Codeforces 11D A Simple Task 統計簡單無向圖中環的個數
題目表述
Given a simple graph, output the number of simple cycles in it. A simple cycle is a cycle with no repeated vertices or edges.
Input
The first line of input contains two integers n and m (1 ≤ n ≤ 19, 0 ≤ m) – respectively the number of vertices and edges of the graph. Each of the subsequent m lines contains two integers a and b, (1 ≤ a, b ≤ n, a ≠ b) indicating that vertices a and b are connected by an undirected edge. There is no more than one edge connecting any pair of vertices.
Output
Output the number of cycles in the given graph.
構思
由於n的數字很小,用比較tricky的思維來看,應該找不到一個多項式演算法,因此我們可以設計一個階層或指數級的演算法。有興趣的同學可以證明該問題是個NP問題。
一個環是由若干個節點以及節點的順序決定的。若用最暴力的方法統計n個節點的無向圖中環的個數,則根據圓排列公式需要列舉
分析重複計算之處
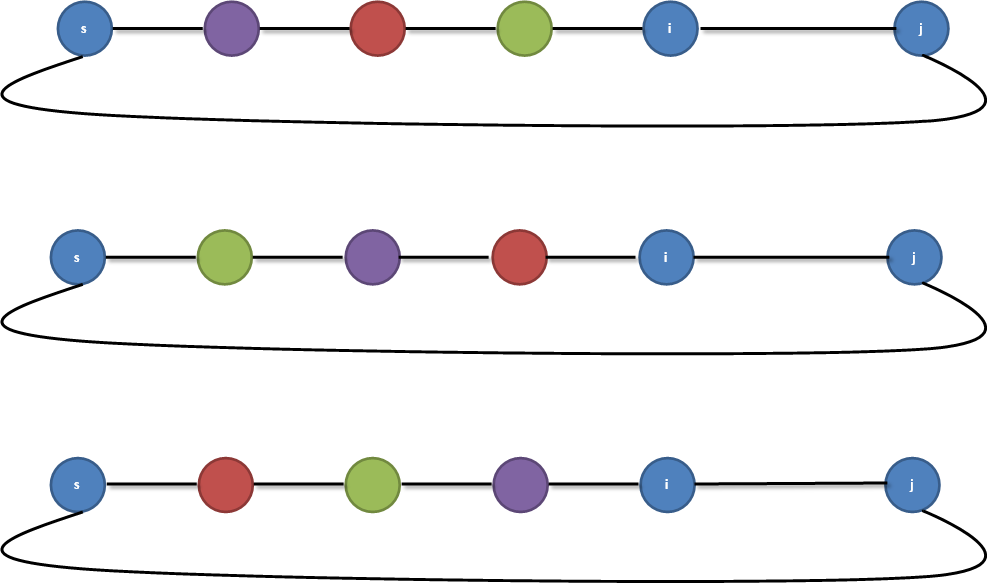
如圖所示的情況,節點s到節點j有一條邊,節點i到節點j有一條邊。
假設我們已經計算出節點s到節點i有3條簡單路徑。
接下來,我們要計算節點s到節點j的簡單環有幾條。根據前面階層級的列舉演算法,我們還要重新計算出節點s到節點i的3條簡單路徑,然後加上節點i到節點j的1條邊,再加上節點s到節點j的1條邊,構成3個簡單環。
實際上,我們並不關心節點s到節點i的簡單路徑是怎樣的,我們只關心節點s到節點i的簡單路徑的條數,就可以計算出節點s到節點j的簡單環的個數。
演算法設計
為了消除重複計算的部分,就很容易想到動態規劃了。我們設計一個狀態{[s][SET][i]}來記錄起點s到終點i的簡單路徑的條數,其中SET表示經過的節點的集合。但由於圓排列的性質,這樣的狀態是有重複的。我們通過指定起點為SET中的最小序號點來消除圓排列帶來的重複,狀態變為{[SET][i]}。還要注意,即使這樣定義狀態,計算簡單環個數的時候仍會將2個節點一條單邊的情況當成環,也會將長度大於2的環正向計算一遍,反向計算一遍。所以我們還要進行後處理。
前向的狀態轉移方程可以寫作:
但這樣的方程並不利於統計簡單環的個數。
後向的狀態轉移方程可以寫作:
設簡單環的個數用統計量
後處理:
由於長度為2的簡單環被統計了進去,所以
程式碼
注意,我們分析過,最多可能有19!個簡單環,所以資料型別得用int64。
/**
* @authors: zhenpeng.fang
* @nickname: dumpling
* @date: 2015-10-10 22:09:52
*/
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <string>
#include <cstring>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
#include <stack>
#include <map>
#include <set>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
#define mp make_pair
typedef long long int64;
const double eps = 1e-6;
const int64 INF64 = 10000000000000000LL;
const int N_NODE = 20;
const int N_EDGE = 400;
int64 cnt = 0;
int64 dp[1<<N_NODE][N_NODE];
int tail[N_NODE], es = 0;
int pre[N_EDGE], e[N_EDGE];
void add(int s, int t){
++es;
pre[es] = tail[s];
tail[s] = es;
e[es] = t;
}
int main(){
int n, m, s, t;
scanf("%d%d", &n, &m);
memset(tail, -1, sizeof(tail));
memset(pre, -1, sizeof(pre));
memset(e, -1, sizeof(e));
for(int i = 0; i < m; ++i){
scanf("%d%d", &s, &t);
add(s - 1, t - 1);
add(t - 1, s - 1);
}
for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i)
dp[1<<i][i] = 1;
for(int ST = 1; ST < (1<<n); ++ST){
for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i){
if(dp[ST][i] == 0) continue;
for(int edge = tail[i]; edge != -1; edge = pre[edge]){
int j = e[edge];
if((ST & (-ST)) > (1 << j)) continue;
if((1 << j) & ST){
if((ST & (-ST)) == (1 << j))
cnt += dp[ST][i];
}else{
dp[ST | (1 << j)][j] += dp[ST][i];
}
}
}
}
cnt = (cnt - m) / 2;
printf("%lld\n", cnt);
return 0;
}