
if (!mInstrumentation.onException(activity, e)) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"Unable to start activity " + component
+ ": " + e.toString(), e);
}
}
return activity;
}註釋1處,通過mInstrumentation.newActivity()方法對Activity進行初始化
public Activity newActivity(ClassLoader cl, String className,
Intent intent)
throws InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException,
ClassNotFoundException {
return (Activity)cl.loadClass(className).newInstance();
}由上我們知道,主要通過反射機制實現Activity的初始化。再來看註釋2,呼叫了Activity.attach(…)方法
final void attach(Context context, ActivityThread aThread, Instrumentation instr, IBinder token,
Application application, Intent intent, ActivityInfo info, CharSequence title,
Activity parent, String id, NonConfigurationInstances lastNonConfigurationInstances,
Configuration config) {
attach(context, aThread, instr, token, 0, application, intent, info, title, parent, id,
lastNonConfigurationInstances, config);
}
final void attach(Context context, ActivityThread aThread,
Instrumentation instr, IBinder token, int ident,
Application application, Intent intent, ActivityInfo info,
CharSequence title, Activity parent, String id,
NonConfigurationInstances lastNonConfigurationInstances,
Configuration config) {
attachBaseContext(context);
mFragments.attachActivity(this);
mWindow = PolicyManager.makeNewWindow(this);
mWindow.setCallback(this);
mWindow.getLayoutInflater().setPrivateFactory(this);
if (info.softInputMode != WindowManager.LayoutParams.SOFT_INPUT_STATE_UNSPECIFIED) {
mWindow.setSoftInputMode(info.softInputMode);
}
if (info.uiOptions != 0) {
mWindow.setUiOptions(info.uiOptions);
}
mUiThread = Thread.currentThread();
mMainThread = aThread;
mInstrumentation = instr;
mToken = token;
mIdent = ident;
mApplication = application;
mIntent = intent;
mComponent = intent.getComponent();
mActivityInfo = info;
mTitle = title;
mParent = parent;
mEmbeddedID = id;
mLastNonConfigurationInstances = lastNonConfigurationInstances;
mWindow.setWindowManager(null, mToken, mComponent.flattenToString(),
(info.flags & ActivityInfo.FLAG_HARDWARE_ACCELERATED) != 0);
if (mParent != null) {
mWindow.setContainer(mParent.getWindow());
}
mWindowManager = mWindow.getWindowManager();
mCurrentConfig = config;
}此方法主要就是對Activity進行了初始化,初始化了許多的屬性,具體如上。我們再看註釋3,方法mInstrumentation.callActivityOnCreate(activity, r.state),我們也來看看原始碼
public void callActivityOnCreate(Activity activity, Bundle icicle) {
if (mWaitingActivities != null) {
synchronized (mSync) {
final int N = mWaitingActivities.size();
for (int i=0; i<N; i++) {
final ActivityWaiter aw = mWaitingActivities.get(i);
final Intent intent = aw.intent;
if (intent.filterEquals(activity.getIntent())) {
aw.activity = activity;
mMessageQueue.addIdleHandler(new ActivityGoing(aw));
}
}
}
}
activity.performCreate(icicle);//核心程式碼
if (mActivityMonitors != null) {
synchronized (mSync) {
final int N = mActivityMonitors.size();
for (int i=0; i<N; i++) {
final ActivityMonitor am = mActivityMonitors.get(i);
am.match(activity, activity, activity.getIntent());
}
}
}
}其實,主要也就是呼叫了Activity的OnCreate()方法,我們繼續來看看
final void performCreate(Bundle icicle) {
onCreate(icicle);
mVisibleFromClient = !mWindow.getWindowStyle().getBoolean(
com.android.internal.R.styleable.Window_windowNoDisplay, false);
mFragments.dispatchActivityCreated();
}的確如此,最後呼叫了Activity的OnCreate方法,從而就啟動了Activity。好了,到這裡,Activity的啟動流程就說完了。
注:原始碼採用android-4.1.1_r1版本,建議下載原始碼然後自己走一遍流程,這樣更能加深理解。