OpenCV-影象處理(02、矩陣的掩膜操作)
1. 獲取影象畫素指標
- CV_Assert(myImage.depth() == CV_8U);
- Mat.ptr(int i=0) 獲取畫素矩陣的指標,索引i表示第幾行,從0開始計行數。
- 獲得當前行指標const uchar* current= myImage.ptr(row );
- 獲取當前畫素點P(row, col)的畫素值 p(row, col) =current[col]
2. 畫素範圍處理saturate_cast
這個函式的功能是確保RGB值得範圍在0~255之間,如下所示:
saturate_cast(-100),返回 0。
saturate_cast(288),返回255
saturate_cast(100),返回100
3. 掩膜操作實現影象對比度調整
紅色是中心畫素,從上到下,從左到右對每個畫素做同樣的處理操作,得到最終結果就是對比度提高之後的輸出影象Mat物件。
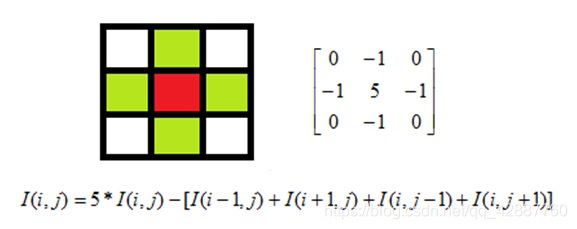
-
矩陣的掩膜操作十分簡單,根據掩膜來重新計算每個畫素的畫素值,掩膜(mask 也被稱為Kernel)
-
掩膜矩陣 3*3 在影象矩陣上移動與影象重合,與每一個重合的畫素點做掩膜操作,
-
公式:中心點掩膜後的顏色資料
-
這裡是3*3的矩陣,所以影象資料的第一行倒數第一行,第一列倒數第一列不做掩膜操作 。其中: i,j 表示畫素的位置,第 i 行,第 j 列, I(i,j) 表示每個通道顏色資料。
-
掩膜操作不是矩陣乘法,由公式可以看出
-
該掩膜矩陣的作用: 掩膜操作可以提高影象對比度,對比度提高可以增加影象感官度、銳化,讓看起來有點模糊的影象更清晰
程式程式碼
#include<opencv2/opencv.hpp>
#include<iostream>
#include<math.h>
using namespace cv;
int main(int argc,char** argv){
Mat src,dst;
src=imread("E:/Experiment/OpenCV/Pictures/dog2.jpg");
if(!src.data){
printf("could not load image ...");
return -1;
}
//CV_Assert(src.depth()==CV_8U);
//掩膜操作
int channels=src.channels();//影象的通道數
int cols=(src.cols)*src.channels();//列數*通道數
int rows=src.rows;//行數
dst=Mat::zeros(src.size(),src.type());//初始化 dst
for(int row=1 ; row<rows-1 ; row++){
const uchar* previous = src.ptr<uchar>(row - 1);//上一行
const uchar* current=src.ptr<uchar>(row);//當前行
const uchar* next =src.ptr<uchar>(row + 1);//下一行
uchar* output=dst.ptr<uchar>(row);
for(int col=1*channels ; col<cols-1*channels ; col++){
//掩膜操作:I(i,j) = 5*I(i,j) - [I(i-1,j)+I(i+1,j)+I(i,j-1)+I(i,j+1)]
output[col] =saturate_cast<uchar>( 5 * current[col] - (previous[col] + next[col] + current[col + channels] + current[col + channels]));
}
}
namedWindow("output1",CV_WINDOW_AUTOSIZE);
imshow("output1",src);
namedWindow("output2",CV_WINDOW_AUTOSIZE);
imshow("output2",dst);
waitKey(0);
return 0;
}
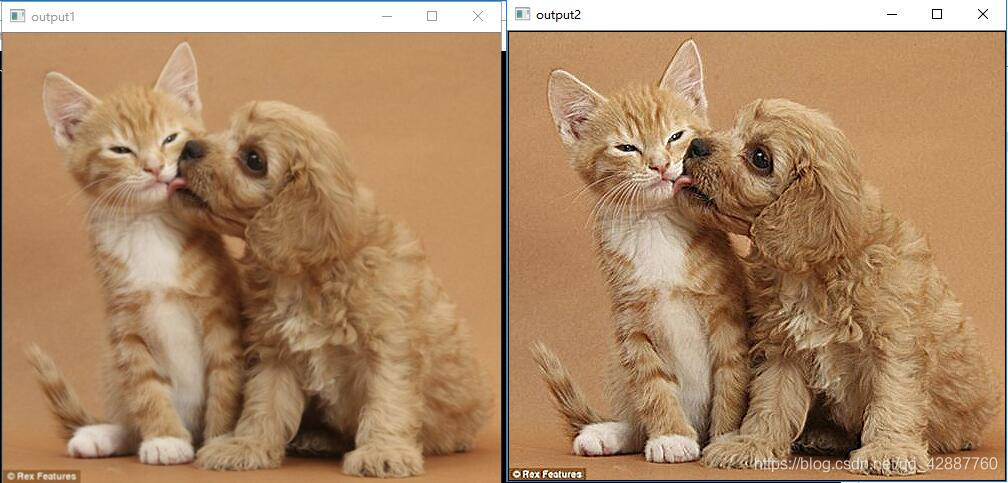
執行效果
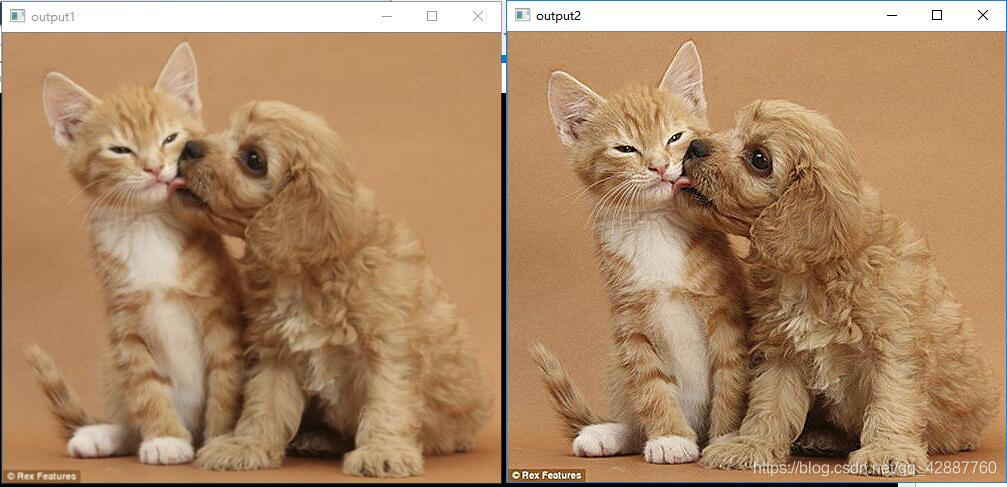
但是如果不使用 saturate_cast 函式
(即:將32行中output[col] =saturate_cast( 5 * current[col] - (previous[col] + next[col] + current[col + channels] + current[col + channels]));
換成output[col] = 5 * current[col] - (previous[col] + next[col] + current[col + channels] + current[col + channels]);),
將會得到以下效果:

4. 函式呼叫filter2D功能
- 定義掩膜:Mat kernel = (Mat_(3,3) << 0, -1, 0, -1, 5, -1, 0, -1, 0);
filter2D( src, dst, src.depth(), kernel );其中src與dst是Mat型別變數、src.depth表示點陣圖深度,有32、24、8等。
程式碼
#include<opencv2/opencv.hpp>
#include<iostream>
#include<math.h>
using namespace cv;
int main(int argc,char** argv){
Mat src,dst;
src=imread("E:/Experiment/OpenCV/Pictures/dog2.jpg");
if(!src.data){
printf("could not load image ...");
return -1;
}
Mat kernel=(Mat_<char>(3,3)<< 0, -1, 0, -1, 5, -1 , 0, -1, 0);
filter2D(src,dst,src.depth(),kernel);
//filter2D(src,dst,-1,kernel);
namedWindow("output1",CV_WINDOW_AUTOSIZE);
imshow("output1",src);
namedWindow("output2",CV_WINDOW_AUTOSIZE);
imshow("output2",dst);
waitKey(0);
return 0;
}
執行效果(與上述程式碼效果一致):
5.測試執行時間
方法一:(需要標頭檔案: time.h )
......
#include <time.h>
......
int main(){
clock_t start, finish;
double duration;
start = clock();
//......
//要執行的內容
//......
finish = clock();
duration = (double)(finish - start) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC;
printf("行優先用時: %f seconds\n", duration);
return 0;
}
方法二:
......
......
int main(){
double t=getTickCount();
//......
//要執行的內容
//......
double timeConsume = (getTickCount() - t) / getTickFrequency();
printf("time consume %.2f",timeConsume);
return 0;
}
案例程式碼:
#include<opencv2/opencv.hpp>
#include<iostream>
#include<math.h>
using namespace cv;
int main(int argc,char** argv){
Mat src,dst;
src=imread("E:/Experiment/OpenCV/Pictures/dog2.jpg");
if(!src.data){
printf("could not load image ...");
return -1;
}
double t=getTickCount();
Mat kernel=(Mat_<char>(3,3)<< 0, -1, 0, -1, 5, -1 , 0, -1, 0);
filter2D(src,dst,src.depth(),kernel);
//filter2D(src,dst,-1,kernel);
double timeConsume = (getTickCount() - t) / getTickFrequency();
printf("time consume %.2f",timeConsume);
namedWindow("output1",CV_WINDOW_AUTOSIZE);
imshow("output1",src);
namedWindow("output2",CV_WINDOW_AUTOSIZE);
imshow("output2",dst);
waitKey(0);
return 0;
}
