TensorFlow 實現多層 LSTM 的 MNIST 分類 + 視覺化
阿新 • • 發佈:2019-01-02
前言
迴圈神經網路(recurrent neural networks, RNNs)及其改進演算法長短期記憶網路(Long Short-Term Memory, LSTM)能夠很好地對時序資料進行建模,其的相關基礎不進行介紹,需要了解可以參考以下文章:
Understanding LSTM Networks
RNN快速入門
YJango的迴圈神經網路——實現LSTM
莫煩 PYTHON:什麼是迴圈神經網路 RNN
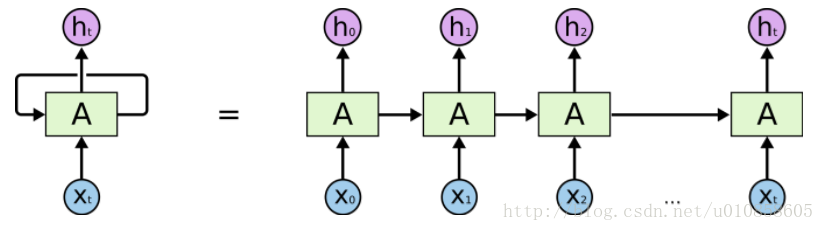
RNNs 展開示意圖:
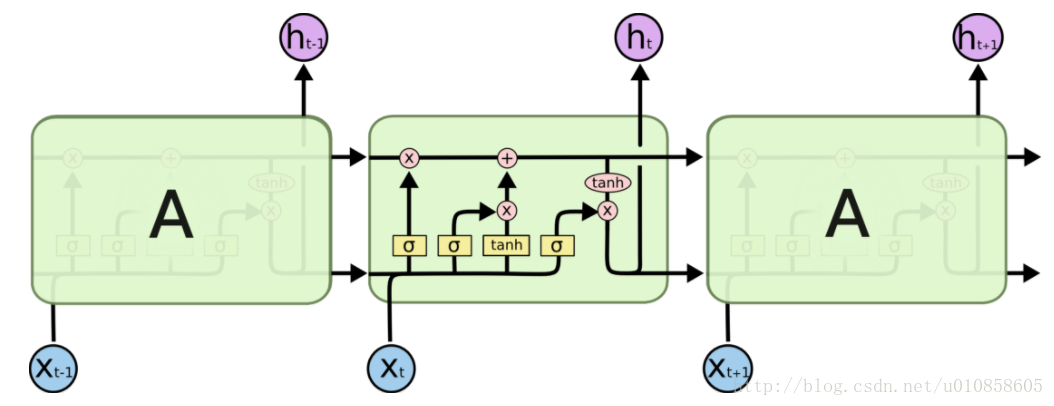
LSTM 結構示意圖:
TensorFlow 實現
採用兩層的 LSTM 實現對 MNIST 手寫數字進行分類,並對訓練過程中的誤差和準確率進行 tensorboard 的視覺化。
1. 初始化引數
這裡 mnist 影象尺寸是 28*28 的,可以看作時序長度 28(影象的寬),輸入為 28(影象的高)
# Hyper Parameters
learning_rate = 0.01 # 學習率
n_steps = 28 # LSTM 展開步數(時序持續長度)
n_inputs = 28 # 輸入節點數
n_hiddens = 64 # 隱層節點數
n_layers = 2 # LSTM layer 層數
n_classes = 10 # 輸出節點數(分類數目) 2. 定義輸入輸出的 placeholder
# tensor placeholder
with tf.name_scope('inputs'):
x = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, n_steps * n_inputs], name='x_input') # 輸入
y = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, n_classes], name='y_input') # 輸出
keep_prob = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, name='keep_prob_input' 3. 定義網路的權重和偏置
# weights and biases
with tf.name_scope('weights'):
Weights = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([n_hiddens, n_classes],stddev=0.1), dtype=tf.float32, name='W')
tf.summary.histogram('output_layer_weights', Weights)
with tf.name_scope('biases'):
biases = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([n_classes]), name='b')
tf.summary.histogram('output_layer_biases', biases)4. RNN 網路結構
# RNN structure
def RNN_LSTM(x, Weights, biases):
# RNN 輸入 reshape
x = tf.reshape(x, [-1, n_steps, n_inputs])
# 定義 LSTM cell
# cell 中的 dropout
def attn_cell():
lstm_cell = tf.contrib.rnn.BasicLSTMCell(n_hiddens)
with tf.name_scope('lstm_dropout'):
return tf.contrib.rnn.DropoutWrapper(lstm_cell, output_keep_prob=keep_prob)
# attn_cell = tf.contrib.rnn.DropoutWrapper(lstm_cell, output_keep_prob=keep_prob)
# 實現多層 LSTM
# [attn_cell() for _ in range(n_layers)]
enc_cells = []
for i in range(0, n_layers):
enc_cells.append(attn_cell())
with tf.name_scope('lstm_cells_layers'):
mlstm_cell = tf.contrib.rnn.MultiRNNCell(enc_cells, state_is_tuple=True)
# 全零初始化 state
_init_state = mlstm_cell.zero_state(batch_size, dtype=tf.float32)
# dynamic_rnn 執行網路
outputs, states = tf.nn.dynamic_rnn(mlstm_cell, x, initial_state=_init_state, dtype=tf.float32, time_major=False)
# 輸出
#return tf.matmul(outputs[:,-1,:], Weights) + biases
return tf.nn.softmax(tf.matmul(outputs[:,-1,:], Weights) + biases)5. 損失函式和優化器
with tf.name_scope('output_layer'):
pred = RNN_LSTM(x, Weights, biases)
tf.summary.histogram('outputs', pred)
# cost
with tf.name_scope('loss'):
#cost = tf.reduce_mean(tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits=pred, labels=y))
cost = tf.reduce_mean(-tf.reduce_sum(y * tf.log(pred),reduction_indices=[1]))
tf.summary.scalar('loss', cost)
# optimizer
with tf.name_scope('train'):
train_op = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(learning_rate=learning_rate).minimize(cost)
# correct_pred = tf.equal(tf.argmax(pred, 1), tf.argmax(y, 1))
# accuarcy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_pred, tf.float32))
with tf.name_scope('accuracy'):
accuracy = tf.metrics.accuracy(labels=tf.argmax(y, axis=1), predictions=tf.argmax(pred, axis=1))[1]
tf.summary.scalar('accuracy', accuracy)
merged = tf.summary.merge_all()
init = tf.group(tf.global_variables_initializer(), tf.local_variables_initializer())6. 訓練
with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(init)
train_writer = tf.summary.FileWriter("E://logs//train",sess.graph)
test_writer = tf.summary.FileWriter("E://logs//test",sess.graph)
# training
step = 1
for i in range(2000):
_batch_size = 128
batch_x, batch_y = mnist.train.next_batch(_batch_size)
sess.run(train_op, feed_dict={x:batch_x, y:batch_y, keep_prob:0.5, batch_size:_batch_size})
if (i + 1) % 100 == 0:
train_result = sess.run(merged, feed_dict={x:batch_x, y:batch_y, keep_prob:1.0, batch_size:_batch_size})
test_result = sess.run(merged, feed_dict={x:test_x, y:test_y, keep_prob:1.0, batch_size:test_x.shape[0]})
train_writer.add_summary(train_result,i+1)
test_writer.add_summary(test_result,i+1)
print("Optimization Finished!")7. 預測
test_x = mnist.test.images
test_y = mnist.test.labels
# prediction
print("Testing Accuracy:", sess.run(accuracy, feed_dict={x:test_x, y:test_y, keep_prob:1.0, batch_size:test_x.shape[0]}))視覺化結果
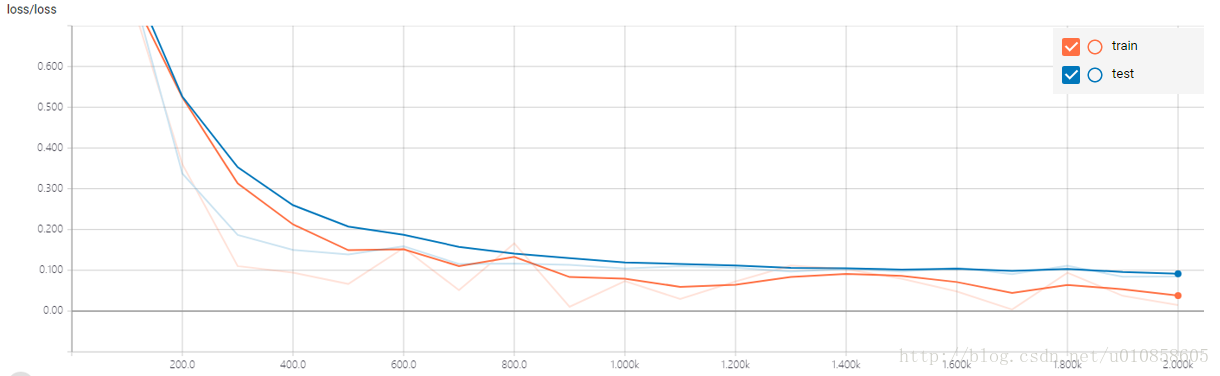
訓練集和測試集的在訓練過程中的誤差變化對比:
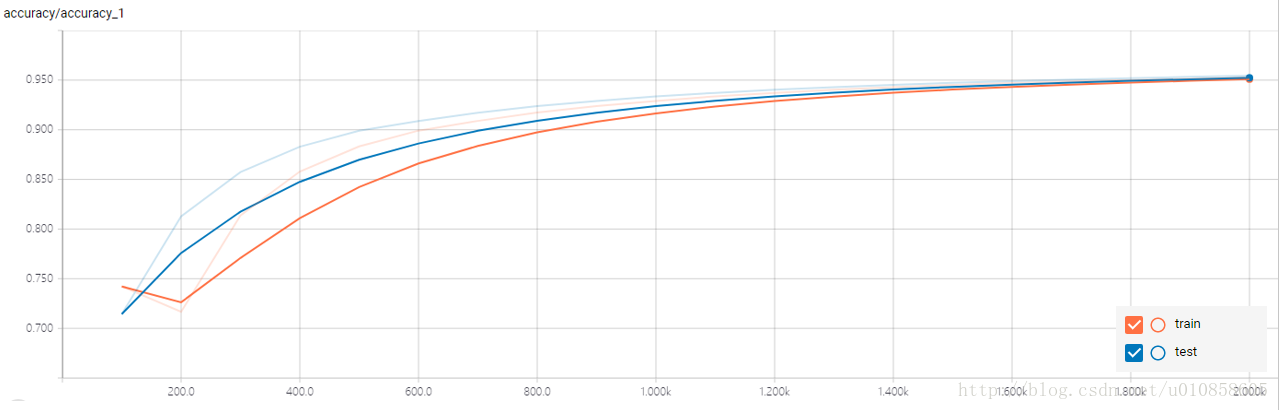
訓練集和測試集的在訓練過程中的預測準確率對比:
附全部程式碼
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data
tf.reset_default_graph()
# Hyper Parameters
learning_rate = 0.01 # 學習率
n_steps = 28 # LSTM 展開步數(時序持續長度)
n_inputs = 28 # 輸入節點數
n_hiddens = 64 # 隱層節點數
n_layers = 2 # LSTM layer 層數
n_classes = 10 # 輸出節點數(分類數目)
# data
mnist = input_data.read_data_sets("E:/Anaconda3/workspace/MNIST_data/", one_hot=True)
test_x = mnist.test.images
test_y = mnist.test.labels
# tensor placeholder
with tf.name_scope('inputs'):
x = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, n_steps * n_inputs], name='x_input') # 輸入
y = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, n_classes], name='y_input') # 輸出
keep_prob = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, name='keep_prob_input') # 保持多少不被 dropout
batch_size = tf.placeholder(tf.int32, [], name='batch_size_input') # 批大小
# weights and biases
with tf.name_scope('weights'):
Weights = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([n_hiddens, n_classes],stddev=0.1), dtype=tf.float32, name='W')
tf.summary.histogram('output_layer_weights', Weights)
with tf.name_scope('biases'):
biases = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([n_classes]), name='b')
tf.summary.histogram('output_layer_biases', biases)
# RNN structure
def RNN_LSTM(x, Weights, biases):
# RNN 輸入 reshape
x = tf.reshape(x, [-1, n_steps, n_inputs])
# 定義 LSTM cell
# cell 中的 dropout
def attn_cell():
lstm_cell = tf.contrib.rnn.BasicLSTMCell(n_hiddens)
with tf.name_scope('lstm_dropout'):
return tf.contrib.rnn.DropoutWrapper(lstm_cell, output_keep_prob=keep_prob)
# attn_cell = tf.contrib.rnn.DropoutWrapper(lstm_cell, output_keep_prob=keep_prob)
# 實現多層 LSTM
# [attn_cell() for _ in range(n_layers)]
enc_cells = []
for i in range(0, n_layers):
enc_cells.append(attn_cell())
with tf.name_scope('lstm_cells_layers'):
mlstm_cell = tf.contrib.rnn.MultiRNNCell(enc_cells, state_is_tuple=True)
# 全零初始化 state
_init_state = mlstm_cell.zero_state(batch_size, dtype=tf.float32)
# dynamic_rnn 執行網路
outputs, states = tf.nn.dynamic_rnn(mlstm_cell, x, initial_state=_init_state, dtype=tf.float32, time_major=False)
# 輸出
#return tf.matmul(outputs[:,-1,:], Weights) + biases
return tf.nn.softmax(tf.matmul(outputs[:,-1,:], Weights) + biases)
with tf.name_scope('output_layer'):
pred = RNN_LSTM(x, Weights, biases)
tf.summary.histogram('outputs', pred)
# cost
with tf.name_scope('loss'):
#cost = tf.reduce_mean(tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits=pred, labels=y))
cost = tf.reduce_mean(-tf.reduce_sum(y * tf.log(pred),reduction_indices=[1]))
tf.summary.scalar('loss', cost)
# optimizer
with tf.name_scope('train'):
train_op = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(learning_rate=learning_rate).minimize(cost)
# correct_pred = tf.equal(tf.argmax(pred, 1), tf.argmax(y, 1))
# accuarcy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_pred, tf.float32))
with tf.name_scope('accuracy'):
accuracy = tf.metrics.accuracy(labels=tf.argmax(y, axis=1), predictions=tf.argmax(pred, axis=1))[1]
tf.summary.scalar('accuracy', accuracy)
merged = tf.summary.merge_all()
init = tf.group(tf.global_variables_initializer(), tf.local_variables_initializer())
with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(init)
train_writer = tf.summary.FileWriter("E://logs//train",sess.graph)
test_writer = tf.summary.FileWriter("E://logs//test",sess.graph)
# training
step = 1
for i in range(2000):
_batch_size = 128
batch_x, batch_y = mnist.train.next_batch(_batch_size)
sess.run(train_op, feed_dict={x:batch_x, y:batch_y, keep_prob:0.5, batch_size:_batch_size})
if (i + 1) % 100 == 0:
#loss = sess.run(cost, feed_dict={x:batch_x, y:batch_y, keep_prob:1.0, batch_size:_batch_size})
#acc = sess.run(accuracy, feed_dict={x:batch_x, y:batch_y, keep_prob:1.0, batch_size:_batch_size})
#print('Iter: %d' % ((i+1) * _batch_size), '| train loss: %.6f' % loss, '| train accuracy: %.6f' % acc)
train_result = sess.run(merged, feed_dict={x:batch_x, y:batch_y, keep_prob:1.0, batch_size:_batch_size})
test_result = sess.run(merged, feed_dict={x:test_x, y:test_y, keep_prob:1.0, batch_size:test_x.shape[0]})
train_writer.add_summary(train_result,i+1)
test_writer.add_summary(test_result,i+1)
print("Optimization Finished!")
# prediction
print("Testing Accuracy:", sess.run(accuracy, feed_dict={x:test_x, y:test_y, keep_prob:1.0, batch_size:test_x.shape[0]}))