springboot結合Rabbitmq例項分析
一.前言
本文介紹springboot整合Rabbitmq的具體使用.rabbitmq採用centos的安裝方式,具體詳細安裝方法可參考前面的文章:https://blog.csdn.net/u010520146/article/details/84454004
二.相關概念
訊息佇列通常有三個概念:傳送訊息(生產者)、佇列、接收訊息(消費者)。RabbitMQ在這個基本概念之上,多做了一層抽象,在傳送訊息和佇列之間,加入了交換機。這樣傳送訊息和佇列就沒有直接關係,而是通過交換機來做轉發,交換機會根據分發策略把訊息轉給佇列。
三.開發例項
本文采用springboot的版本為1.5.9.RELEASE
1.pom.xml加入
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-amqp</artifactId>
</dependency>
2.配置檔案 application.yml中加入
其中注意埠號為5672
spring:
rabbitmq:
host: 192.168.153.135
port: 5672
username: 3.配置檔案
(1) 建立連線工廠例項,配置連線資訊
@Configuration
public class RabbitConfig {
private final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(this.getClass());
@Value("${spring.rabbitmq.host}")
private String host;
@Value("${spring.rabbitmq.port}") (2)例項化RabbitTemplate 訊息模板
@Bean
@Scope(ConfigurableBeanFactory.SCOPE_PROTOTYPE)
//必須是prototype型別
public RabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate() {
RabbitTemplate template = new RabbitTemplate(connectionFactory());
return template;
}
(3) 例項化A.B.C.D佇列,以供測試
public static final String QUEUE_A = "QUEUE_A";
public static final String QUEUE_B = "QUEUE_B";
public static final String QUEUE_C = "QUEUE_C";
public static final String QUEUE_D = "QUEUE_D";
/**
* 例項化佇列
* @return
*/
@Bean
public Queue queueA() {
return new Queue(QUEUE_A, true); //佇列持久
}
@Bean
public Queue queueB() {
return new Queue(QUEUE_B, true); //佇列持久
}
@Bean
public Queue queueC() {
return new Queue(QUEUE_C, true); //佇列持久
}
@Bean
public Queue queueD() {
return new Queue(QUEUE_D, true); //佇列持久
}
(4) 例項化4種不同交換機以供測試
FanoutExchange: 將訊息分發到所有的繫結佇列,無routingkey的概念
HeadersExchange :通過新增屬性key-value匹配
DirectExchange:按照routingkey分發到指定佇列
TopicExchange:多關鍵字匹配
public static final String EXCHANGE_A = "ecchange_fanout";
public static final String EXCHANGE_B = "exchange_direct";
public static final String EXCHANGE_C = "exchange_header";
public static final String EXCHANGE_D = "exchange_topic";
@Bean
public FanoutExchange fanoutExchange() {
return new FanoutExchange(EXCHANGE_A);
}
@Bean
public DirectExchange directExchange() {
return new DirectExchange(EXCHANGE_B);
}
@Bean
public HeadersExchange headersexchange() {
return new HeadersExchange(EXCHANGE_C);
}
@Bean
public TopicExchange topicexchange() {
return new TopicExchange(EXCHANGE_D);
}
(5) 繫結佇列到交換機
針對DirectExchange交換機:把佇列A繫結到交換機上面
@Bean
public Binding bindingA() {
return BindingBuilder.bind(queueA()).to(directExchange()).with(RabbitConfig.ROUTINGKEY_A);
}
針對FanoutExchange交換機,將A.B.C佇列繫結到交換機A上面
@Bean
Binding bindingExchangeB(Queue queueB, FanoutExchange fanoutExchange) {
return BindingBuilder.bind(queueB).to(fanoutExchange);
}
@Bean
Binding bindingExchangeC(Queue queueC, FanoutExchange fanoutExchange) {
return BindingBuilder.bind(queueC).to(fanoutExchange);
}
@Bean
Binding bindingExchangeD(Queue queueD, FanoutExchange fanoutExchange) {
return BindingBuilder.bind(queueD).to(fanoutExchange);
}
針對主題模式交換機 字首匹配到topic.即可接受
@Bean
Binding bindingExchangeMessage2(Queue queueD, TopicExchange exchange) {
return BindingBuilder.bind(queueD).to(exchange).with("topic.#");
}
針對主題模式交換機 字首匹配到topic.lss0555 即可接受
@Bean
Binding bindingExchangeMessage(Queue queueC, TopicExchange exchange) {
return BindingBuilder.bind(queueC).to(exchange).with("topic.lss0555");
}
4.例項化5個訊息接收器以供測試使用
1.QueueAReceiver_A
QueueAReceiver_A繫結的是訊息佇列QUEUE_A
@Component
public class QueueAReceiver_A {
private final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(this.getClass());
@RabbitHandler
@RabbitListener(queues = RabbitConfig.QUEUE_A)
public void process(String msg) {
logger.info("接收處理佇列A訊息: " +msg);
}
}
2.QueueBReceiver_B1
QueueAReceiver_B1繫結的是訊息佇列QUEUE_B
@Component
public class QueueBReceiver_B1 {
private final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(this.getClass());
@RabbitHandler
@RabbitListener(queues = RabbitConfig.QUEUE_B)
public void process(String content) {
logger.info("接收處理佇列B1訊息: " + content);
}
}
3.QueueBReceiver_B2
QueueAReceiver_B2繫結的是訊息佇列QUEUE_B
@Component
public class QueueBReceiver_B2 {
private final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(this.getClass());
@RabbitHandler
@RabbitListener(queues = RabbitConfig.QUEUE_B)
public void process(String content) {
logger.info("接收處理佇列B2訊息: " + content);
}
}
4.QueueBReceiver_C
QueueAReceiver_C繫結的是訊息佇列QUEUE_C
@Component
public class QueueBReceiver_C {
private final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(this.getClass());
@RabbitHandler
@RabbitListener(queues = RabbitConfig.QUEUE_C)
public void process(String content) {
logger.info("接收處理佇列C訊息: " + content);
}
}
5.QueueBReceiver_D
QueueAReceiver_D繫結的是訊息佇列QUEUE_D
@Component
public class QueueBReceiver_D {
private final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(this.getClass());
@RabbitHandler
@RabbitListener(queues = RabbitConfig.QUEUE_D)
public void process(String content) {
logger.info("接收處理佇列D訊息: " + content);
}
}
5.不同模式測試
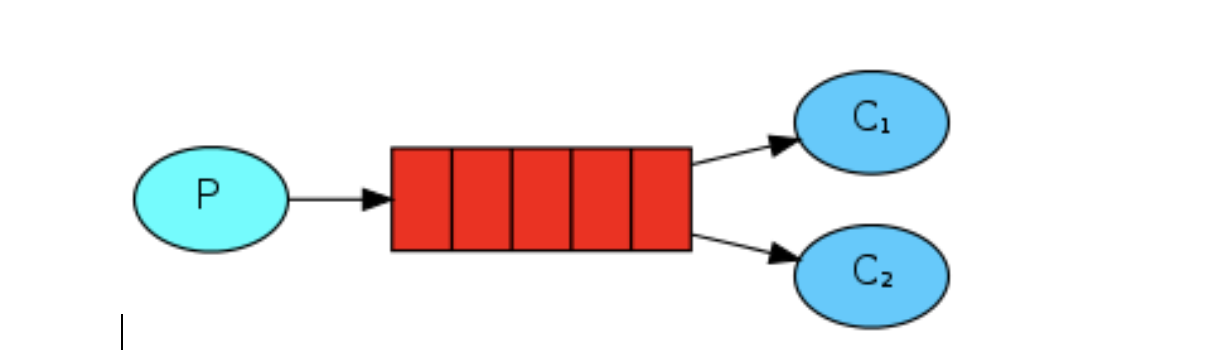
一 .單傳送單接收
如下圖所示:P代表生產者,C代表消費者,紅色程式碼訊息佇列。P將訊息傳送到訊息佇列,C對訊息進行處理
1.建立一個生產者
傳送訊息到訊息佇列A,相應的佇列接收器是QueueAReceiver_A
@Autowired
private RabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate;
public void sendMsg1(String content) {
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend(RabbitConfig.QUEUE_A,content);
}
2.建立一個測試用例
@Autowired
RabbitMsgProduct msgProducer;
@GetMapping("/sendMsg1")
public String sendMsg1(String msg){
msgProducer.sendMsg1(msg);
return "success";
}
訪問 http://localhost:8085/sendMsg1?msg=hello
結果如下,符合預期
INFO c.e.s.r.MsgReceive.QueueAReceiver_A - 接收處理佇列A訊息: hello
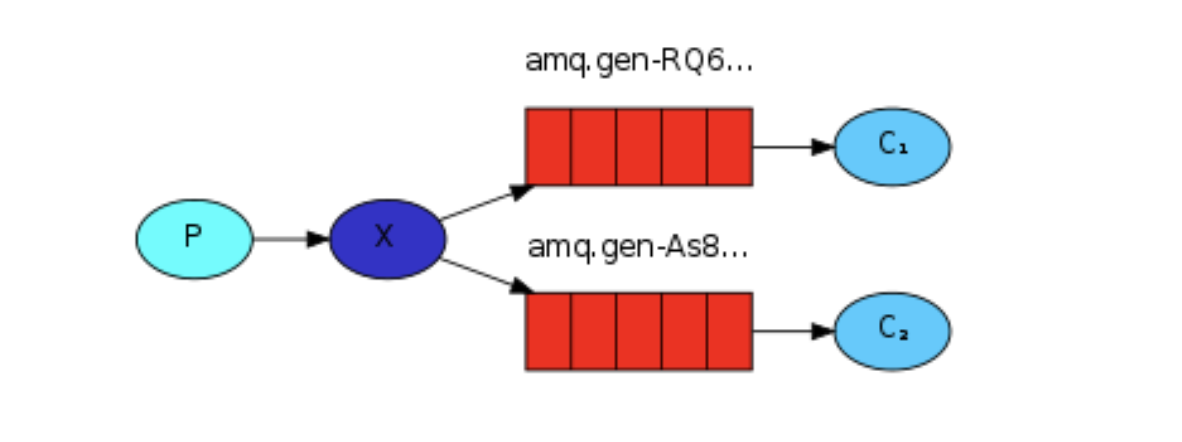
二 .工作模式(競爭)
競爭消費者如下圖:一個生產者,一個佇列,多個消費者。
同樣是點對點模式,但是在消費者之間,對消費佇列是有一些規則策略的,如:公平分發策略,輪詢分發策略等等。
1.建立訊息生產者
繫結到訊息佇列B,相應的訊息佇列接收器有QueueBReceiver_B1,QueueBReceiver_B2
public void sendMsg2(String content) {
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend(RabbitConfig.QUEUE_B,content);
}
2.新建一個測試用例
@GetMapping("/sendMsg2")
public String sendMsg2(String msg){
msgProducer.sendMsg2(msg);
return "success";
}
多次訪問: http://localhost:8085/sendMsg2?msg=hello
結果如下,符合預期
INFO c.e.s.r.M.QueueBReceiver_B2 - 接收處理佇列B2訊息: hello
INFO c.e.s.r.M.QueueBReceiver_B1 - 接收處理佇列B1訊息: hello
INFO c.e.s.r.M.QueueBReceiver_B2 - 接收處理佇列B2訊息: hello
三.釋出訂閱模式
如下圖:生產者將訊息不是直接傳送到佇列,而是傳送到X交換機,然後由交換機發送給兩個佇列,兩個消費者各自監聽一個佇列,來消費訊息。
這種方式實現同一個訊息被多個消費者消費。工作模式是同一個訊息只能有一個消費者。
1.新建一個訊息生產者
首先建立三個佇列QUEUE_A,QUEUE_B,QUEUE_C
然後建立交換機 fanoutExchange ,再將三個佇列繫結到該交換機上,這幾步在前面配置檔案已有說明。
接著,新建訊息生產者,將訊息傳送到交換機ecchange_fanout上
public void sendMsg3(String content) {
CorrelationData correlationId = new CorrelationData(UUID.randomUUID().toString());
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend(RabbitConfig.EXCHANGE_A, RabbitConfig.ROUTINGKEY_A, content, correlationId);
}
2.新建測試用例
@GetMapping("/sendMsg3")
public String sendMsg3(String msg){
msgProducer.sendMsg3(msg);
return "success";
}
訪問: http://localhost:8085/sendMsg3?msg=hello
結果如下,符合預期
INFO c.e.s.r.M.QueueBReceiver_B2 - 接收處理佇列B2訊息: hello
INFO c.e.s.r.MsgReceive.QueueBReceiver_C - 接收處理佇列C訊息: hello
INFO c.e.s.r.MsgReceive.QueueBReceiver_D - 接收處理佇列D訊息: hello
如果繫結的是DirectExchange型別交換機,該交換機繫結的是訊息佇列QUEUE_A,則新建訊息生產者
public void sendMsg4(String content) {
CorrelationData correlationId = new CorrelationData(UUID.randomUUID().toString());
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend(RabbitConfig.EXCHANGE_B, RabbitConfig.ROUTINGKEY_A, content, correlationId);
}
測試,訪問: http://localhost:8085/sendMsg4?msg=hello
結果如下,只有接收器QueueAReceiver_A收到訊息,符合預期
INFO c.e.s.r.MsgReceive.QueueAReceiver_A - 接收處理佇列A訊息: hello
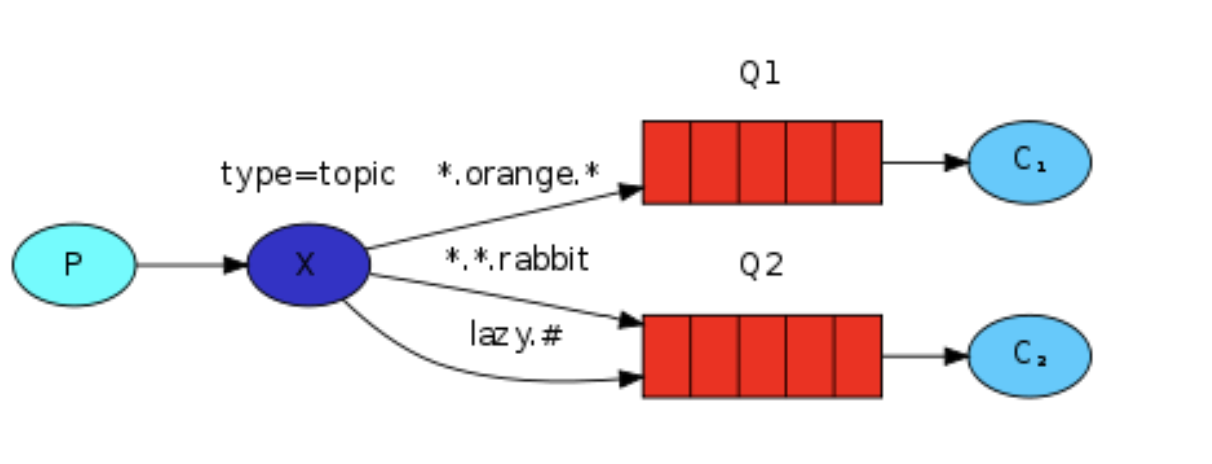
四.主題模式
如下圖所示:傳送端不只按固定的routing key傳送訊息,而是按字串匹配發送,接收端同樣如此,符號#匹配一個或多個詞,符號*匹配不多不少一個詞。
1.新建訊息生產者
首先建立TopicExchange型別交換機,即
@Bean
public TopicExchange topicexchange() {
return new TopicExchange(EXCHANGE_D);
}
然後建立不同匹配模式繫結到訊息佇列
//針對主題模式交換機,繫結到訊息佇列C 字首匹配到topic.lss0555 即可接受
@Bean
Binding bindingExchangeMessage(Queue queueC, TopicExchange exchange) {
return BindingBuilder.bind(queueC).to(exchange).with("topic.lss0555");
}
//針對主題模式交換機,繫結到訊息佇列D 字首匹配到topic. 即可接受
@Bean
Binding bindingExchangeMessage2(Queue queueD, TopicExchange exchange) {
return BindingBuilder.bind(queueD).to(exchange).with("topic.#");
}
新建3個訊息生產者,傳送訊息到到交換機上,匹配關鍵字,以供測試使用
匹配關鍵字 topic.12345
public void sendMsg6_1(String content) {
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend(RabbitConfig.EXCHANGE_D, "topic.12345", content);
}
匹配關鍵字 topic.lss0555
public void sendMsg6_2(String content) {
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend(RabbitConfig.EXCHANGE_D, "topic.lss0555", content);
}
匹配關鍵字 topic.lss05556666
public void sendMsg6_3(String content) {
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend(RabbitConfig.EXCHANGE_D, "topic.lss05556666", content);
}
訪問方法 sendMsg6_1
結果如下,符合預期
INFO c.e.s.r.MsgReceive.QueueBReceiver_D - 接收處理佇列D訊息: hello
訪問方法 sendMsg6_2
結果如下,符合預期
INFO c.e.s.r.MsgReceive.QueueBReceiver_C - 接收處理佇列C訊息: hello
INFO c.e.s.r.MsgReceive.QueueBReceiver_D - 接收處理佇列D訊息: hello
訪問方法 sendMsg6_3
結果如下,符合預期
INFO c.e.s.r.MsgReceive.QueueBReceiver_D - 接收處理佇列D訊息: hello