從Android 6.0原始碼的角度剖析Window內部機制原理
在從Android 6.0原始碼的角度剖析UI介面架構的文章中,我們瞭解到每個Activity都對應著一個Window,Window是一個抽象的概念,它的具體表現形式是View。每一個Window都對應著一個View和一個ViewRootImpl,Window和View通過ViewRootImpl來建立聯絡。對於Window來說,WindowManager是外界訪問Window的入口,Window的具體實現位於WindowManagerService中,WindowManager和WindowManagerService是一個互動是一個IPC過程。總之,Android中所有的檢視(Activity、Dialog或Toast等)都是依附在Window來呈現的,Window實際是View的直接管理者。
WindowManager是用於與Window管理器互動的介面,它繼承於介面ViewManager,可通過Context.getSystemService(Context.WINDOW_SERVICE)方式獲取WindowManager的例項。ViewManager提供了三個操作Window的方法,即addView()、updateViewLayout()、removeView(),它們分別實現Window內容的新增、更新、刪除操作。ViewManager原始碼如下:
public interface ViewManager{
public void addView(View view, ViewGroup.LayoutParams params);
public 然而,通過檢視WindowManager的原始碼發現,WindowManager並沒有實現上述三個方法,根據以往的開發經驗,原始碼中應該有個WindowManager的繼承類,用於實現上述三個方法。因此,我們在…\frameworks\base\core\java\android\view目錄下找到了WindowManagerImpl,它雖然實現了addView()、removeView()、updateViewLayout()三個方法,但是卻並沒有真正實現相關功能邏輯,而是直接”委託”WindowManagerGlobal
public final class WindowManagerImpl implements WindowManager {
// 操作view邏輯具體實現類
private final WindowManagerGlobal mGlobal = WindowManagerGlobal.getInstance();
private final Display mDisplay;
// mParentWindow在Activity被建立時呼叫Activity的attach方法例項化
private final Window mParentWindow;
private IBinder mDefaultToken;
public WindowManagerImpl(Display display) {
this(display, null);
}
private WindowManagerImpl(Display display, Window parentWindow) {
mDisplay = display;
mParentWindow = parentWindow;
}
public WindowManagerImpl createLocalWindowManager(Window parentWindow) {
return new WindowManagerImpl(mDisplay, parentWindow);
}
// 例項化WindowManagerImpl
public WindowManagerImpl createPresentationWindowManager(Display display) {
return new WindowManagerImpl(display, mParentWindow);
}
// 新增view到Window
@Override
public void addView(@NonNull View view, @NonNull ViewGroup.LayoutParams params) {
applyDefaultToken(params);
mGlobal.addView(view, params, mDisplay, mParentWindow);
}
// 更新window中的view
@Override
public void updateViewLayout(@NonNull View view, @NonNull ViewGroup.LayoutParams params) {
applyDefaultToken(params);
mGlobal.updateViewLayout(view, params);
}
// 從Window中刪除view
@Override
public void removeView(View view) {
mGlobal.removeView(view, false);
}
@Override
public void removeViewImmediate(View view) {
mGlobal.removeView(view, true);
}
@Override
public Display getDefaultDisplay() {
return mDisplay;
}
...
}1. 新增view到Window
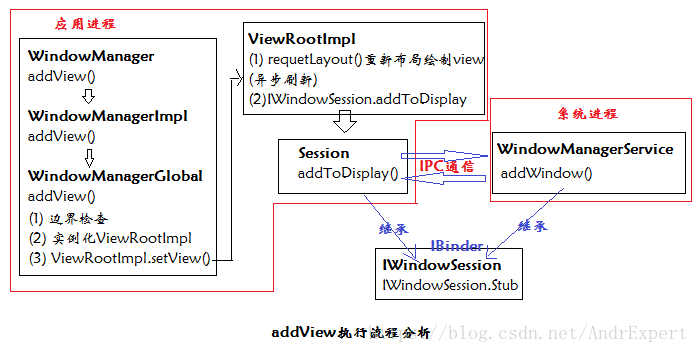
由上述分析可知,當我們需要將一個View新增到Activity對應的Window中時,呼叫WindowManager的addView()方法,該方法最終會呼叫WindowManagerGlobal的addView()方法來實現具體的功能邏輯。在開始分析之前,我們先看下WindowManagerGlobal的幾個重要的成員變數:
// 存放所有要新增到視窗的view
private final ArrayList<View> mViews = new ArrayList<View>();
// 存放繪製view的viewRootImpl,每一個view對應一個ViewRootImpl
private final ArrayList<ViewRootImpl> mRoots = new ArrayList<ViewRootImpl>();
// 存放所有view對應的LayoutParams
private final ArrayList<WindowManager.LayoutParams> mParams =
new ArrayList<WindowManager.LayoutParams>();
// 存放將要被移除的view
private final ArraySet<View> mDyingViews = new ArraySet<View>(); 其中,mViews為儲存所有要新增到Window中View的集合;mRoots為儲存View相對應的具體實現類ViewRootImpl的集合;mParams為儲存View相對應引數類WindowManager.LayoutParams的集合;mDyingViews 為儲存將要被移除View的集合。WindowManagerGlobal的addView()具體執行流程如下:
首先,addView()方法會對傳入的引數進行相關的邊界檢查;其次,通過findViewLocked()方法遍歷查詢mViews(View集合)中是否存在這個需要被add的view,如果存在(index>=0)即表明該View被重複則要麼執行從Window移除該View的操作或丟擲異常"View .. has already been added to the window manager."(很熟悉吧^_^);接著,建立view的實現類ViewRootImpl的例項root,為view設定佈局引數wparams,並將view、root、wparams新增到相關的集合中。由此可知,每一個View都對應著一個ViewRootImpl、LayoutParams,其中前者為View的具體實現類,LayoutParams為View的佈局引數;最後,呼叫ViewRootImpl的setView()方法完成後面的繪製過程,setView內部會通過requetLayout來完成非同步重新整理請求。
public void addView(View view, ViewGroup.LayoutParams params,
Display display, Window parentWindow) {
// (1) 邊界處理
if (view == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("view must not be null");
}
if (display == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("display must not be null");
}
if (!(params instanceof WindowManager.LayoutParams)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Params must be WindowManager.LayoutParams");
}
final WindowManager.LayoutParams wparams = (WindowManager.LayoutParams) params;
if (parentWindow != null) {
parentWindow.adjustLayoutParamsForSubWindow(wparams);
} else {
// If there's no parent, then hardware acceleration for this view is
// set from the application's hardware acceleration setting.
final Context context = view.getContext();
if (context != null
&& (context.getApplicationInfo().flags
& ApplicationInfo.FLAG_HARDWARE_ACCELERATED) != 0) {
wparams.flags |= WindowManager.LayoutParams.FLAG_HARDWARE_ACCELERATED;
}
}
ViewRootImpl root;
View panelParentView = null;
synchronized (mLock) {
// Start watching for system property changes.
if (mSystemPropertyUpdater == null) {
mSystemPropertyUpdater = new Runnable() {
@Override public void run() {
synchronized (mLock) {
for (int i = mRoots.size() - 1; i >= 0; --i) {
mRoots.get(i).loadSystemProperties();
}
}
}
};
SystemProperties.addChangeCallback(mSystemPropertyUpdater);
}
// (2) 獲取view在集合中的下標
// 如果index>=0說明該view已經被新增到window中
int index = findViewLocked(view, false);
if (index >= 0) {
// 如果打算移除該view,如果是執行ViewRootImpl的doDie
// 無需等待MSG_DIE訊息,直接從view佇列中移除
if (mDyingViews.contains(view)) {
// Don't wait for MSG_DIE to make it's way through root's queue.
mRoots.get(index).doDie();
} else {
// 重複新增,丟擲"has already been added to the window manager"異常
throw new IllegalStateException("View " + view
+ " has already been added to the window manager.");
}
// The previous removeView() had not completed executing. Now it has.
}
// If this is a panel window, then find the window it is being
// attached to for future reference.
if (wparams.type >= WindowManager.LayoutParams.FIRST_SUB_WINDOW &&
wparams.type <= WindowManager.LayoutParams.LAST_SUB_WINDOW) {
final int count = mViews.size();
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
if (mRoots.get(i).mWindow.asBinder() == wparams.token) {
panelParentView = mViews.get(i);
}
}
}
// (3) 例項化view對應的ViewRootImpl
root = new ViewRootImpl(view.getContext(), display);
view.setLayoutParams(wparams);
// 將與view相關新增到集合中
mViews.add(view);
mRoots.add(root);
mParams.add(wparams);
}
// do this last because it fires off messages to start doing things
// (4) 最後,執行ViewRootImpl的setView方法完成add view任務
// // 執行繪製流程重新佈局
// requestLayout();
try {
root.setView(view, wparams, panelParentView);
} catch (RuntimeException e) {
// BadTokenException or InvalidDisplayException, clean up.
synchronized (mLock) {
final int index = findViewLocked(view, false);
if (index >= 0) {
removeViewLocked(index, true);
}
}
throw e;
}
} 從上面的分析可知,addView執行到root.setView(…)後,setView()內部首先會通過requetLayout()來完成非同步重新整理請求,該方法會呼叫scheduleTraversals()方法執行繪製View流程,也就是說,scheduleTraversals()方法實際是View繪製的入口。(View的繪製流程請參考:從Android 6.0原始碼的角度剖析View的繪製流程);然後呼叫IWindowSession的addToDisplay方法將view新增到Window中。相關原始碼如下:
public void setView(View view, WindowManager.LayoutParams attrs, View panelParentView) {
...
// Schedule the first layout -before- adding to the window
// manager, to make sure we do the relayout before receiving
// any other events from the system.
// 執行繪製流程重新佈局
// 呼叫scheduleTraversals()
requestLayout();
if ((mWindowAttributes.inputFeatures
& WindowManager.LayoutParams.INPUT_FEATURE_NO_INPUT_CHANNEL) == 0) {
mInputChannel = new InputChannel();
}
try {
mOrigWindowType = mWindowAttributes.type;
mAttachInfo.mRecomputeGlobalAttributes = true;
collectViewAttributes();
// 執行IWindowSession的addToDisplay方法實現view新增
res = mWindowSession.addToDisplay(mWindow, mSeq, mWindowAttributes,
getHostVisibility(), mDisplay.getDisplayId(),
mAttachInfo.mContentInsets, mAttachInfo.mStableInsets,
mAttachInfo.mOutsets, mInputChannel);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
mAdded = false;
mView = null;
mAttachInfo.mRootView = null;
mInputChannel = null;
mFallbackEventHandler.setView(null);
unscheduleTraversals();
setAccessibilityFocus(null, null);
throw new RuntimeException("Adding window failed", e);
} finally {
if (restore) {
attrs.restore();
}
}
...
}
@Override
public void requestLayout() {
if (!mHandlingLayoutInLayoutRequest) {
checkThread();
mLayoutRequested = true;
// View繪製入口
scheduleTraversals();
}
} IWindowSession是一個抽象介面,它的addToDisplay方法具體的邏輯必定實在IWindowSession的子類中實現,根據IWindowSession的命名可推得,這個子類就是Session,Session類繼承於IWindowSession.Stub,是一個final類,每個應用通常有一個Session物件與視窗管理器(Window Manager)互動。通過檢視原始碼可知,addToDisplay()方法並沒有實現相關的view新增邏輯,而是交給WindowManagerService的addWindow()方法來實現。有過跨程序通訊(IPC)開發的朋友應該看到IWindowSession、Session以及WindowManagerService的程式碼結構應該很熟悉,實際上IWindowSession是一個Binder物件,Session、WindowManagerService均繼承於IWindowSession.Stub,只是Session物件位於你開發的應用程序中,而WindowManagerService在系統程序中,即addView()操作實質上是一次跨程序呼叫(IPC)。addToDisplay()原始碼如下:
@Override
public int addToDisplay(IWindow window, int seq, WindowManager.LayoutParams attrs,
int viewVisibility, int displayId, Rect outContentInsets, Rect outStableInsets,
Rect outOutsets, InputChannel outInputChannel) {
// mService為WindowManagerService的例項
return mService.addWindow(this, window, seq, attrs, viewVisibility, displayId,
outContentInsets, outStableInsets, outOutsets, outInputChannel);
} 至此,通過WindowManager的addView()方法將view新增到Window中的工作原理大概就剖析完畢了,至於WindowManagerService是如何實現真正的新增邏輯的,我們在Activity的Window建立過程章節再詳談。下圖為原始碼中執行流程:
2. 從Window刪除view
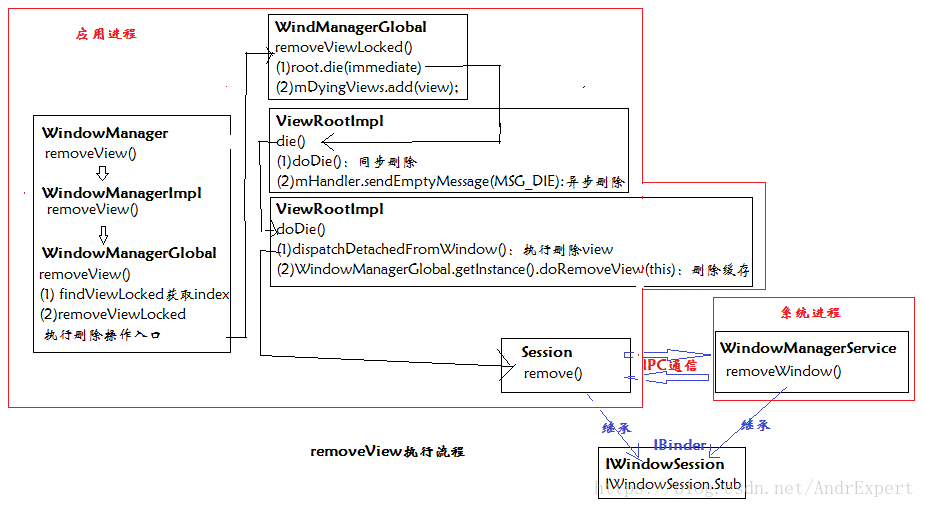
與呼叫WindowManager的addView()類似,WindowManager呼叫removeView()方法從Window中刪除指定view是從WindowManagerGlobal的removeView()方法開始的。首先,該方法會呼叫findViewLocked()方法獲取被刪除view在mViews集合中的下標,並根據下標從獲取快取在ViewRootImpl中的View例項,以便後面判斷View物件是否為同一個;然後,呼叫removeViewLocked方法執行具體的刪除邏輯。WindowManagerGlobal的removeView()方法、removeViewLocked()方法原始碼如下:
public void removeView(View view, boolean immediate) {
if (view == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("view must not be null");
}
// (1)獲取要刪除view位於mViews集合中的下標
// 然後根據下標取出view例項
synchronized (mLock) {
int index = findViewLocked(view, true);
View curView = mRoots.get(index).getView();
// (2) 執行刪除邏輯
removeViewLocked(index, immediate);
if (curView == view) {
return;
}
throw new IllegalStateException("Calling with view " + view
+ " but the ViewAncestor is attached to " + curView);
}
}
private void removeViewLocked(int index, boolean immediate) {
// 根據下標獲取ViewRootImpl物件
ViewRootImpl root = mRoots.get(index);
// 獲取快取在ViewRootImpl的View物件
View view = root.getView();
if (view != null) {
InputMethodManager imm = InputMethodManager.getInstance();
if (imm != null) {
imm.windowDismissed(mViews.get(index).getWindowToken());
}
}
// mGlobal.removeView(view, false);
// 即immediate=false
boolean deferred = root.die(immediate);
if (view != null) {
view.assignParent(null);
if (deferred) {
mDyingViews.add(view);
}
}
} removeViewLocked(index, immediate)方法主要做2件事情:
(1) 根據Index下標獲取儲存在mRoots快取中的ViewRootImpl物件,同時獲取快取在ViewRootImpl的View例項;
(2) 呼叫ViewRootImpl物件的die(immediate)方法,該方法會根據傳入的immediate引數決定刪除view的方式,即如果immediate && !mIsInTraversal為真,則呼叫doDie()方法執行立即執行刪除操作(同步刪除),否則,只是使用Handler傳送傳送一個MSG_DIE訊息,然後將要刪除的view新增到mDyingViews集合中表示待刪除。Handler收到該訊息後再在handleMessage()方法中呼叫doDie()執行刪除操作(非同步刪除)。ViewRootImpl的die()方法原始碼如下:
boolean die(boolean immediate) {
// 同步刪除
if (immediate && !mIsInTraversal) {
doDie();
return false;
}
if (!mIsDrawing) {
destroyHardwareRenderer();
} else {
Log.e(TAG, "Attempting to destroy the window while drawing!\n" +
" window=" + this + ", title=" + mWindowAttributes.getTitle());
}
// 非同步刪除,使用Handler傳送一個MSG_DIE訊息
mHandler.sendEmptyMessage(MSG_DIE);
return true;
} 接下來,我們詳細分析下ViewRootImpl的doDie()方法,該方法完成最終刪除的邏輯。首先,檢查當前執行緒是否為UI執行緒,否則丟擲異常”Only the original thread that created a view hierarchy can touch its views”,也就是說,我們呼叫WindowManager的removeView()方法必須在UI執行緒(主執行緒)中進行;其次,呼叫dispatchDetachedFromWindow()方法完成真正刪除View的邏輯,包括三個部分:(1)做一些垃圾回收工作(比如清楚資料和消除、移除回撥);(2)呼叫View的dispatchDetachedFromWindow()和onDetachedFromWindow()方法,以通知View從Window中移除事件;(3)呼叫Session的remove(mWindow)方法刪除Window,該方法最終會呼叫WindowManagerService的removeWindow(this,window)方法。由此可見,執行WindowManager的removeView()方法同樣是一個IPC過程。最後,呼叫WindowManagerGlobal的doRemoveView方法重新整理資料,包括mRoots、mParams和mDyingViews,以實現將當前Window所關聯的物件從快取中刪除。ViewRootImpl的doDie()原始碼如下:
void doDie() {
// 檢查當前執行緒是否為主執行緒,即UI執行緒
// 否則丟擲Only the original thread that created a view hierarchy can touch its views.
checkThread();
if (LOCAL_LOGV) Log.v(TAG, "DIE in " + this + " of " + mSurface);
synchronized (this) {
if (mRemoved) {
return;
}
mRemoved = true;
// 執行view刪除邏輯
if (mAdded) {
dispatchDetachedFromWindow();
}
if (mAdded && !mFirst) {
destroyHardwareRenderer();
if (mView != null) {
int viewVisibility = mView.getVisibility();
boolean viewVisibilityChanged = mViewVisibility != viewVisibility;
if (mWindowAttributesChanged || viewVisibilityChanged) {
// If layout params have been changed, first give them
// to the window manager to make sure it has the correct
// animation info.
try {
if ((relayoutWindow(mWindowAttributes, viewVisibility, false)
& WindowManagerGlobal.RELAYOUT_RES_FIRST_TIME) != 0) {
// IPC操作,結束繪製
mWindowSession.finishDrawing(mWindow);
}
} catch (RemoteException e) {
}
}
mSurface.release();
}
}
mAdded = false;
}
// 執行WindowManagerGlobal的doRemoveView方法完成移除
// 只是刪除快取中的資料
WindowManagerGlobal.getInstance().doRemoveView(this);
} removeView原始碼執行流程如下:
3. 更新Window中的view
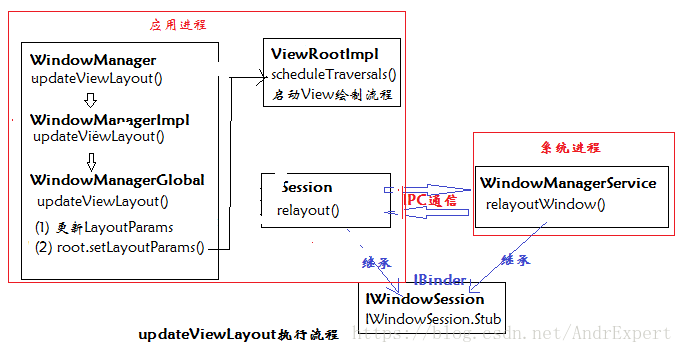
與呼叫WindowManager的addView()類似,WindowManager呼叫updateViewLayout()方法更新Window中指定的view是從WindowManagerGlobal的updateViewLayout()方法開始的。 updateViewLayout()方法比較簡單,首先它需要更新View的LayoutParams並替換老的LayoutParams,接著再通過ViewRootImpl的setLayoutParams()方法更新ViewRootImpl中的LayoutParams,該方法最終會呼叫ViewRootImpl的scheduleTraversals()方法重新對View進行佈局,包括測量、佈局、重繪這三個過程。WindowManagerGlobal的updateViewLayout()原始碼如下:
public void updateViewLayout(View view, ViewGroup.LayoutParams params) {
// 邊界處理
if (view == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("view must not be null");
}
if (!(params instanceof WindowManager.LayoutParams)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Params must be WindowManager.LayoutParams");
}
// 更新View的佈局引數
final WindowManager.LayoutParams wparams = (WindowManager.LayoutParams)params;
view.setLayoutParams(wparams);
synchronized (mLock) {
// 獲取view對應的ViewRootImpl物件
int index = findViewLocked(view, true);
ViewRootImpl root = mRoots.get(index);
// 更新mParams集合中的wparams
mParams.remove(index);
mParams.add(index, wparams);
// 執行
root.setLayoutParams(wparams, false);
}
} 由從Android 6.0原始碼的角度剖析View的繪製流程可知,除了View本身的重繪以外,ViewRootImpl還會通過Session的relayout()方法來更新Window的檢視,這個過程最終由WindowManagerService的relayoutWindow()來實現。由此可見,WindowManager的updateViewLayout()也是一次IPC操作。updateViewLayout原始碼執行流程如下: