Java學習筆記(17)-static和final
阿新 • • 發佈:2019-01-03
static final
static:靜態的,只能在類內部使用,可以修飾:屬性,方法,內部類,靜態程式碼塊
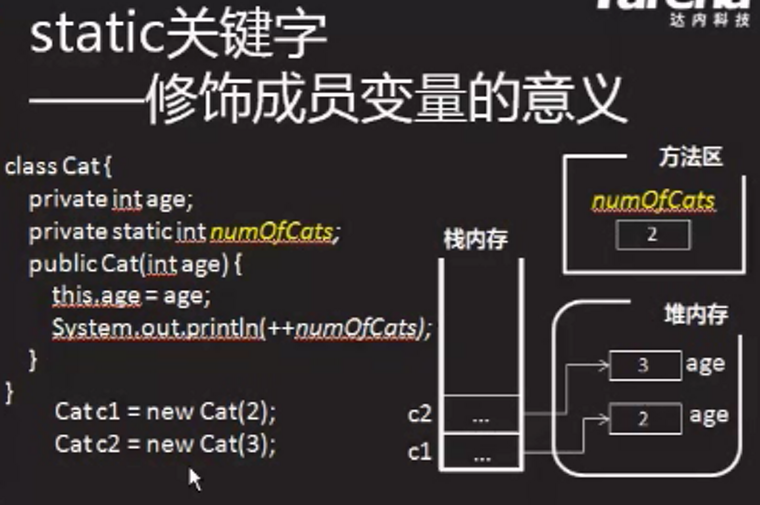
靜態修飾的成員:屬於類級別的成員,是全體類例項共享的資源
靜態屬性:只有一份,全體例項共享,類似於全域性變數
靜態方法:屬於類的方法,使用類名直接呼叫,不需要建立物件,而且靜態方法中沒有隱含引數this,
不能訪問當前物件資源
靜態程式碼塊:在類載入期間執行,只執行一次,可以用於資源的載入
final:最終的,可以修飾:類,方法,變數(屬性,區域性變數)
final的類:不能再繼承
final的方法:不能再重寫
final的方法和類,阻止了動態代理模式!
動態代理模式廣泛的應用在:Spring Hibernate Struts2
企業程式設計規範:不允許使用final的方法和類!
final的變數:final變數只能初始化一次,不能再修改!
常量
public static final double PI = 3.14;
package day03; /* * 靜態變數:靜態變數只有“一份” * 1 靜態變數在類載入期間初始化,存在方法區中 * 2 是全體物件共享的一份變數 * 3 經常使用類名訪問靜態變數 */ public class Demo07 { public static void main(String[] args) { Cat c1 = new Cat(5); Cat c2 = new Cat(6); System.out.println(c1.age+","+c2.age+","+Cat.numOfCats); } } class Cat{ int age;//例項變數,每個物件有一份 static int numOfCats = 0;//靜態變數,只有一份 public Cat(int age){ this.age = age; numOfCats++; } }
package day03; /* * 靜態方法 * 靜態方法使用類名呼叫,是屬於類的方法 * 靜態方法中沒有this變數,不能訪問當前物件 * 靜態方法一般用於與當前物件無關的工具方法 * 如:Math.sqrt() Arrays.sort() */ public class Demo08 { public static void main(String[] args) { Point p1 = new Point(3,4); Point p2 = new Point(6,8); //在物件上呼叫方法,當前物件隱含傳遞給隱含引數this System.out.println(p1.distance(p2));//distance(p1,p2) double d = Point.distance(p1,p2); //靜態方法呼叫時候不傳遞隱含的當前物件引數 } } class Point{ int x; int y; public Point(int x,int y){ this.x = x; this.y = y; } //靜態方法中沒有隱含引數this!在靜態方法中沒有this //在靜態方法中不能訪問this的屬性和方法! public static double distance(Point p1,Point p2){ int a = p1.x - p2.x; int b = p1.y - p2.y; return Math.sqrt(a*a+b*b); } //計算當前點(this)到另外一個點(other)的距離 public double distance(/*Point this*/Point other){ int a = this.x - other.x; int b = this.y - other.y; double c = Math.sqrt(a*a+b*b); return c; } }
package day03;
/*
* final類不能繼承子型別了, 可以防止子類對父型別的修改
* 工作中很少使用final的類
*/
public class Demo09 {
public static void main(String[] args){
}
}
final class Coo{}
//class Uoo extends Coo{}//編譯錯誤final類不能繼承子類
//class MyString extends String{}//編譯錯誤
//class MyInt extends Integer{}
//class MyMath extends Math{}package day03;
/*
* final 的方法不能被子類重寫了
*/
public class Demo10 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
}
}
class A{
public final void test(){
}
}
class B extends A{
//public void test(){}//編譯錯誤,子類不能重寫父類final方法
}package day03;
/*
* true false null 不是關鍵字!是字面量
* 關鍵字:if else while for class public
* final 修飾的變數
* final的變數只能初始化(賦值一次),不能再修改!
*/
public class Demo11 {
public static void main(String[] args){
//final修飾的區域性變數
final int a;
a = 5;//初始化!
//a = 8;//編譯錯誤
int b = 5;
b = 100;
b++;
// this.test(2,3);//非靜態方法用物件來掉,而現在再靜態方法裡沒有this
Demo11.test(5, 6);
// test(5,6);//同一個類裡,類名可以省略,靜態只能調靜態的
}
public static void test(final int a,int b){
//a++;//編譯錯誤,不能再修改
System.out.println(a);
b++;
}
}
package day03;
/*
* final表示初始化不能再修改
* static表示只有一個
* static final 共同修飾的叫常量
* 常量:PI是直接數的代名詞,是名字
* 字面量:直接寫出數值3.1415926535897
* 巨集觀說:字面量和常量都成為常量!
*/
public class Demo12 {
public static final double PI = 3.1415926535897;
public static void main(String[] args) {
Dog d1 = new Dog();
Dog d2 = new Dog();
//d1.id = 8;
System.out.println(d1.id+","+d2.id+","+Dog.numOfDogs);
}
}
class Dog{
final int id;//例項變數,每個物件一份,不能再次修改
static int numOfDogs=0;//靜態,只有一份
public Dog(){
id = numOfDogs++;
}
}
package day04;
public class Demo02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Foo f = new Koo();
}
}
class Foo{
int a = 1;
public Foo(){this.test();}
private void test(){
//私有方法不能繼承,也不能重寫
System.out.println("Foo test() "+a);
}
}
class Koo extends Foo{
int b = 2;
public void test(){
System.out.println("Koo test()"+a+", " +b);
}
}package day04;
public class Demo03 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
new Goo();
new Goo();
}
}
class Goo{
{//程式碼塊,在建立物件時候執行!類似於構造器的作用
System.out.println("HI");
}
static{//靜態程式碼塊,在類的載入期間執行,只執行一次
System.out.println("loading Goo.class");
}
}package day04;
import java.util.Arrays;
/*
* final變數只能初始化一次,不能再修改!
*/
public class Demo04 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
final String s = "ABC";
// s = "A";
final String[] ary = {"a","b"};
//ary:陣列變數,ary[0]陣列元素
ary[0] ="Tom";//陣列元素可以修改
// ary = null ;陣列變數不能修改
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(ary));
final Hoo h = new Hoo();
h.a = 8;
//h.b = 9;
//h = null;
}
}
class Hoo{
int a = 4;
final int b = 8;
}