基於Tensorflow訓練物體、人像識別的模型
阿新 • • 發佈:2019-01-04
領導突發奇想一個idea,於是踏上了瞭解Tensorflow機器學習框架之路,踩過很多坑,做個記錄。各位看官看的時候有些訓練方式可能已經過時或者不對,見諒。
參考文件
環境配置:
- ubuntu 16.0.4
- Python 2.7
- tensorflow cpu版本 1.4.1
訓練過程:
- 使用labelImg工具標註圖片,生成相應的註釋檔案.xml,注意圖片和xml不要放在同一個資料夾
- 下載官方推薦的model
git clone https://github.com/tensorflow/models.gitcd 到models/research目錄下新增路徑
# From tensorflow/models/research import os
import glob
import pandas as pd
import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET
def xml_to_csv(path):
xml_list = []
print("*********",glob.glob(path + '/*.xml'))
for xml_file in glob.glob(path + '/*.xml'):
tree = ET.parse(xml_file)
root = tree.getroot()
for python generate_tfrecord.py --csv_input=sunglasses_test_labels.csv --output_path=sunglass_test.record
"""
Usage:
# From tensorflow/models/
# Create train data:
python generate_tfrecord.py --csv_input=data/train_labels.csv --output_path=train.record
# Create test data:
python generate_tfrecord.py --csv_input=data/test_labels.csv --output_path=test.record
"""
from __future__ import division
from __future__ import print_function
from __future__ import absolute_import
import os
import io
import pandas as pd
import tensorflow as tf
from PIL import Image
from object_detection.utils import dataset_util
from collections import namedtuple, OrderedDict
flags = tf.app.flags
flags.DEFINE_string('csv_input', '', 'Path to the CSV input')
flags.DEFINE_string('output_path', '', 'Path to output TFRecord')
FLAGS = flags.FLAGS
# TO-DO replace this with label map
def class_text_to_int(row_label):
print('********',row_label)
if row_label == 'hat': // 使用圖片標註的label
return 1
else:
None
def split(df, group):
data = namedtuple('data', ['filename', 'object'])
gb = df.groupby(group)
return [data(filename, gb.get_group(x)) for filename, x in zip(gb.groups.keys(), gb.groups)]
def create_tf_example(group, path):
print("-------------")
with tf.gfile.GFile(os.path.join(path, '{}'.format(group.filename)), 'rb') as fid:
encoded_jpg = fid.read()
encoded_jpg_io = io.BytesIO(encoded_jpg)
image = Image.open(encoded_jpg_io)
width, height = image.size
filename = group.filename.encode('utf8')
image_format = b'jpg'
xmins = []
xmaxs = []
ymins = []
ymaxs = []
classes_text = []
classes = []
for index, row in group.object.iterrows():
xmins.append(row['xmin'] / width)
xmaxs.append(row['xmax'] / width)
ymins.append(row['ymin'] / height)
ymaxs.append(row['ymax'] / height)
classes_text.append(row['class'].encode('utf8'))
classes.append(class_text_to_int(row['class']))
tf_example = tf.train.Example(features=tf.train.Features(feature={
'image/height': dataset_util.int64_feature(height),
'image/width': dataset_util.int64_feature(width),
'image/filename': dataset_util.bytes_feature(filename),
'image/source_id': dataset_util.bytes_feature(filename),
'image/encoded': dataset_util.bytes_feature(encoded_jpg),
'image/format': dataset_util.bytes_feature(image_format),
'image/object/bbox/xmin': dataset_util.float_list_feature(xmins),
'image/object/bbox/xmax': dataset_util.float_list_feature(xmaxs),
'image/object/bbox/ymin': dataset_util.float_list_feature(ymins),
'image/object/bbox/ymax': dataset_util.float_list_feature(ymaxs),
'image/object/class/text': dataset_util.bytes_list_feature(classes_text),
'image/object/class/label': dataset_util.int64_list_feature(classes),
}))
return tf_example
def main(_):
print("-------------")
writer = tf.python_io.TFRecordWriter(FLAGS.output_path)
path = os.path.join(os.getcwd(), 'images_hat') //圖片檔案路徑
examples = pd.read_csv(FLAGS.csv_input)
grouped = split(examples, 'filename')
for group in grouped:
tf_example = create_tf_example(group, path)
writer.write(tf_example.SerializeToString())
writer.close()
output_path = os.path.join(os.getcwd(), FLAGS.output_path)
print('Successfully created the TFRecords: {}'.format(output_path))
if __name__ == '__main__':
tf.app.run()5.生成指定的 train.record。接下來指定標籤名稱,仿照models/ object_detection/data/ pet_label_map.pbtxt,重新建立一個檔案,指定標籤名
item {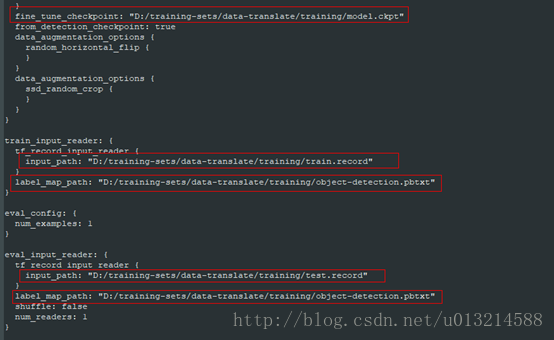
id: 1
name: 'dog'
}6.開啟 object_detection/samples/configs/ssd_mobilenet_v1_pets.config進行編輯修改,將num值改成自己需要訓練識別的object種類個數
首先上這裡下載預訓練model,推薦第一個,將第一行的路徑指向下載的ssd_mobilenet_v1_coco/model.ckpt,接下來圈紅的改為自己的record、pbtxt路徑


