Tensorflow學習之Autoencoder(二)圖片降維並還原圖片
阿新 • • 發佈:2019-01-06

實現功能:
用Tensorflow實現Autoencoder,通過對圖片特徵的壓縮並解壓,將結果與原始資料進行對比,觀察處理過後的資料是不是和原始資料很相像。(這裡會用到MNIST資料)
實現程式碼:
import tensorflow as tf import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt # Import MNIST data from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data mnist = input_data.read_data_sets("/tmp/data", one_hot= False) # Visualize decoder setting # Parameter learning_rate = 0.01 training_epochs = 5 # 五組訓練 batch_size = 256 display_step = 1 examples_to_show = 10 # Network Parameters n_input = 784 # MNIST data input (img shape: 28*28) # tf Graph input(only pictures) X = tf.placeholder("float",[None, n_input]) # hidden layer settings n_hidden_1 = 256 # 1st layer num features n_hidden_2 = 128 # 2nd layer num features weights = { 'encoder_h1':tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([n_input,n_hidden_1])), 'encoder_h2': tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([n_hidden_1,n_hidden_2])), 'decoder_h1': tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([n_hidden_2,n_hidden_1])), 'decoder_h2': tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([n_hidden_1, n_input])), } biases = { 'encoder_b1': tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([n_hidden_1])), 'encoder_b2': tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([n_hidden_2])), 'decoder_b1': tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([n_hidden_1])), 'decoder_b2': tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([n_input])), } # Building the encoder def encoder(x): # Encoder Hidden layer with sigmoid activation #1 layer_1 = tf.nn.sigmoid(tf.add(tf.matmul(x, weights['encoder_h1']), biases['encoder_b1'])) # encoder Hidden layer with sigmoid activation #2 layer_2 = tf.nn.sigmoid(tf.add(tf.matmul(layer_1, weights['encoder_h2']), biases['encoder_b2'])) return layer_2 # Building the decoder def decoder(x): # decoder Hidden layer with sigmoid activation #1 layer_1 = tf.nn.sigmoid(tf.add(tf.matmul(x, weights['decoder_h1']), biases['decoder_b1'])) # Decoder Hidden layer with sigmoid activation #2 layer_2 = tf.nn.sigmoid(tf.add(tf.matmul(layer_1, weights['decoder_h2']), biases['decoder_b2'])) return layer_2 # Construct model encoder_op = encoder(X) # 128 Features decoder_op = decoder(encoder_op) # 784 Features # Prediction y_pred = decoder_op # After # Targets (Labels) are the input data. y_true = X # Before # Define loss and optimizer, minimize the squared error cost = tf.reduce_mean(tf.pow(y_true - y_pred, 2)) optimizer = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(learning_rate).minimize(cost) # Launch the graph with tf.Session() as sess: # tf 馬上就要廢棄tf.initialize_all_variables()這種寫法 # 替換成下面: sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer()) total_batch = int(mnist.train.num_examples/batch_size) # Training cycle for epoch in range(training_epochs): # Loop over all batches for i in range(total_batch): batch_xs, batch_ys = mnist.train.next_batch(batch_size) # max(x) = 1, min(x) = 0 # Run optimization op (backprop) and cost op (to get loss value) _, c = sess.run([optimizer, cost], feed_dict={X: batch_xs}) # Display logs per epoch step if epoch % display_step == 0: print("Epoch:", '%04d' % (epoch+1), "cost=", "{:.9f}".format(c)) print("Optimization Finished!") # # Applying encode and decode over test set encode_decode = sess.run( y_pred, feed_dict={X: mnist.test.images[:examples_to_show]}) # Compare original images with their reconstructions f, a = plt.subplots(2, 10, figsize=(10, 2)) for i in range(examples_to_show): a[0][i].imshow(np.reshape(mnist.test.images[i], (28, 28))) a[1][i].imshow(np.reshape(encode_decode[i], (28, 28))) plt.show()
實現效果:
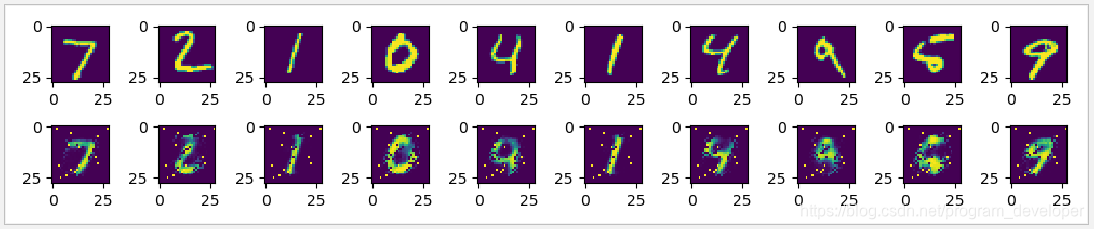
第一行圖片是真實的minist資料集中的圖片。
第二行圖片是minist資料集中的圖片經過自動編碼器之後還原出來的圖片。
Reference:
