Java ArrayList集合常用方法
建立物件:與其他普通的引用資料型別建立方式完全相同,但要指定容器中儲存的資料型別:
ArrayList<要儲存元素的資料型別> 變數名 = new ArrayList<要儲存元素的資料型別>();
集合中儲存的元素,只能為<>括號中指定的資料型別元素;
“<要儲存元素的資料型別>”中的資料型別必須是引用資料型別,不能是基本資料型別;
下面給出8種基本資料型別所對應的引用資料型別表示形式:
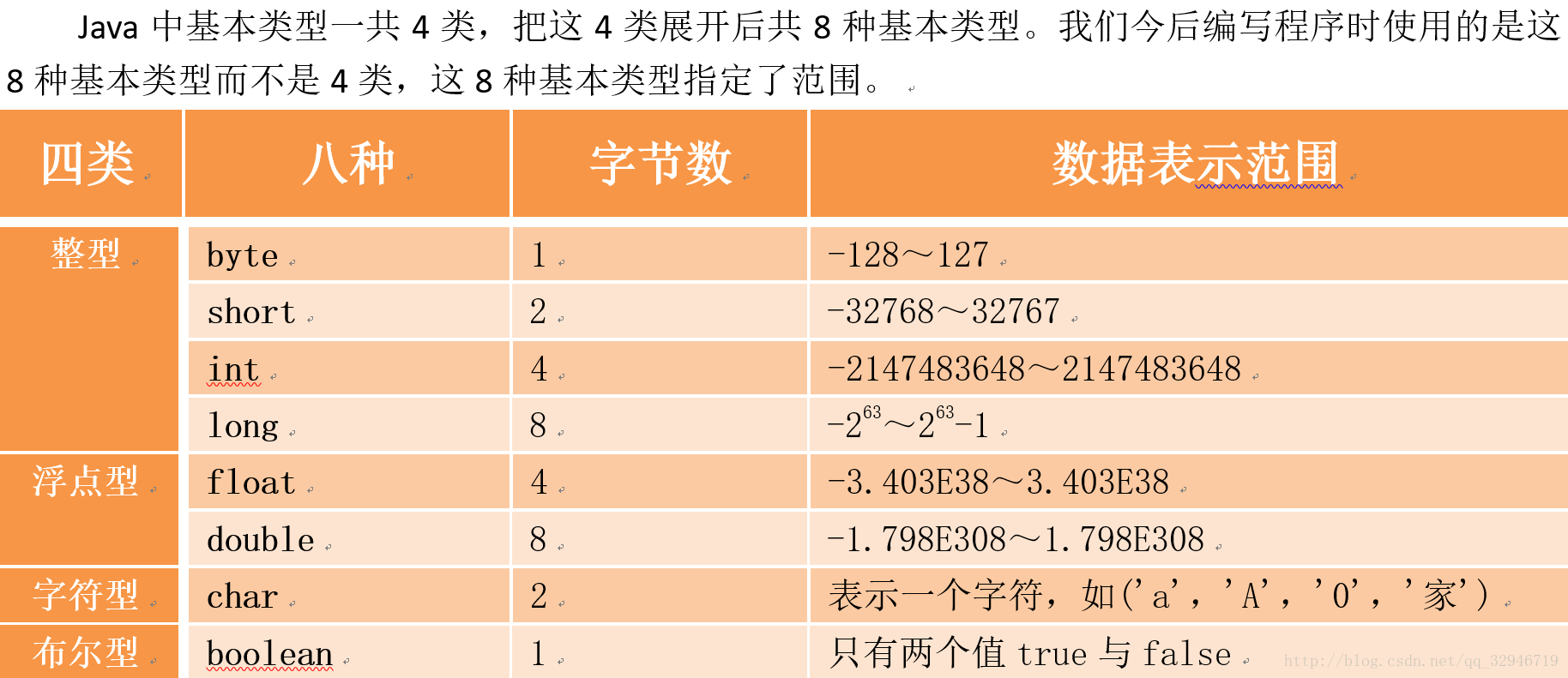
基本資料型別 對應的引用資料型別表示形式
byte Byte
short Short
Int Integer
long Long
float Float
double Double
char Character
boolean Boolean
附上java基本型別
常用方法
方法宣告 功能描述
boolean add(Object obj) 將指定元素obj追加到集合的末尾
Object get(int index) 返回集合中指定位置上的元素
int size() 返回集合中的元素個數
boolean add(int index, Object obj) 將指定元素obj插入到集合中指定的位置
Object remove(int index) 從集合中刪除指定index處的元素,返回該元素
void clear() 清空集合中所有元素
Object set(int index, Object obj) 用指定元素obj替代集合中指定位置上的元素
ArrayList原始碼解析
package java.util;
public class ArrayList<E> extends AbstractList<E>
implements List<E>, RandomAccess, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable
{
// 序列版本號
private static final long serialVersionUID = 8683452581122892189L;
// 預設容量大小
private static final