2018 10-708 (CMU) Probabilistic Graphical Models {Lecture 2} [Directed GMs: Bayesian Networks]
https://kayhan.dbmi.pitt.edu/sites/default/files/lecture2.pdf




P(sequence) given both dices are fair

x2 → x4
↗ ↘
x1 x5
↘ ↗
x3
P(x5) = P(X1) P(X2|X1) P(X3|X1) P(X4|X2) P(X5|X3,X4)



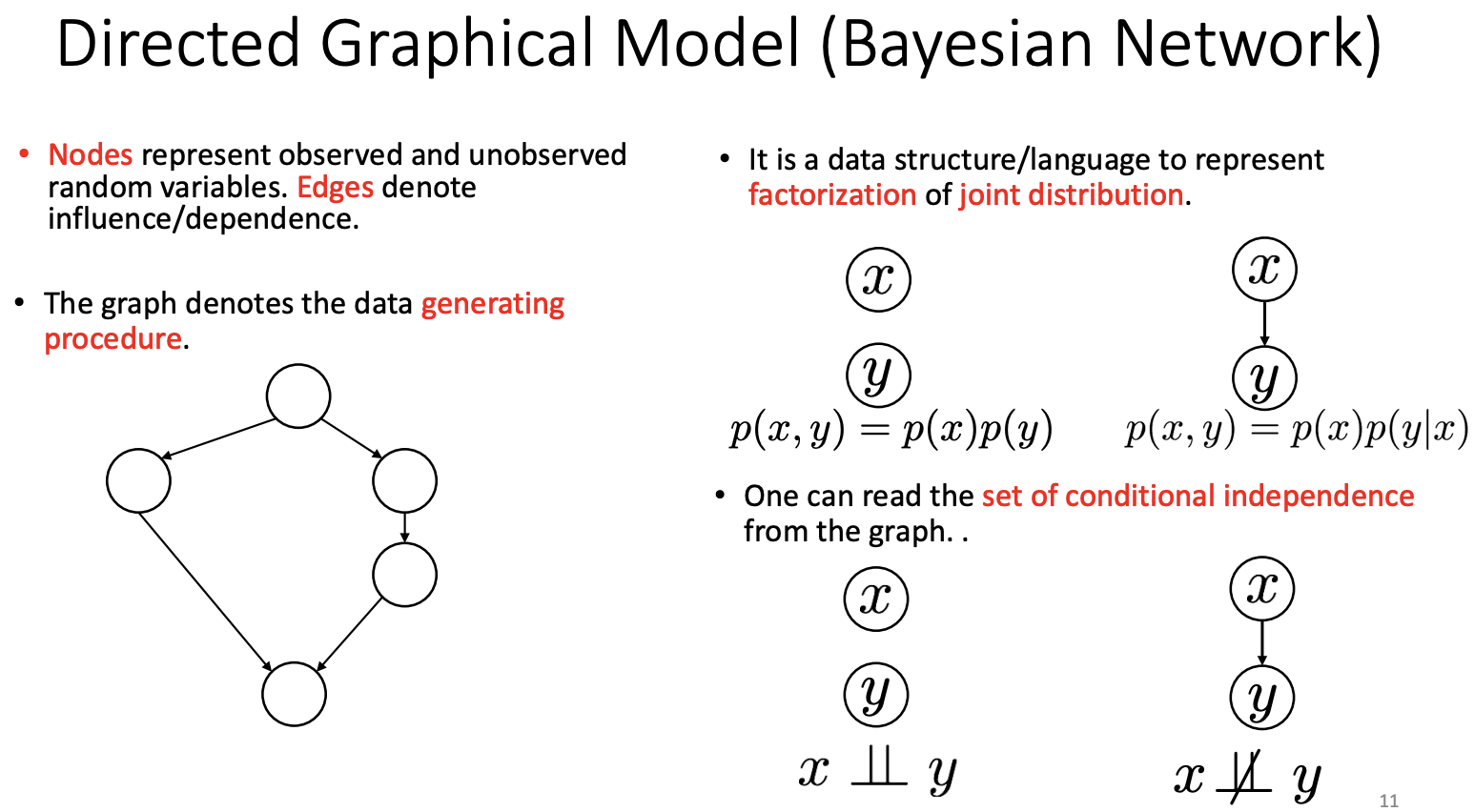
Directed Acyclic Graphical (DAG)
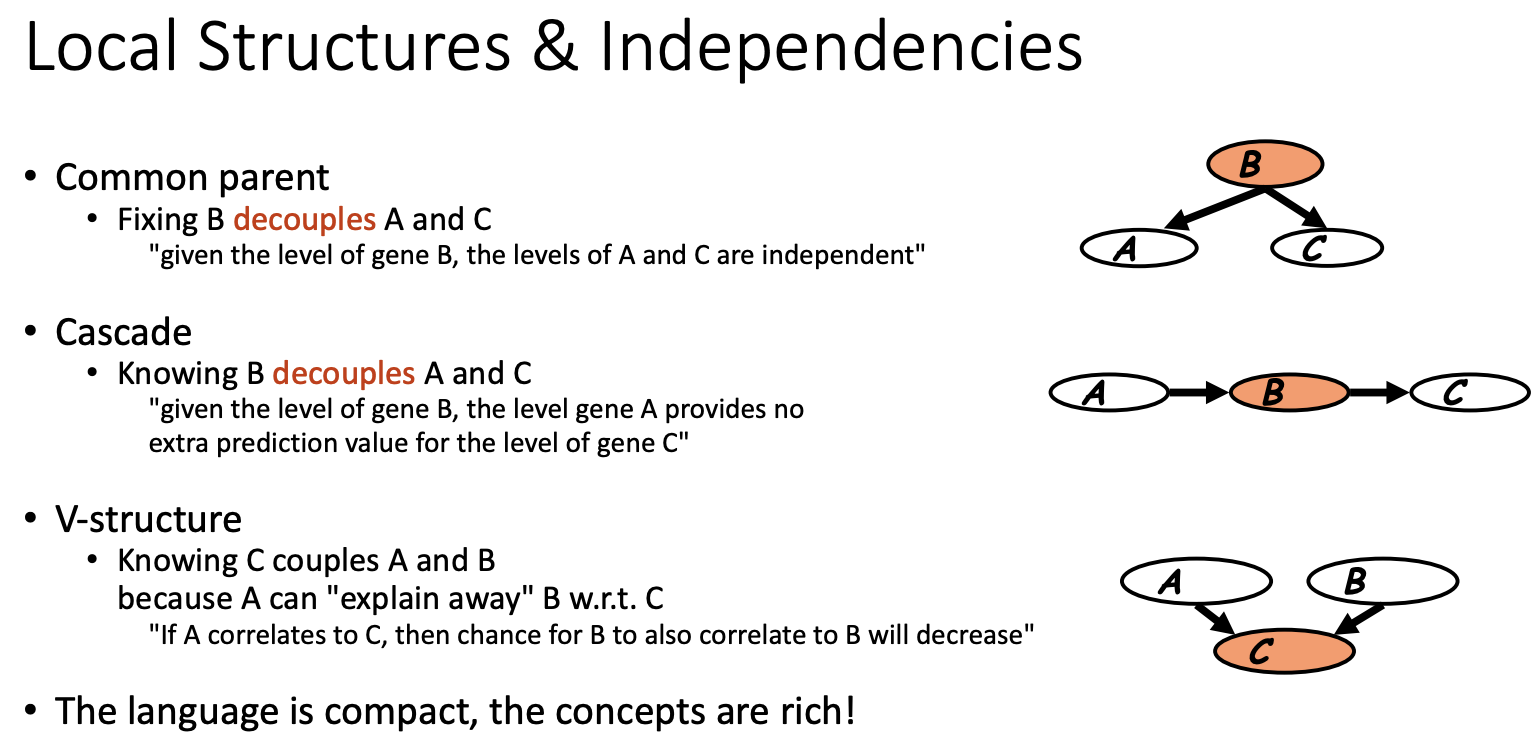

Wrong: I(g) = {A ⊥ C | B}
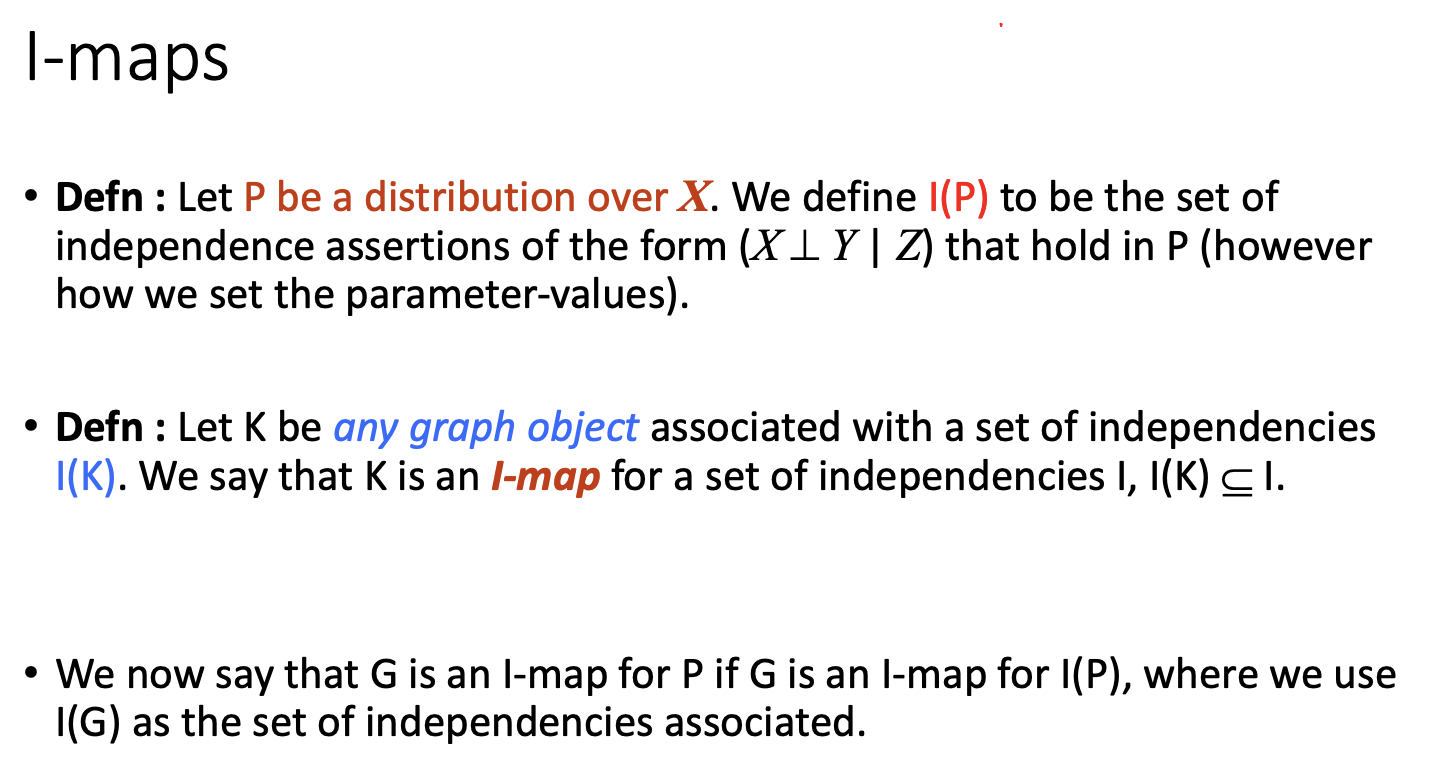
A,B,C has 2^N * 2^N * 2^N ($2^(N^3)$) combinations of graph.
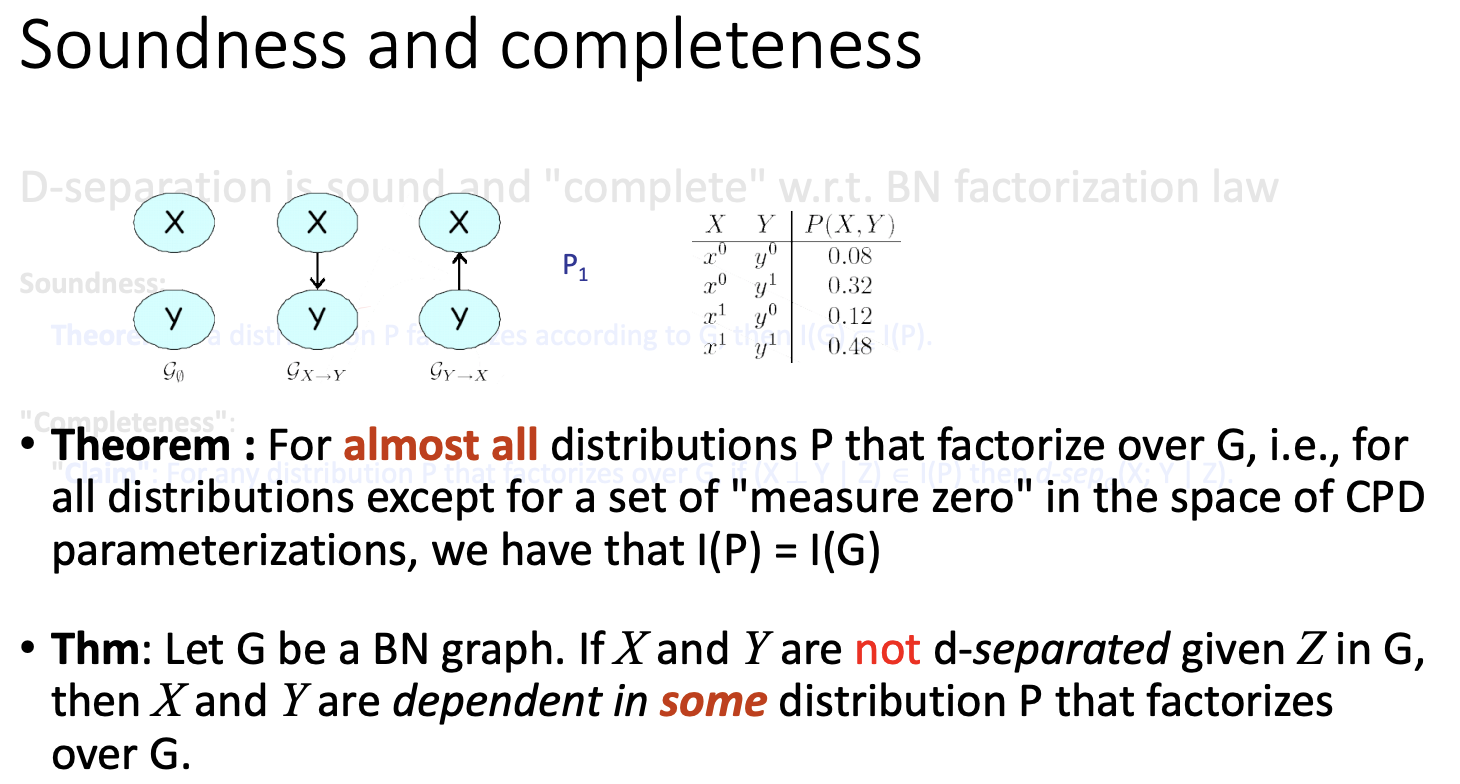
I(G) \subset I(P)
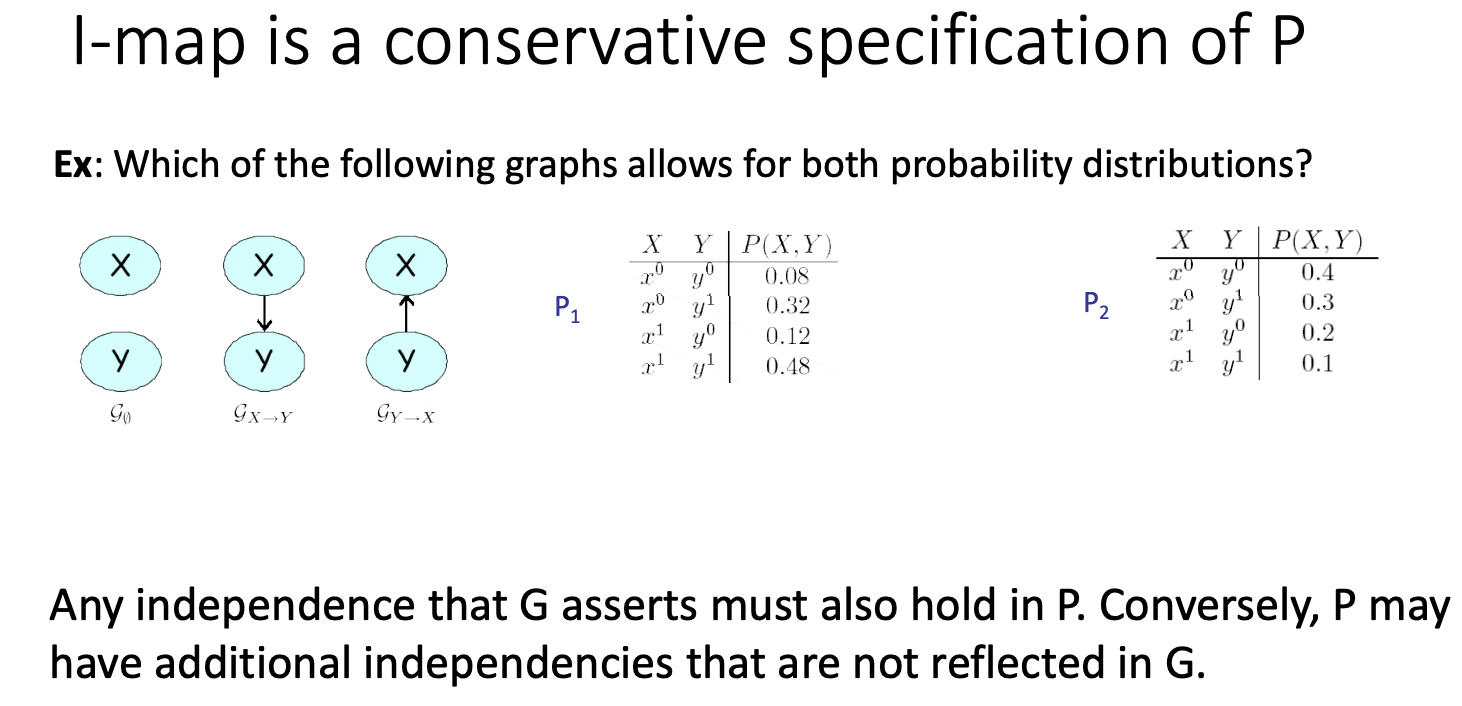
G0's I-map: I(G_0) = {X⊥Y}
G1's I-map: I(G_1) = \O
G2's I-map: I(G_2) = \o


https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=yDs_q6jKHb0
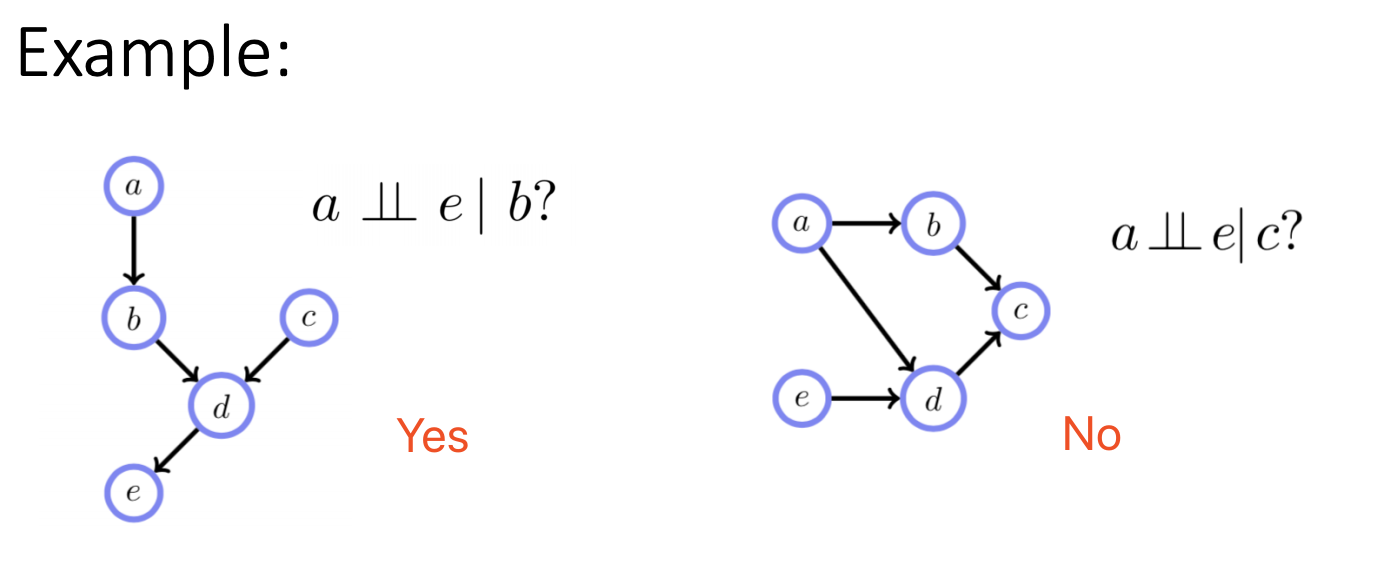
D-Separation
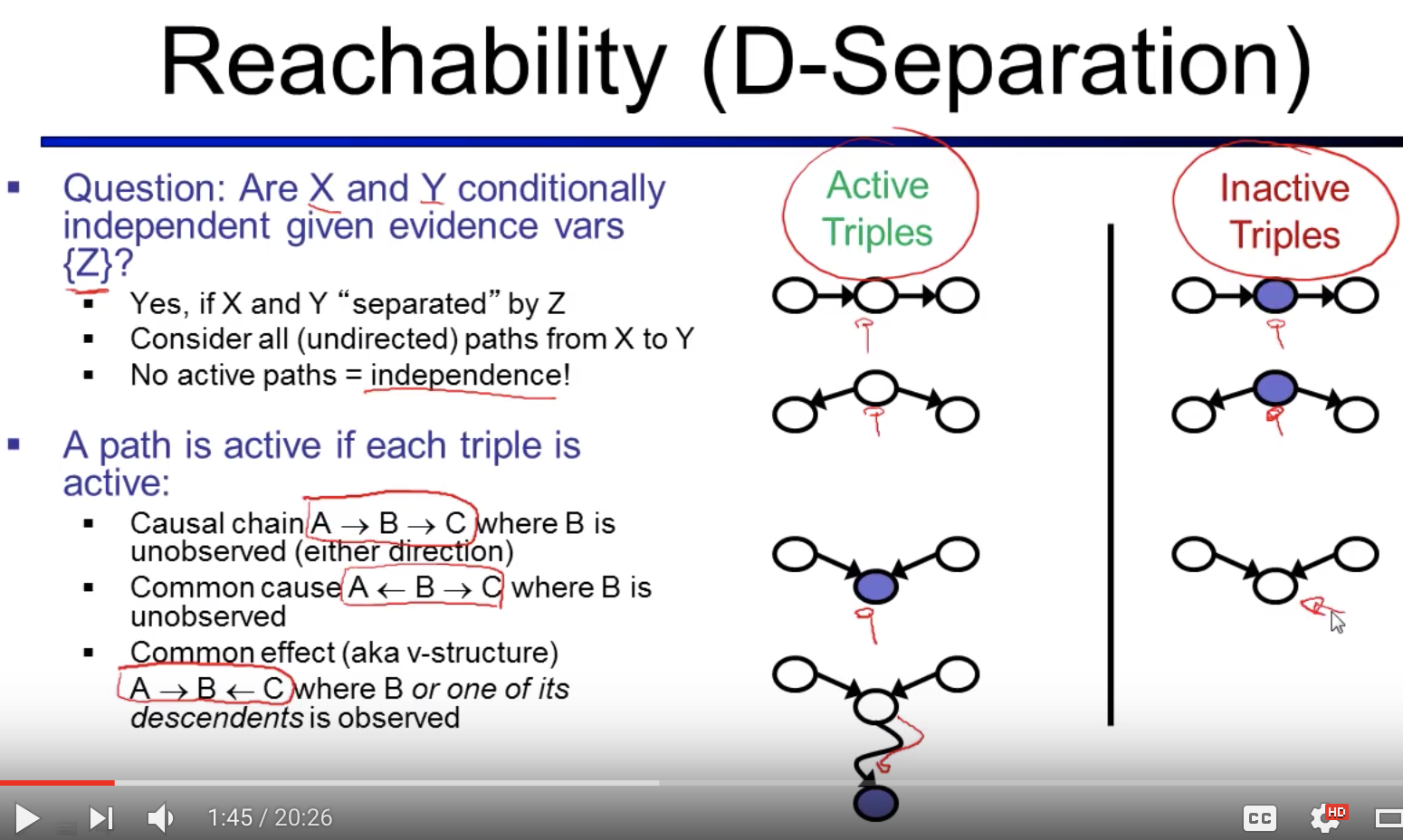
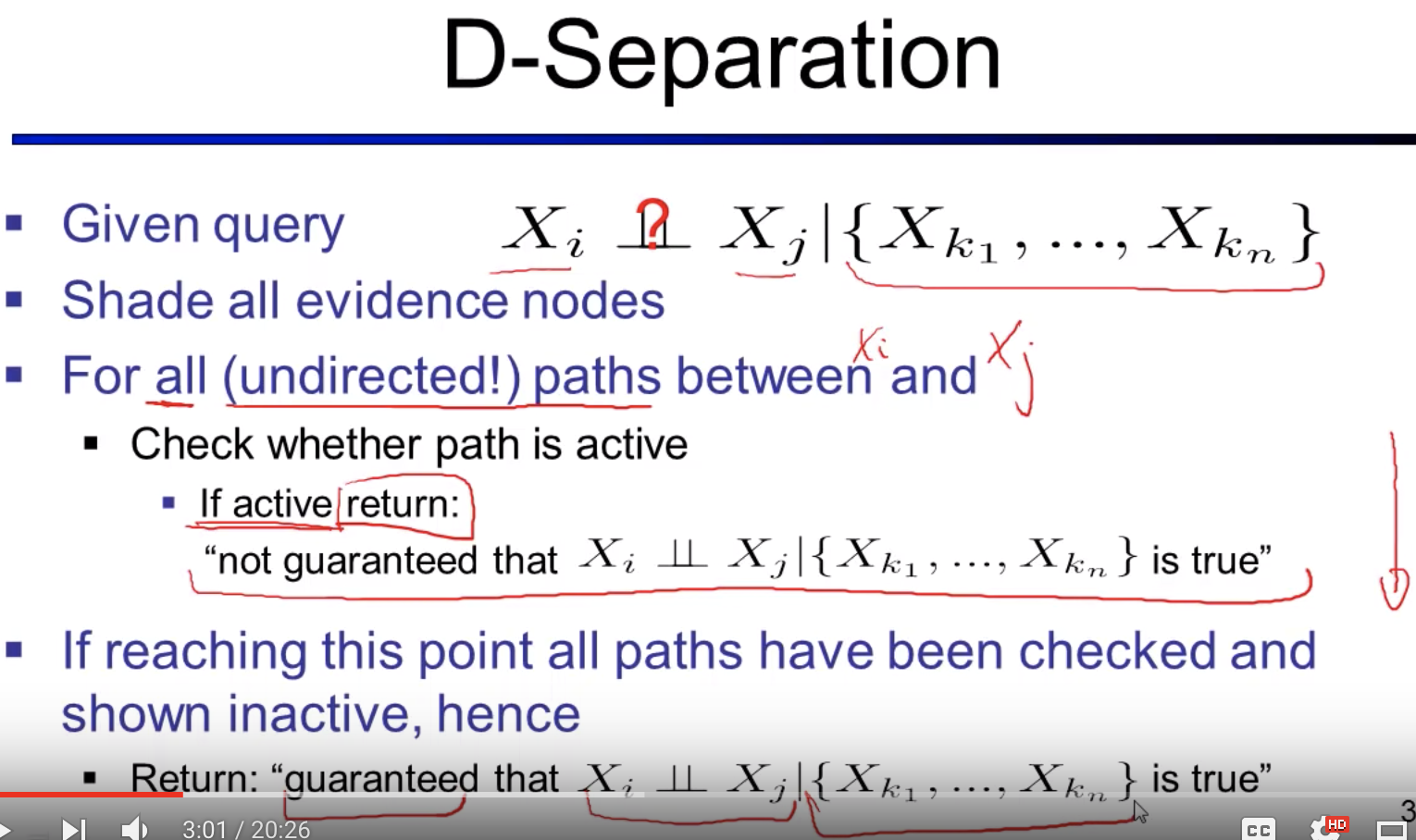

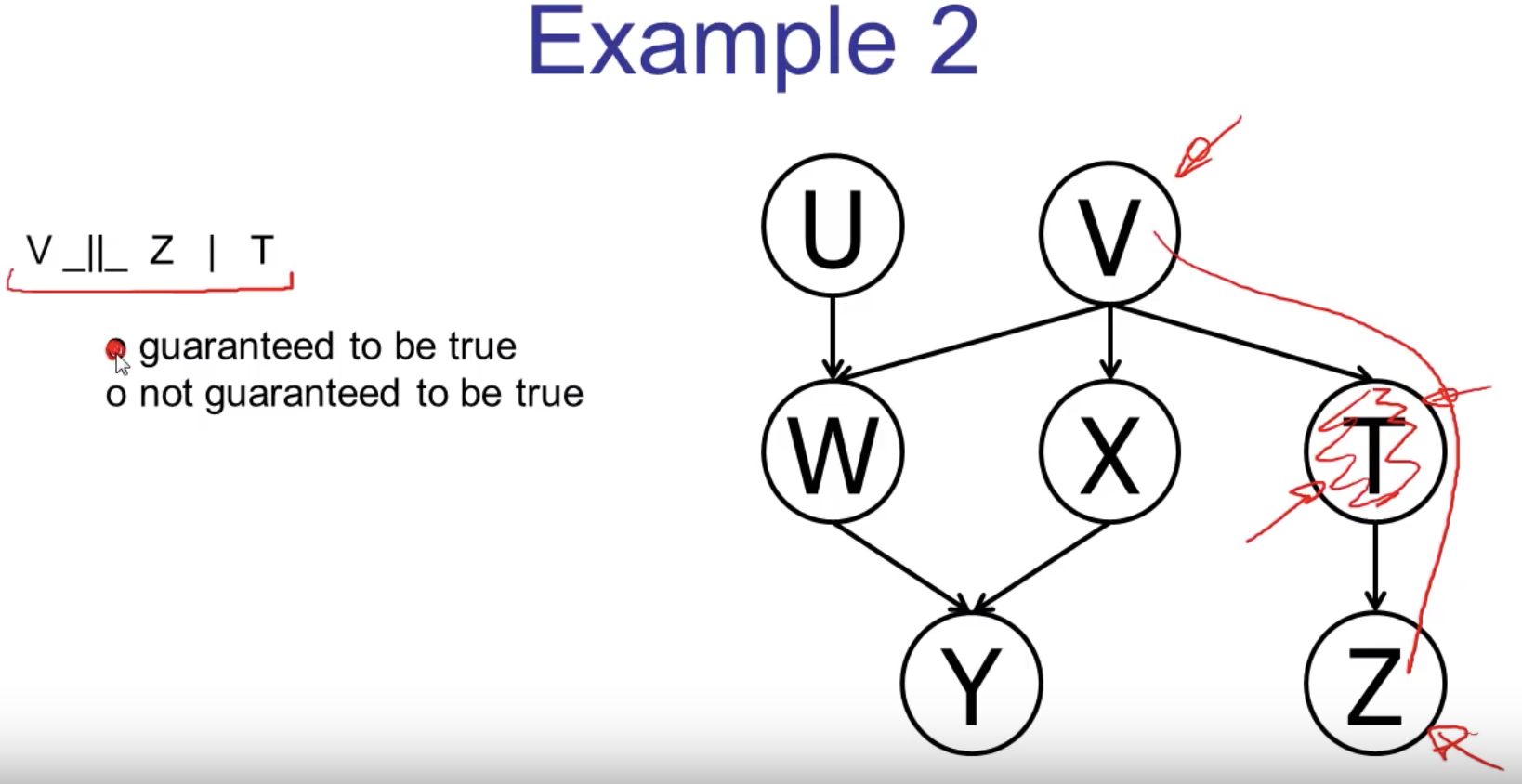


... More examples
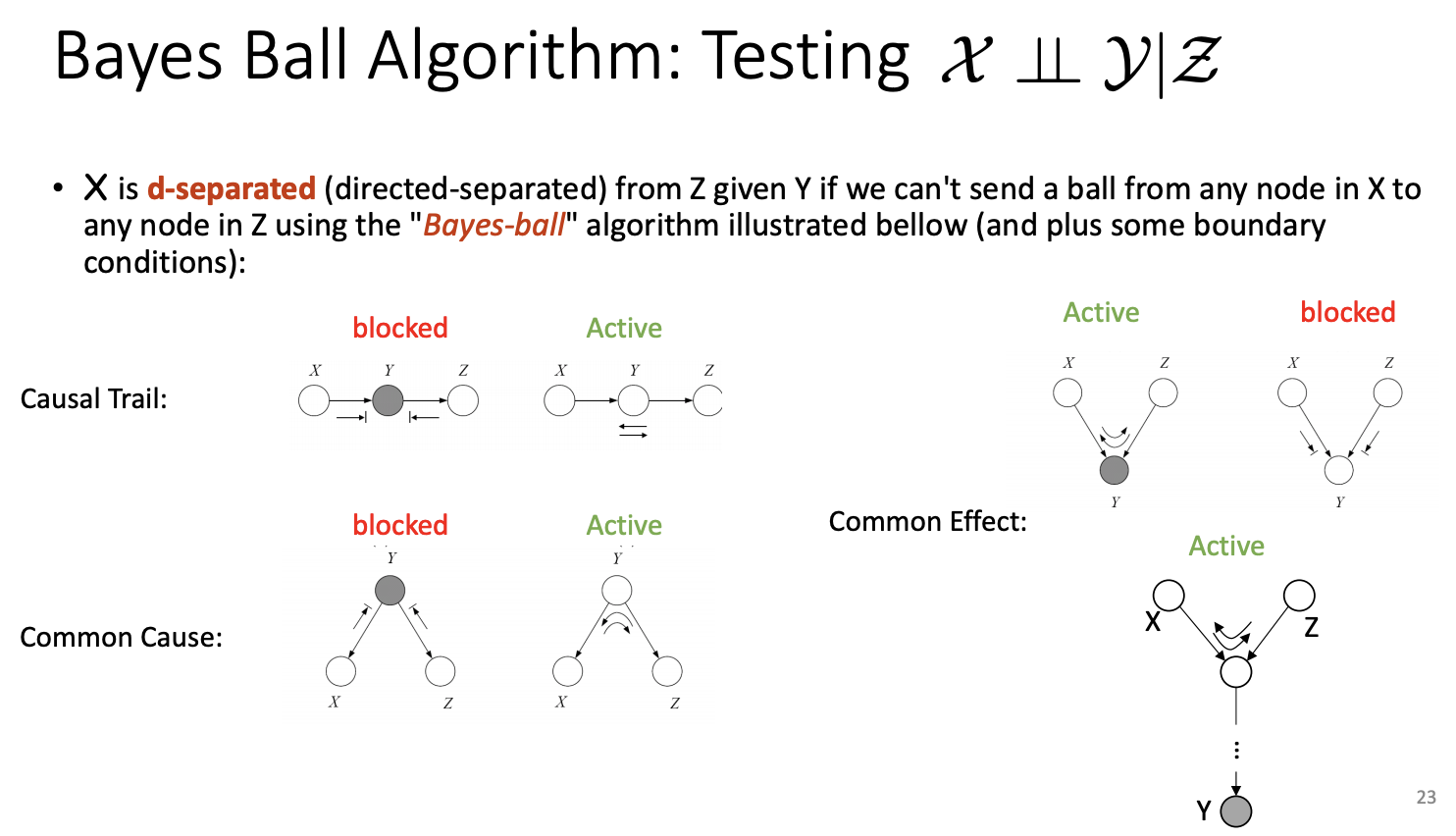

https://stats.stackexchange.com/questions/258012/explanation-of-i-map-in-a-markov-bayesian-network
Explanation of I-map in a Markov/Bayesian network


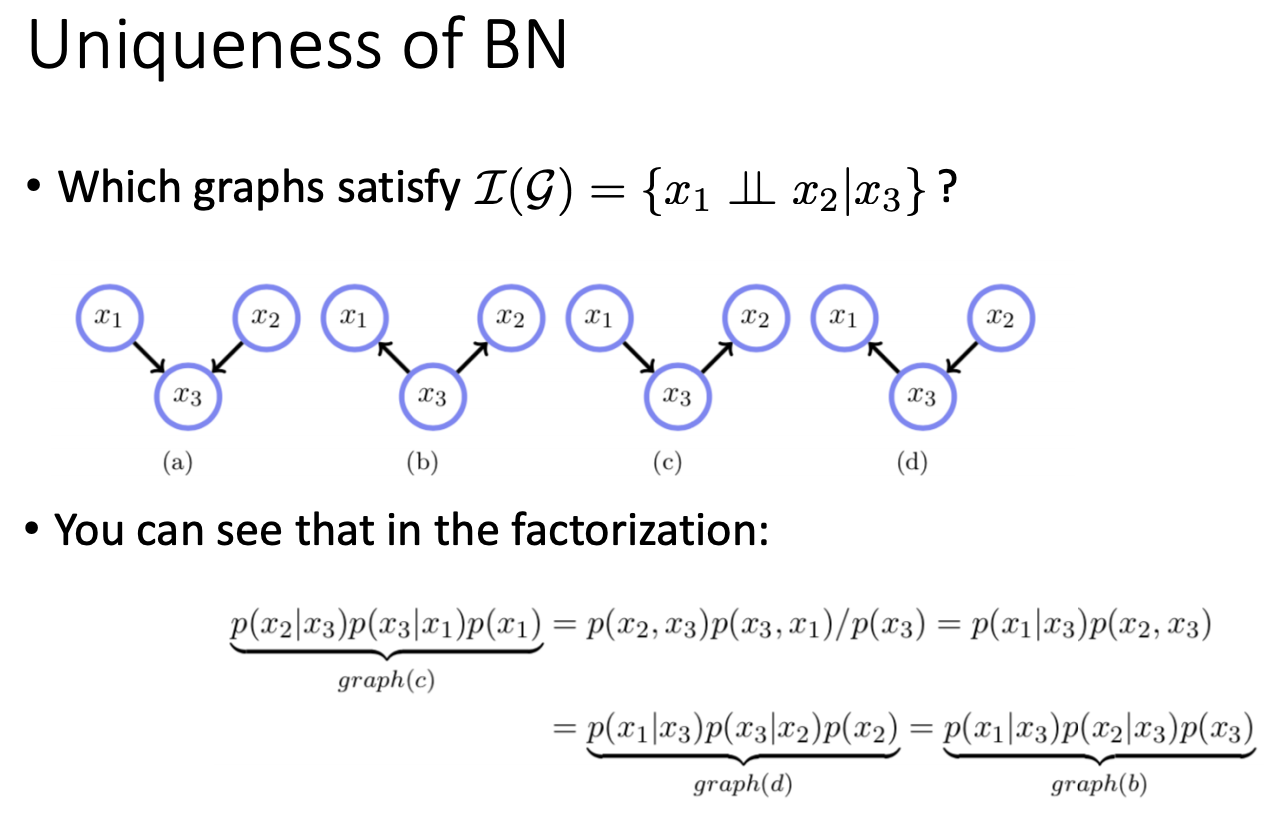
(a) satisfies


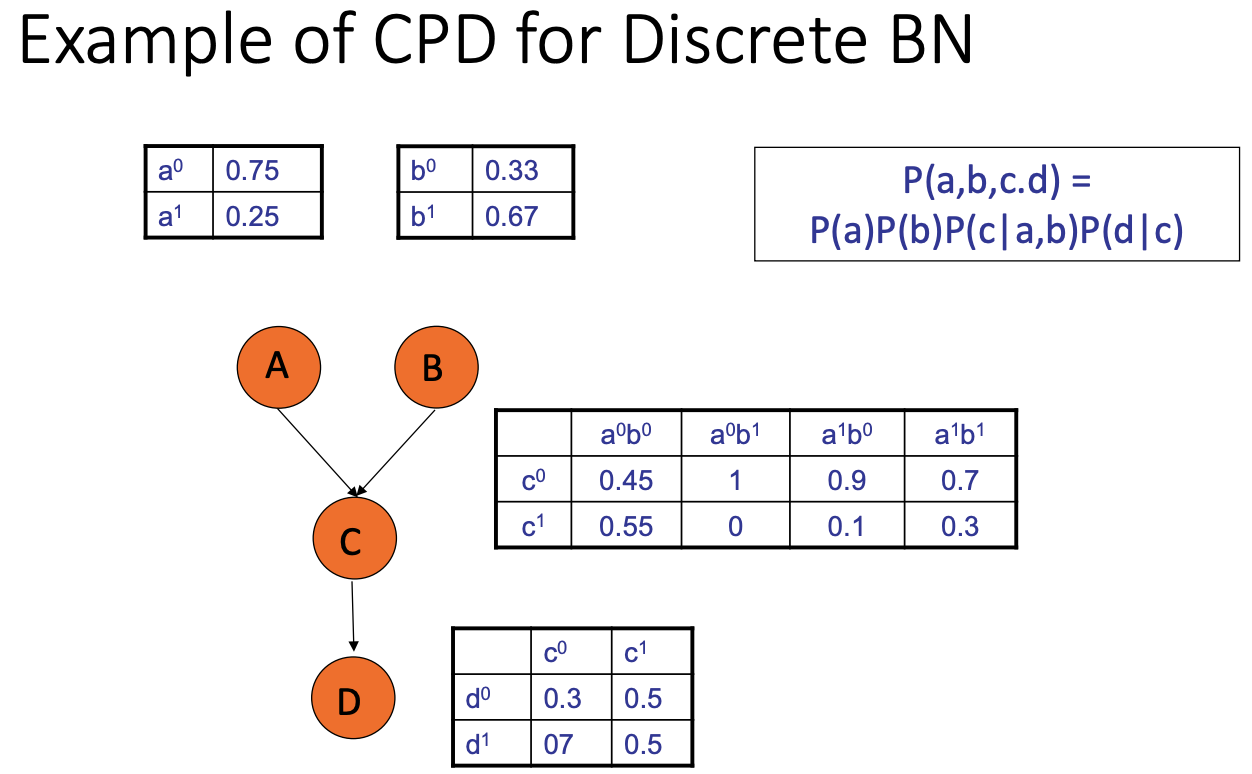
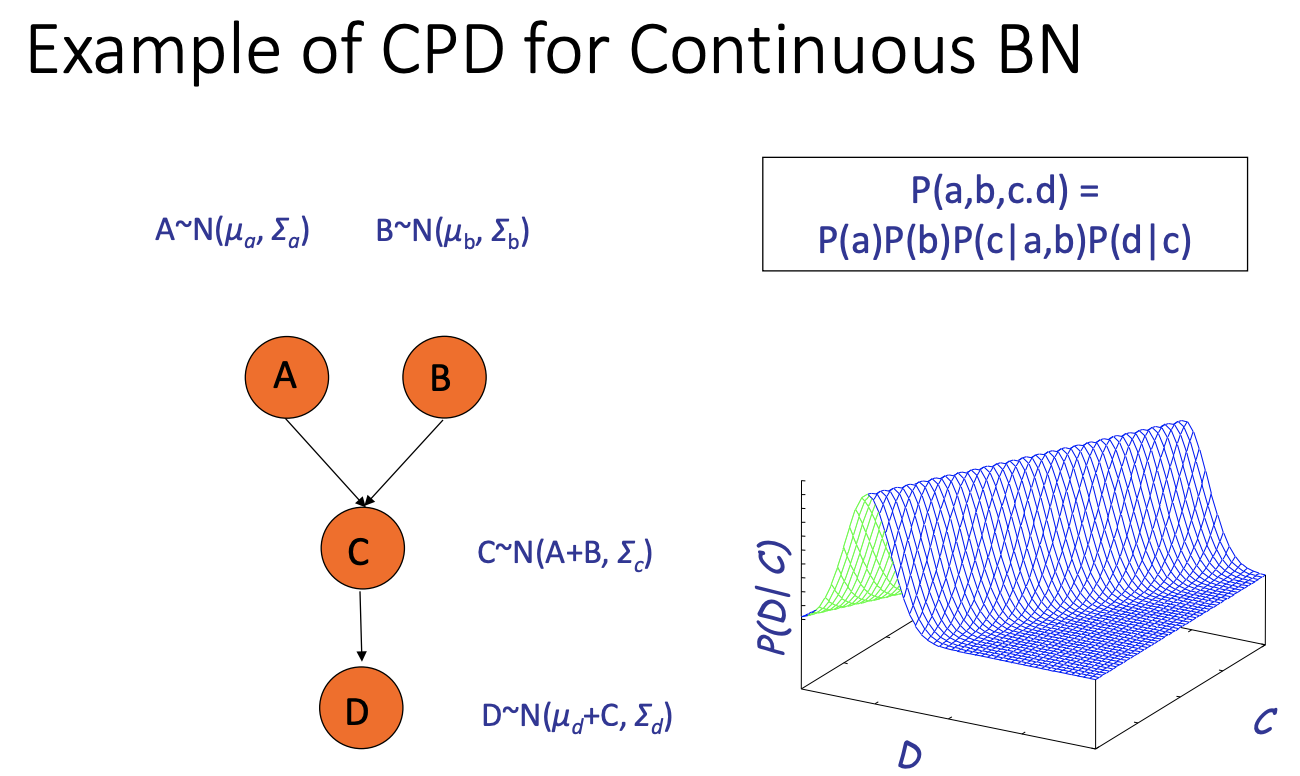
BN: Bayesian Network
CPD: conditional probability distribution
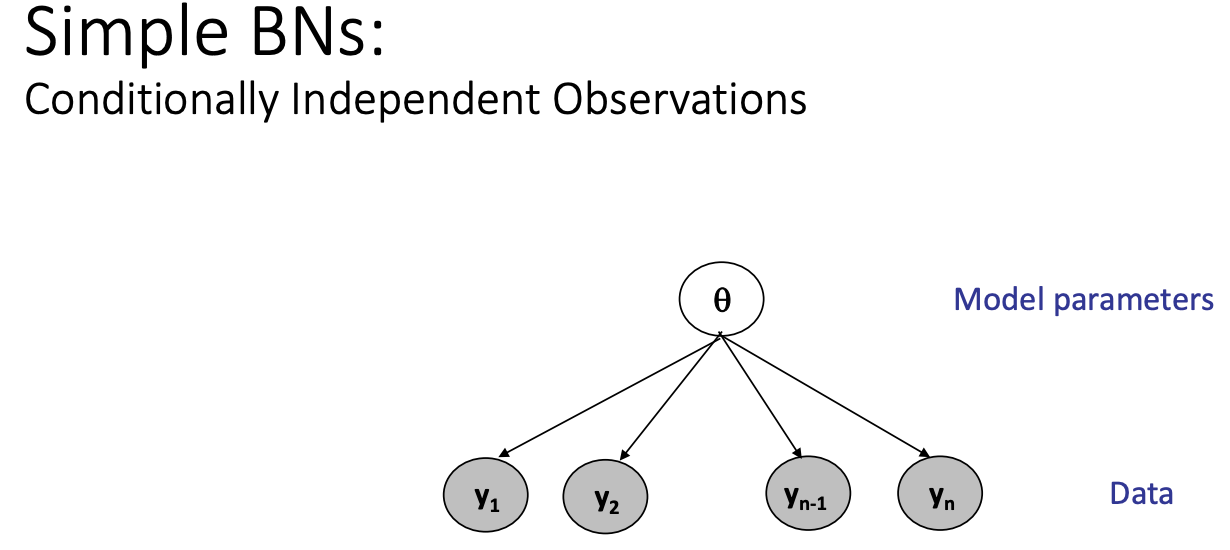


\theta_1 and \theta_k are outside of the box