二叉排序樹SDUT
阿新 • • 發佈:2018-12-31
SDUT題目連結二叉排序樹
做這道題的時候WA了好多遍,在網上找到了一些思路,在此和我的思路進行對比。

九度提供的演算法設計思路是:對輸入的數字序列構建二叉排序樹,並對它們進行前序和中序的遍歷,依次比較遍歷結果是否相同,若相同則說明兩棵二叉排序樹相同,否則不同。
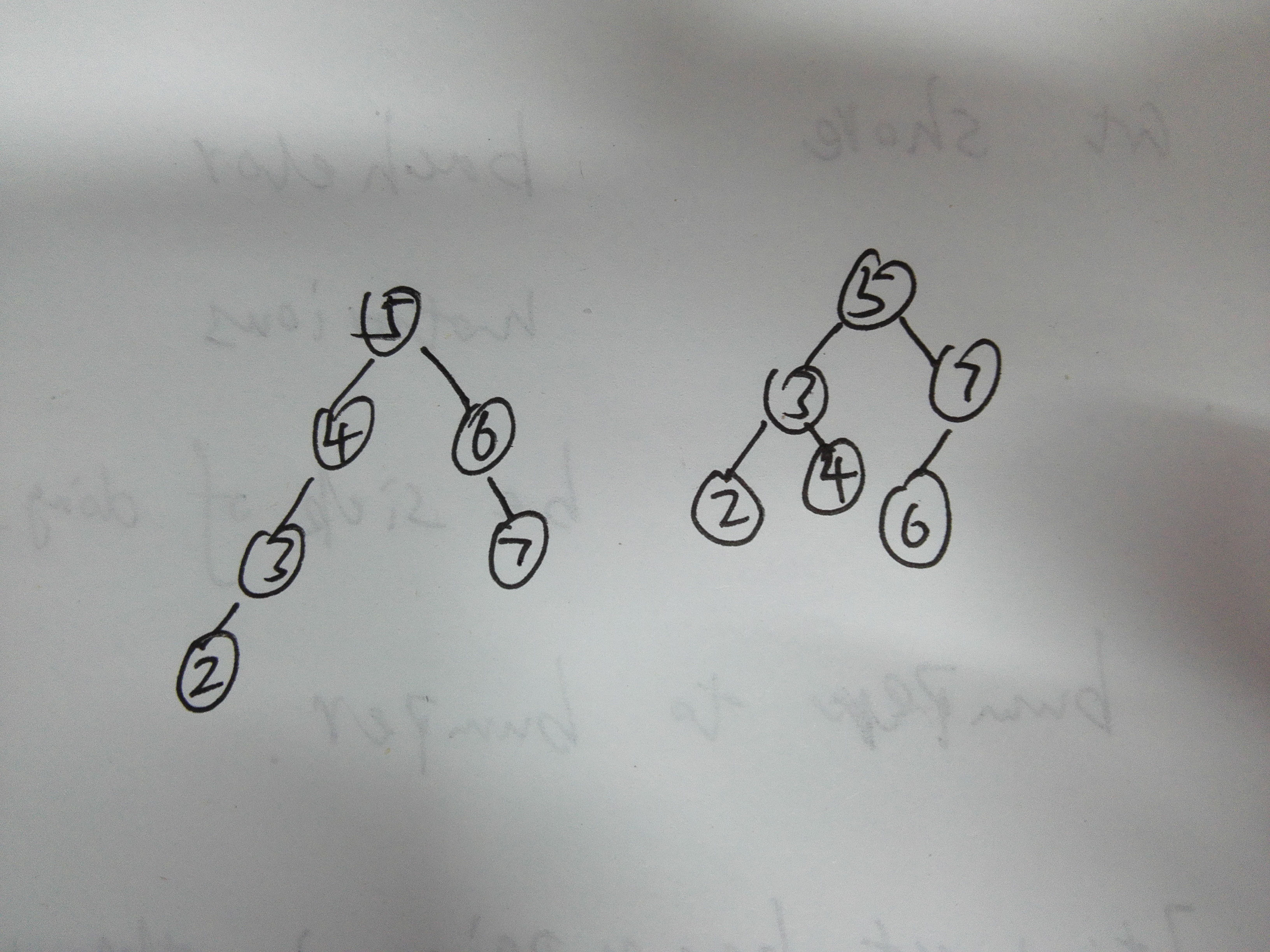
這個設計思路是沒有問題的,但是有點畫蛇添足的成份。那麼這個“蛇足”是什麼呢?試想一下二叉排序樹的性質,如果對二叉排序樹來說,對其進行中序遍歷,那麼無論一組數字按照怎樣的順序構建,其中序遍歷後得到的序列都是一樣的。例如題目給的測試例項,{5,6,7,4,3,2}和{5,7,6,3,4,2},他們構造的二叉排序樹如下:
其中序遍歷得到序列都是{2,3,4,5,6,7}。所以說進行中序遍歷作為判斷的一項是“蛇足”。
對於該題,我們只須對建立的二叉樹進行先序遍歷,或者後序遍歷得到它們的遍歷序列進行比較即可。
//preMain儲存原二叉樹先序遍歷的序列
//preOther儲存與原二叉樹比較的二叉樹的先序遍歷的序列
char preMain[11], preOther[11];
struct BSTNode{
int value;
BSTNode *lchild;
BSTNode *rchild;
};
BSTNode* allocateNode()
{
if (BSTNode * 以上內容轉載於https://www.cnblogs.com/tgycoder/p/4974497.html
下面是我A的程式碼
具體思路:1.先對第一個序列建樹。
2.對所需要比較的序列建樹。
3.然後比較兩者的樹。
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
struct tree
{
char data;
struct tree *l,*r;
};
char a[20],b[20];
struct tree *creat(struct tree *root,char key)
{
if(root==NULL)
{
root=(struct tree *)malloc(sizeof(struct tree ));
root->data=key;
root->l=NULL;
root->r=NULL;
return root;
}
if(key>root->data)
root->r=creat(root->r,key);
else
root->l=creat(root->l,key);
return root;
}
int cmp(struct tree *root1,struct tree *root2)
{
if(root1==NULL&&root2==NULL) **//如果比較到最後一個,則可以滿足條件**
return 1;
else if(root1!=NULL&&root2!=NULL)
{
if(root1->data!=root2->data)
{
return 0;
}
else if(cmp(root1->l,root2->l)&&cmp(root1->r,root2->r))
return 1;
}
else **//這個else指的是當其中一個為空時,即兩者長度不一樣,返回值當然也是0**
return 0;
} **//下面還有另一種比較函式的寫法,思路也是一樣的,只不過換了一種形式**
int main()
{
int t,n,m,i;
struct tree *root1,*root2;
while(~scanf("%d",&t))
{
if(t==0)
break;
scanf("%s",a);
n=strlen(a);
root1=NULL;
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
{
root1=creat(root1,a[i]);
}
while(t--)
{
root2=NULL;
scanf("%s",b);
m=strlen(b);
for(i=0;i<m;i++)
{
root2=creat(root2,b[i]);
}
if(cmp(root1,root2)==1)
printf("YES\n");
else
printf("NO\n");
}
}
return 0;
}
這是另外一種比較函式的形式,相比上面那個更精簡一點,也易懂。
int cmp(struct tree *root1,struct tree *root2)
{
if(root1==NULL&&root2==NULL)
return 1;
else if(root1==NULL||root2==NULL)
return 0;
else if(root1->data!=root2->data)
return 0;
else if(cmp(root1->l,root2->l)&&cmp(root1->r,root2->r))
return 1;
}