hadoop2.6.0原始碼剖析-客戶端(第二部分--DistributedFileSystem)
DistributedFileSystem這個類在包package org.apache.hadoop.hdfs中,為使用者開發基於HDFS的應用程式提供了API,這個類有幾個成員變數:
private Path workingDir;
private URI uri;
private String homeDirPrefix = DFSConfigKeys.DFS_USER_HOME_DIR_PREFIX_DEFAULT;
DFSClient dfs;
private boolean verifyChecksum = true;
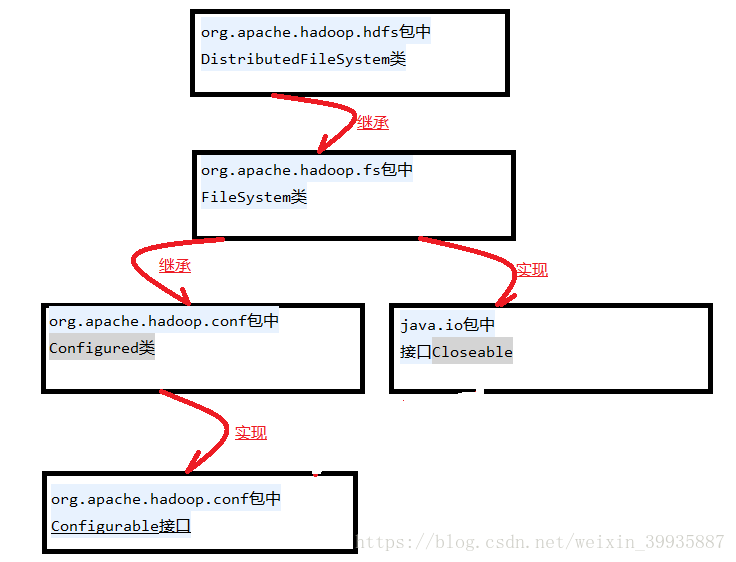
DistributedFileSystem類的繼承關係如下:
既然DistributedFileSystem類是用來對開發人員提供api介面服務的,那麼開發人員該如何去使用它呢?我們看一下下面的例子:
//讀取配置檔案
Configuration conf = new Configuration();
//獲取檔案系統
FileSystem fs = FileSystem.get(URI.create("hdfs://hadoop1:9000"),conf);
Path srcPath = new Path(path);
//呼叫mkdir()建立目錄,(可以一次性建立,以及不存在的父目錄)
boolean flag = fs.mkdirs(srcPath);
if(flag) {
System.out.println("create dir ok!");
}else {
System.out.println("create dir failure");
}
//關閉檔案系統
fs.close();
我們發現,例子中直接使用了DistributedFileSystem父類FileSystem,而沒有使用DistributedFileSystem,這個是為什麼呢?接下來我們到FileSystem類的get方法中:
/** Returns the FileSystem for this URI's scheme and authority. The scheme
* of the URI determines a configuration property name,
* <tt>fs.<i>scheme</i>.class</tt> whose value names the FileSystem class.
* The entire URI is passed to the FileSystem instance's initialize method.
*/
public static FileSystem get(URI uri, Configuration conf) throws IOException {
//uri是hdfs檔案的路徑
//下面用到了URI類,關於這個類的使用,可以到https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_39935887/article/details/81432814和https://www.jianshu.com/p/58b9245a6f16中瞭解詳情
String scheme = uri.getScheme();//獲取一個url中的協議,比如https或者http等
String authority = uri.getAuthority();
if (scheme == null && authority == null) { // use default FS
return get(conf);//如果協議和域名都為null,那麼就採用預設的FS
}
if (scheme != null && authority == null) { // no authority
URI defaultUri = getDefaultUri(conf);//如果有協議,但是沒有authority,那麼就呼叫getDefaultUri函式
if (scheme.equals(defaultUri.getScheme()) // if scheme matches default
&& defaultUri.getAuthority() != null) { // & default has authority
return get(defaultUri, conf); // return default
}
}
String disableCacheName = String.format("fs.%s.impl.disable.cache", scheme);
if (conf.getBoolean(disableCacheName, false)) {
return createFileSystem(uri, conf);
}
return CACHE.get(uri, conf);
}
我們進入到get(conf)函式中:
/**
* Returns the configured filesystem implementation.
* @param conf the configuration to use
*/
public static FileSystem get(Configuration conf) throws IOException {
return get(getDefaultUri(conf), conf);
}
這裡面呼叫了getDefaultUri函式,我們進入到這個函式中看看
/** Get the default filesystem URI from a configuration.
* @param conf the configuration to use
* @return the uri of the default filesystem
*/
public static URI getDefaultUri(Configuration conf) {
//conf.get(FS_DEFAULT_NAME_KEY, DEFAULT_FS)用來獲取名稱,同時如果該名稱是被廢棄的,那麼就通過fixName來進行修 //復,並提示
return URI.create(fixName(conf.get(FS_DEFAULT_NAME_KEY, DEFAULT_FS)));
}
這裡面首先呼叫Configuration類中的get函式,用來獲取一個url地址,其中:
FS_DEFAULT_NAME_KEY值為fs.defaultFS
DEFAULT_FS值為file:///
我們現在進入Configuration類的get函式中:
/**
* Get the value of the <code>name</code>. If the key is deprecated,
* it returns the value of the first key which replaces the deprecated key
* and is not null.
* If no such property exists,
* then <code>defaultValue</code> is returned.
*
* @param name property name, will be trimmed before get value.
* @param defaultValue default value.
* @return property value, or <code>defaultValue</code> if the property
* doesn't exist.
*/
public String get(String name, String defaultValue) {
//返回name在可能被廢棄的情況下可以採用的新的key名稱
String[] names = handleDeprecation(deprecationContext.get(), name);
String result = null;
for(String n : names) {
result = substituteVars(getProps().getProperty(n, defaultValue));
}
return result;
}
deprecationContext.get()會返回一個DeprecationContext型別物件,關於該類的詳細描述可以看Configuration類相關介紹,我們現在來分析hadleDeprecation函式,程式碼如下:
/**
* Checks for the presence of the property <code>name</code> in the
* deprecation map. Returns the first of the list of new keys if present
* in the deprecation map or the <code>name</code> itself. If the property
* is not presently set but the property map contains an entry for the
* deprecated key, the value of the deprecated key is set as the value for
* the provided property name.
*
* @param name the property name
* @return the first property in the list of properties mapping
* the <code>name</code> or the <code>name</code> itself.
*/
private String[] handleDeprecation(DeprecationContext deprecations,
String name) {
if (null != name) {
name = name.trim();
}
ArrayList<String > names = new ArrayList<String>();
//判斷name是否存在於deprecations中,即name是否是被廢棄key
if (isDeprecated(name)) {
//如果是,那麼就獲取到替換key和相應的描述
DeprecatedKeyInfo keyInfo = deprecations.getDeprecatedKeyMap().get(name);
//列印警告日誌,提示該key屬於被廢棄的,應該用新key來替換
warnOnceIfDeprecated(deprecations, name);
//遍歷替換的新key
for (String newKey : keyInfo.newKeys) {
if(newKey != null) {
//將新key新增到names佇列中
names.add(newKey);
}
}
}
if(names.size() == 0) {
//如果不屬於廢棄的key,那麼就直接新增到names中
names.add(name);
}
//遍歷可以替換的新key
for(String n : names) {
//獲取新key要替換的廢棄key
String deprecatedKey = deprecations.getReverseDeprecatedKeyMap().get(n);
//如果要廢棄的key不為null,而且Properties類物件overlay中不包含新key,同時overlay中包含廢棄key,那麼就將新key作為名稱,值為 //老key對應的值分別儲存到properties和overlay中。
if (deprecatedKey != null && !getOverlay().containsKey(n) &&
getOverlay().containsKey(deprecatedKey)) {
getProps().setProperty(n, getOverlay().getProperty(deprecatedKey));
getOverlay().setProperty(n, getOverlay().getProperty(deprecatedKey));
}
}
//將新key陣列返回。
return names.toArray(new String[names.size()]);
}
說白了handleDeprecation函式就是判斷name是否是被廢棄的key,如果是那麼就從deprecations中找到替代的新key並返回。接下來執行程式碼:
for(String n : names) {
//根據key值
result = substituteVars(getProps().getProperty(n, defaultValue));
}
對新的替代key進行遍歷,通過getProps().getProperty(n, defaultValue)獲取到n(類似於xml中的<name></name>)對應的value(類似於xml中的<value></value>),如果沒有找到那麼就採用defaultValue預設值。然後看看substituteVars函式,
private String substituteVars(String expr) {
if (expr == null) {
return null;
}
Matcher match = VAR_PATTERN.matcher("");
String eval = expr;
for(int s=0; s<MAX_SUBST; s++) {
match.reset(eval);
if (!match.find()) {
return eval;
}
String var = match.group();
var = var.substring(2, var.length()-1); // remove ${ .. }
String val = null;
try {
val = System.getProperty(var);
} catch(SecurityException se) {
LOG.warn("Unexpected SecurityException in Configuration", se);
}
if (val == null) {
val = getRaw(var);
}
if (val == null) {
return eval; // return literal ${var}: var is unbound
}
// substitute
eval = eval.substring(0, match.start())+val+eval.substring(match.end());
}
throw new IllegalStateException("Variable substitution depth too large: "
+ MAX_SUBST + " " + expr);
}
substituteVars主要是用來將key轉換一下,例如key值為${hadoop.tmp.dir}/dfs/name,那麼會將${hadoop.tmp.dir}轉換成相應的實際值,然後替換${hadoop.tmp.dir}並返回,關於這方面的詳解,請看訪問
我們回到FileSystem類的getDefaultUri函式中,return URI.create(fixName(conf.get(FS_DEFAULT_NAME_KEY, DEFAULT_FS)));
這行程式碼中conf.get(FS_DEFAULT_NAME_KEY, DEFAULT_FS))返回FS_DEFAULT_NAME_KEY這個key的對應的值,也就是xml中的value,然後呼叫fixName函式,如果get中返回的值為local,那麼說明為本地路徑,那麼fixName函式返回file:///,如果包含/字元,那麼說明是一個遠端路徑,在前面新增hdfs://,比如值為hadoop/dfs/name,那麼fixName函式呼叫後返回hdfs://hadoop/dfs/name。然後呼叫create函式建立URI,路徑為hdfs://hadoop/dfs/name。回到FileSystem get(URI uri, Configuration conf)函式中,繼續執行下面的程式碼:
//如果URI路徑為hdfs://hadoop/dfs/name,那麼scheme就為hdfs,disableCacheName就為fs.hdfs.impl.disable.cache
String disableCacheName = String.format("fs.%s.impl.disable.cache", scheme);
//那麼此時disableCacheName為fs.hdfs.impl.disable.cache
//到配置類物件conf中去找name為fs.hdfs.impl.disable.cache(相當於xml中的<name></name>)對應的值,如果找到了那麼返回相應的值,否則返回false。
if (conf.getBoolean(disableCacheName, false)) {
//如果找到了,那麼開始建立檔案物件
return createFileSystem(uri, conf);
}
return CACHE.get(uri, conf);
//我們開始進入createFileSystem函式中,程式碼如下:
private static FileSystem createFileSystem(URI uri, Configuration conf
) throws IOException {
Class<?> clazz = getFileSystemClass(uri.getScheme(), conf);
if (clazz == null) {
throw new IOException("No FileSystem for scheme: " + uri.getScheme());
}
FileSystem fs = (FileSystem)ReflectionUtils.newInstance(clazz, conf);
fs.initialize(uri, conf);
return fs;
}
例子中"hdfs://hadoop1:9000"通過呼叫getScheme()函式,返回值是hdfs,我們進入到getFileSystemClass函式中:
public static Class<? extends FileSystem> getFileSystemClass(String scheme,Configuration conf) throws IOException {
if (!FILE_SYSTEMS_LOADED) {
loadFileSystems();
}
Class<? extends FileSystem> clazz = null;
if (conf != null) {
clazz = (Class<? extends FileSystem>) conf.getClass("fs." + scheme + ".impl", null);
}
if (clazz == null) {
clazz = SERVICE_FILE_SYSTEMS.get(scheme);
}
if (clazz == null) {
throw new IOException("No FileSystem for scheme: " + scheme);
}
return clazz;
}
從程式碼中可以看出,該函式會首先從Configuration獲取到fs.hdfs.impl對應的class,由於Configuration載入了配置檔案,所以會到配置檔案中找到fs.hdfs.impl對應的class,而該class為org.apache.hadoop.hdfs.DistributedFileSystem,所以在createFileSystem函式中:
FileSystem fs = (FileSystem)ReflectionUtils.newInstance(clazz, conf);
fs.initialize(uri, conf);
先建立該clazz,然後再進行初始化,我們進入到org.apache.hadoop.hdfs.DistributedFileSystem下的initialize函式,
@Override
public void initialize(URI uri, Configuration conf) throws IOException {
super.initialize(uri, conf);
setConf(conf);
//host為hadoop1
String host = uri.getHost();
if (host == null) {
throw new IOException("Incomplete HDFS URI, no host: "+ uri);
}
homeDirPrefix = conf.get(
DFSConfigKeys.DFS_USER_HOME_DIR_PREFIX_KEY,
DFSConfigKeys.DFS_USER_HOME_DIR_PREFIX_DEFAULT);
//建立DFSClient物件
this.dfs = new DFSClient(uri, conf, statistics);
//建立URI,值為hdfs://hadoop1:9000
this.uri = URI.create(uri.getScheme()+"://"+uri.getAuthority());
//設定工作目錄
this.workingDir = getHomeDirectory();
}
我們先進入super.initialize(uri,conf)中,程式碼如下:
/** Called after a new FileSystem instance is constructed.
* @param name a uri whose authority section names the host, port, etc.
* for this FileSystem
* @param conf the configuration
*/
public void initialize(URI name, Configuration conf) throws IOException {
//呼叫父類的初始化
statistics = getStatistics(name.getScheme(), getClass());
resolveSymlinks = conf.getBoolean(
CommonConfigurationKeys.FS_CLIENT_RESOLVE_REMOTE_SYMLINKS_KEY,
CommonConfigurationKeys.FS_CLIENT_RESOLVE_REMOTE_SYMLINKS_DEFAULT);
}
至此,DistributedFileSystem就結束了,現在進入到DFSClient中,開始檔案資料的讀寫操作。