kubeadm安裝K8S單master雙節點叢集
阿新 • • 發佈:2019-01-04
宿主機:
master:172.16.40.97
node1:172.16.40.98
node2:172.16.40.99
# 一、k8s初始化環境:(三臺宿主機)
關閉防火牆和selinux
systemctl stop firewalld && systemctl disable firewalld sed -ri '/^[^#]*SELINUX=/s#=.+$#=disabled#' /etc/selinux/config setenforce 0
設定時間同步客戶端
yum install chrony -y cat <<EOF > /etc/chrony.conf server ntp.aliyun.com iburst stratumweight 0 driftfile /var/lib/chrony/drift rtcsync makestep 10 3 bindcmdaddress 127.0.0.1 bindcmdaddress ::1 keyfile /etc/chrony.keys commandkey 1 generatecommandkey logchange 0.5 logdir /var/log/chrony EOF systemctl restart chronyd
各主機之間相互DNS解析和ssh登入
略
升級核心
wget -O /etc/yum.repos.d/epel.repo http://mirrors.aliyun.com/repo/epel-7.repo yum install wget git jq psmisc -y wget -O /etc/yum.repos.d/epel.repo http://mirrors.aliyun.com/repo/epel-7.repo yum install https://mirrors.aliyun.com/saltstack/yum/redhat/salt-repo-latest-2.el7.noarch.rpm sed -i "s/repo.saltstack.com/mirrors.aliyun.com\/saltstack/g" /etc/yum.repos.d/salt-latest.repo yum update -y
更新重啟
自選版本
export Kernel_Vsersion=4.18.9-1
wget http://mirror.rc.usf.edu/compute_lock/elrepo/kernel/el7/x86_64/RPMS/kernel-ml{,-devel}-${Kernel_Vsersion}.el7.elrepo.x86_64.rpm
yum localinstall -y kernel-ml*
檢視這個核心裡是否有這個核心模組
find /lib/modules -name '*nf_conntrack_ipv4*' -type f
修改核心啟動順序,預設啟動的順序應該為1,升級以後核心是往前面插入,為0(如果每次啟動時需要手動選擇哪個核心,該步驟可以省略)
grub2-set-default 0 && grub2-mkconfig -o /etc/grub2.cfg
使用下面命令看看確認下是否啟動預設核心指向上面安裝的核心
grubby --default-kernel
docker官方的核心檢查指令碼建議(RHEL7/CentOS7: User namespaces disabled; add ‘user_namespace.enable=1’ to boot command line),使用下面命令開啟
grubby --args="user_namespace.enable=1" --update-kernel="$(grubby --default-kernel)"
重新載入核心
reboot
需要設定/etc/sysctl.d/k8s.conf的系統引數
cat <<EOF > /etc/sysctl.d/k8s.conf net.ipv4.ip_forward = 1 net.bridge.bridge-nf-call-ip6tables = 1 net.bridge.bridge-nf-call-iptables = 1 fs.may_detach_mounts = 1 vm.overcommit_memory=1 vm.panic_on_oom=0 fs.inotify.max_user_watches=89100 fs.file-max=52706963 fs.nr_open=52706963 net.netfilter.nf_conntrack_max=2310720 EOF sysctl --system
檢查系統核心和模組是否適合執行 docker (僅適用於 linux 系統)
curl https://raw.githubusercontent.com/docker/docker/master/contrib/check-config.sh > check-config.sh bash ./check-config.sh
安裝docker-ce
curl -fsSL "https://get.docker.com/" | bash -s -- --mirror Aliyun
mkdir -p /etc/docker/
cat>/etc/docker/daemon.json<<EOF
{
"registry-mirrors": ["https://fz5yth0r.mirror.aliyuncs.com"],
"storage-driver": "overlay2",
"storage-opts": [
"overlay2.override_kernel_check=true"
],
"log-driver": "json-file",
"log-opts": {
"max-size": "100m",
"max-file": "3"
}
}
EOF
設定docker開機啟動,CentOS安裝完成後docker需要手動設定docker命令補全
yum install -y epel-release bash-completion && cp /usr/share/bash-completion/completions/docker /etc/bash_completion.d/ systemctl enable --now docker
#二、安裝k8s叢集**
三臺宿主機進行kubectl kubelet kubeadm安裝:
cat <<EOF > /etc/yum.repos.d/kubernetes.repo [kubernetes] name=Kubernetes baseurl=https://mirrors.aliyun.com/kubernetes/yum/repos/kubernetes-el7-x86_64/ enabled=1 gpgcheck=1 repo_gpgcheck=1 gpgkey=https://mirrors.aliyun.com/kubernetes/yum/doc/yum-key.gpg https://mirrors.aliyun.com/kubernetes/yum/doc/rpm-package-key.gpg EOF yum install -y kubelet kubeadm kubectl systemctl enable kubelet
master宿主機忽略交換分割槽未關閉warning:
cat <<EOF > /etc/sysconfig/kubelet KUBELET_EXTRA_ARGS=--fail-swap-on=false EOF systemctl daemon-reload
master節點進行kubeadm初始化
kubeadm init --kubernetes-version=v1.13.1 --pod-network-cidr=10.244.0.0/16 --service-cidr=10.96.0.0/16 --ignore-preflight-errors=Swap --image-repository=registry.cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/google_containers
*[init] Using Kubernetes version: v1.13.1 [preflight] Running pre-flight checks [preflight] Pulling images required for setting up a Kubernetes cluster [preflight] This might take a minute or two, depending on the speed of your internet connection [preflight] You can also perform this action in beforehand using ‘kubeadm config images pull’ [kubelet-start] Writing kubelet environment file with flags to file “/var/lib/kubelet/kubeadm-flags.env” [kubelet-start] Writing kubelet configuration to file “/var/lib/kubelet/config.yaml” [kubelet-start] Activating the kubelet service [certs] Using certificateDir folder “/etc/kubernetes/pki” [certs] Generating “ca” certificate and key [certs] Generating “apiserver-kubelet-client” certificate and key [certs] Generating “apiserver” certificate and key [certs] apiserver serving cert is signed for DNS names [master kubernetes kubernetes.default kubernetes.default.svc kubernetes.default.svc.cluster.local] and IPs [10.96.0.1 172.16.40.97] [certs] Generating “front-proxy-ca” certificate and key [certs] Generating “front-proxy-client” certificate and key [certs] Generating “etcd/ca” certificate and key [certs] Generating “etcd/server” certificate and key [certs] etcd/server serving cert is signed for DNS names [master localhost] and IPs [172.16.40.97 127.0.0.1 ::1] [certs] Generating “etcd/peer” certificate and key [certs] etcd/peer serving cert is signed for DNS names [master localhost] and IPs [172.16.40.97 127.0.0.1 ::1] [certs] Generating “etcd/healthcheck-client” certificate and key [certs] Generating “apiserver-etcd-client” certificate and key [certs] Generating “sa” key and public key [kubeconfig] Using kubeconfig folder “/etc/kubernetes” [kubeconfig] Writing “admin.conf” kubeconfig file [kubeconfig] Writing “kubelet.conf” kubeconfig file [kubeconfig] Writing “controller-manager.conf” kubeconfig file [kubeconfig] Writing “scheduler.conf” kubeconfig file [control-plane] Using manifest folder “/etc/kubernetes/manifests” [control-plane] Creating static Pod manifest for “kube-apiserver” [control-plane] Creating static Pod manifest for “kube-controller-manager” [control-plane] Creating static Pod manifest for “kube-scheduler” [etcd] Creating static Pod manifest for local etcd in “/etc/kubernetes/manifests” [wait-control-plane] Waiting for the kubelet to boot up the control plane as static Pods from directory “/etc/kubernetes/manifests”. This can take up to 4m0s [apiclient] All control plane components are healthy after 20.003620 seconds [uploadconfig] storing the configuration used in ConfigMap “kubeadm-config” in the “kube-system” Namespace [kubelet] Creating a ConfigMap “kubelet-config-1.13” in namespace kube-system with the configuration for the kubelets in the cluster [patchnode] Uploading the CRI Socket information “/var/run/dockershim.sock” to the Node API object “master” as an annotation [mark-control-plane] Marking the node master as control-plane by adding the label “node-role.kubernetes.io/master=’’” [mark-control-plane] Marking the node master as control-plane by adding the taints [node-role.kubernetes.io/master:NoSchedule] [bootstrap-token] Using token: 2s9xxt.8lgyw6yzt21qq8xf [bootstrap-token] Configuring bootstrap tokens, cluster-info ConfigMap, RBAC Roles [bootstraptoken] configured RBAC rules to allow Node Bootstrap tokens to post CSRs in order for nodes to get long term certificate credentials [bootstraptoken] configured RBAC rules to allow the csrapprover controller automatically approve CSRs from a Node Bootstrap Token [bootstraptoken] configured RBAC rules to allow certificate rotation for all node client certificates in the cluster [bootstraptoken] creating the “cluster-info” ConfigMap in the “kube-public” namespace [addons] Applied essential addon: CoreDNS [addons] Applied essential addon: kube-proxy Your Kubernetes master has initialized successfully! To start using your cluster, you need to run the following as a regular user: mkdir -p $HOME/.kube sudo cp -i /etc/kubernetes/admin.conf $HOME/.kube/config sudo chown $(id -u):$(id -g) $HOME/.kube/config You should now deploy a pod network to the cluster. Run “kubectl apply -f [podnetwork].yaml” with one of the options listed at: https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/cluster-administration/addons/ You can now join any number of machines by running the following on each node as root: kubeadm join 172.16.40.97:6443 –token 2s9xxt.8lgyw6yzt21qq8xf –discovery-token-ca-cert-hash sha256:c141fb0608b4b83136272598d2623589d73546762abc987391479e8e049b0d76*
各節點用kubectl訪問訪問叢集
mkdir -p $HOME/.kube cp -i /etc/kubernetes/admin.conf $HOME/.kube/config chown $(id -u):$(id -g) $HOME/.kube/config
接下來我們來安裝flannel網路外掛
wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/sky-daiji/k8s-yaml/master/kube-flannel.yml kubectl apply -f kube-flannel.yml
master節點檢視叢集狀態
[[email protected] ~]# kubectl get cs NAME STATUS MESSAGE ERROR controller-manager Healthy ok scheduler Healthy ok etcd-0 Healthy {"health": "true"}
新增各節點進去叢集
kubeadm join 172.16.40.97:6443 --token 2s9xxt.8lgyw6yzt21qq8xf --discovery-token-ca-cert-hash sha256:c141fb0608b4b83136272598d2623589d73546762abc987391479e8e049b0d76
檢視節點是否都新增到叢集裡
[[email protected] ~]# kubectl get node NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION master Ready master 15m v1.13.1 node1 Ready <none> 13m v1.13.1 node2 Ready <none> 13m v1.13.1
檢視k8s各自元件執行情況
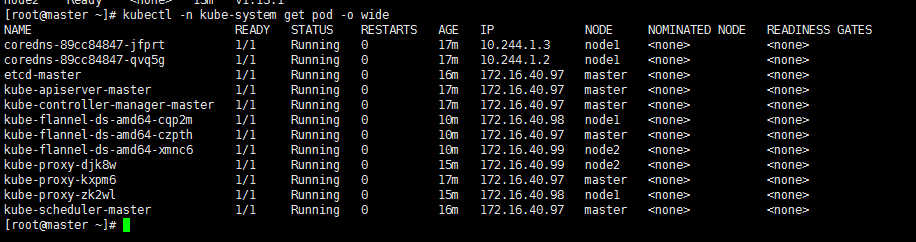
安裝kuber-dashboard外掛
wget https://github.com/sky-daiji/k8s-yaml/blob/master/kubernetes-dashboard.yaml wget https://github.com/sky-daiji/k8s-yaml/blob/master/admin-token.yaml kubectl apply -f kubernetes-dashboard.yaml -f admin-token.yaml
檢視kubernetes-dashboard外掛安裝是否成功
kubectl get pod -n kube-system |grep kubernetes-dashboard
訪問Dashboard
https://172.16.40.97:30091
選擇Token令牌模式登入。
kubectl describe secret/$(kubectl get secret -n kube-system |grep admin|awk '{print $1}') -n kube-system
