spring 框架中的依賴注入(IOC--設值注入)---使用xml簡單配置檔案---的具體例項的簡單實現
阿新 • • 發佈:2019-01-01
體現了具體專案工程裡面的分層,dao,daoImpl,service,serviceImpl,action。讓你真正的理解這為啥分層。
畢竟當年我剛剛畢業的時候,再找工作我就不是很清楚為什麼有這麼幾層。
只是知道,昂!就是有這麼幾層。不就是邏輯清楚些嘛。
這回答只是皮毛的皮毛而已!!!
哎,好傻。畢竟我不是Java專業的,雖然也是計算機專業的學生。
到新公司的時候,發現serviceImpl和daoImpl直接沒有啦,很簡單就是controler,service,Repository。
原來這些東西都是和註解掛鉤的。
要真正理解這些個東西,就得了解下spring的配置檔案,是如何去注入bean的,各個不同的註解,都是幹嘛的。
當然這個例子就是使用xml配置檔案,實現設值依賴注入。暫時不牽扯到註解的使用。
分幾個檔案,如下:
先是各個元件,dao,daoImpl,service,serviceImpl,action。
1.PersonDao
package lxk.test.spring.mvc;
interface PersonDao {
void savePerson();
void updatePerson();
}
3.PersonServicepackage lxk.test.spring.mvc; public class PersonDaoImpl implements PersonDao { public void savePerson() { System.out.println("save person"); } public void updatePerson() { System.out.println("update person"); } }
package lxk.test.spring.mvc;
/**
* Access can be package-private 所以可以省略介面的public宣告
*/
interface PersonService {
//介面內部預設都是public的
void savePerson();
void updatePerson();
}
5.PersonActionpackage lxk.test.spring.mvc; public class PersonServiceImpl implements PersonService { private PersonDao personDao; public PersonDao getPersonDao() { return personDao; } public void setPersonDao(PersonDao personDao) { this.personDao = personDao; } public void savePerson() { this.personDao.savePerson(); } public void updatePerson() { this.personDao.updatePerson(); } }
package lxk.test.spring.mvc;
public class PersonAction {
private PersonService personService;
public PersonService getPersonService() {
return personService;
}
public void setPersonService(PersonService personService) {
this.personService = personService;
}
public void savePerson() {
this.personService.savePerson();
}
public void updatePerson() {
this.personService.updatePerson();
}
}
然後是main方法和xml配置檔案
6.main
package lxk.test.spring.mvc;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.FileSystemXmlApplicationContext;
public class MainTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("file:E:/xxx/intellij_work/TrunkNew/src/main/java/lxk/test/spring/mvc/applicationContext.xml");
//ApplicationContext context = new FileSystemXmlApplicationContext("file:E:/xxx/intellij_work/TrunkNew/src/main/java/lxk/test/spring/mvc/applicationContext.xml");
ApplicationContext context = new FileSystemXmlApplicationContext("src/main/java/lxk/test/spring/mvc/applicationContext.xml");
PersonAction personAction = (PersonAction) context.getBean("personAction");
personAction.updatePerson();
}
}
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-2.5.xsd">
<!--
將如下的三個bean納入到spring容器管理,
(實際注入的是各個介面的實現類,畢竟 只有實現類才真正實現具體方法(雖然在bean中看起來是介面形式宣告的屬性))
personAction
personServiceImpl (面向介面程式設計:所以簡寫為介面名稱)
personDaoImpl (面向介面程式設計:所以簡寫為介面名稱)
-->
<bean id="personDao" class="lxk.test.spring.mvc.PersonDaoImpl"/>
<bean id="personService" class="lxk.test.spring.mvc.PersonServiceImpl">
<property name="personDao" ref="personDao"/>
</bean>
<bean id="personAction" class="lxk.test.spring.mvc.PersonAction">
<property name="personService" ref="personService"/>
</bean>
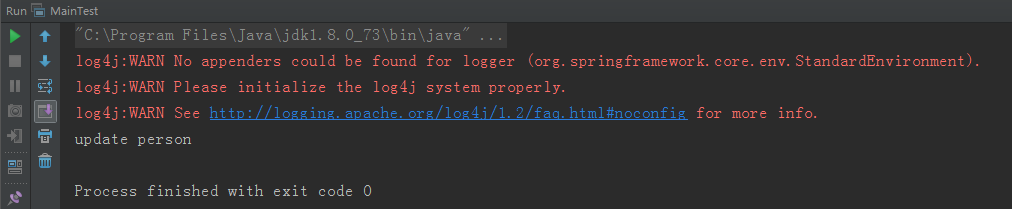
</beans>然後就是執行結果圖:
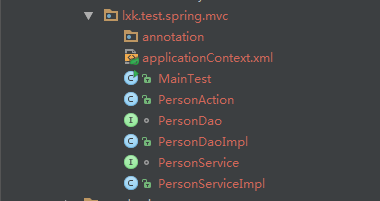
檔案的位置圖:
最後就是對上面的程式碼做一些說明:
因為要用到依賴注入---DI(IOC---控制反轉)的設值注入模式,所以,
要使用的三個bean在對應的檔案裡面都有對應的setter和getter,這是容器在設值注入的時候需要使用的,
在下次使用註解來注入的時候,這些getter和setter都可以省略了,程式碼看起來也就簡潔多啦。
而且,配置檔案中也不需要配置那麼多的bean啦,一個掃描搞定。這種注入也是實際開發使用的。當然還會多一點點的引入檔案