faster rcnn原始碼解析
之前一直是使用faster rcnn對其中的程式碼並不是很瞭解,這次剛好復現mask rcnn就仔細閱讀了faster rcnn,主要參考程式碼是pytorch-faster-rcnn ,部分參考和借用了以下部落格的圖片
[1] CNN目標檢測(一):Faster RCNN詳解
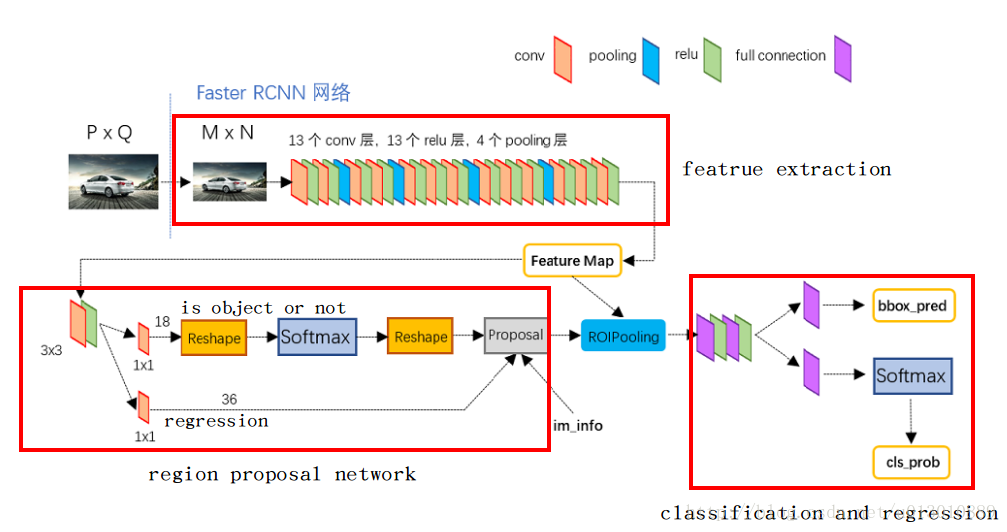
整體框架
- 首先圖片進行放縮到W*H,然後送入vgg16(去掉了pool5),得到feature map(W/16, H/16)
- 然後feature map上每個點都對應原圖上的9個anchor,送入rpn層後輸出兩個: 這9個anchor前背景的概率以及4個座標的迴歸
- 每個anchor經過迴歸後對應到原圖,然後再對應到feature map經過roi pooling後輸出7*7大小的map
- 最後對這個7*7的map進行分類和再次迴歸
(此處均為大體輪廓,具體細節見後面)
資料層
- 主要利用工廠模式適配各種資料集 factory.py中利用lambda表示式(泛函)
- 自定義適配自己資料集的類,繼承於imdb
- 主要針對資料集中生成roidb,對於每個圖片保持其中含有的所有的box座標(0-index)及其類別,然後順便儲存它的面積等引數,最後記錄所有圖片的index及其根據index獲取絕對地址的方法
# factory.py
from datasets.mydataset import mydataset
for dataset in ['xxdataset']:
for RPN
anchors生成
經過feature extraction後,feature map的大小是(W/16, H/16), 記為(w,h),然後每個feature map每個點生成k個anchor,論文中設定了3中ratio, 3種scale 共產生了w*h*9個anchors
# # array([[ -83., -39., 100., 56.],
# [-175., -87., 192., 104.],
# [-359., -183., 376., 200.],
# [ -55., -55., 72., 72.],
# [-119., -119., 136., 136.],
# [-247., -247., 264., 264.],
# [ -35., -79., 52., 96.],
# [ -79., -167., 96., 184.],
# [-167., -343., 184., 360.]])
# 先以左上角(0,0)為例生成9個anchor,然後在向右向下移動,生成整個feature map所有點對應的anchoranchors前背景和座標預測
正如整體框架上畫的那樣,feature map後先跟了一個3*3的卷積,然後分別用2個1*1的卷積,預測feature map上每個點對應的9個anchor屬於前背景的概率(9*2)和4個迴歸的座標(9*4)
# rpn
self.rpn_net = nn.Conv2d(self._net_conv_channels, cfg.RPN_CHANNELS, [3, 3], padding=1)
self.rpn_cls_score_net = nn.Conv2d(cfg.RPN_CHANNELS, self._num_anchors * 2, [1, 1])
self.rpn_bbox_pred_net = nn.Conv2d(cfg.RPN_CHANNELS, self._num_anchors * 4, [1, 1])
rpn = F.relu(self.rpn_net(net_conv))
rpn_cls_score = self.rpn_cls_score_net(rpn) # batch * (num_anchors * 2) * h * w
rpn_bbox_pred = self.rpn_bbox_pred_net(rpn) # batch * (num_anchors * 4) * h * wanchor target
對上一步產生的anchor分配target label,1前景or0背景or-1忽略,以便訓練rpn(只有分配了label的才能計算loss,即參與訓練)
無NMS
1. 對於每個gt box,找到與他iou最大的anchor然後設為正樣本
2. 對於每個anchor只要它與任意一個gt box iou>0.7即設為正樣本
3. 對於每個anchor它與任意一個gt box iou都<0.3即設為負樣本
4. 不是正也不是負的anchor被忽略
注意
正樣本的數量由num_fg = int(cfg.TRAIN.RPN_FG_FRACTION * cfg.TRAIN.RPN_BATCHSIZE)控制,預設是256*0.5=128,即最多有128個正樣本參與rpn的訓練. 假如正樣本有1234個,則隨機抽1234-128個正樣本將其label設定為-1,即忽略掉,當然正樣本也有可能不足128個,那就都保留下來.
負樣本的數量由num_bg = cfg.TRAIN.RPN_BATCHSIZE - np.sum(labels == 1),同理如果超額也為多餘的忽略.
TRAIN.RPN_FG_FRACTION控制參與rpn訓練的正樣本的數量
注意在RPN階段需要的配置引數都有RPN字首,與後面的fast rcnn的引數區別開
# Max number of foreground examples
# __C.TRAIN.RPN_FG_FRACTION = 0.5
# Total number of examples
#__C.TRAIN.RPN_BATCHSIZE = 256
# subsample positive labels if we have too many
num_fg = int(cfg.TRAIN.RPN_FG_FRACTION * cfg.TRAIN.RPN_BATCHSIZE)
fg_inds = np.where(labels == 1)[0]
if len(fg_inds) > num_fg:
disable_inds = npr.choice(
fg_inds, size=(len(fg_inds) - num_fg), replace=False)
labels[disable_inds] = -1
# subsample negative labels if we have too many
num_bg = cfg.TRAIN.RPN_BATCHSIZE - np.sum(labels == 1)
bg_inds = np.where(labels == 0)[0]
if len(bg_inds) > num_bg:
disable_inds = npr.choice(
bg_inds, size=(len(bg_inds) - num_bg), replace=False)
labels[disable_inds] = -1Fast RCNN
proposal
對RPN產生的anchor進行處理,有NMS
1. 首先利用4個座標迴歸值對預設的w*h*9個anchor進行座標變換生成proposal
2. 然後利用前景概率對這些proposal進行降序排列,然後留下RPN_PRE_NMS_TOP_N個proposal 訓練是留下12000,測試是留下6000
3. 對剩下的proposal進行NMS處理,閾值是0.7
4. 對於剩下的proposal,只留下RPN_POST_NMS_TOP_N,訓練是2000,測試是300
最終剩下的proposal即為rois了
proposal target
對留下的proposal(train:2000, test沒有這個階段,因為測試不知道gt無法分配)分配target label,屬於具體哪一個類別,以便訓練後面的分類器, 下面以train階段的某個圖片為例即該張圖片有2000個proposal,gt中含有15個類別的box(不含背景) (全庫有20個類別)
# Minibatch size (number of regions of interest [ROIs])
# __C.TRAIN.BATCH_SIZE = 128
# Fraction of minibatch that is labeled foreground (i.e. class > 0)
# __C.TRAIN.FG_FRACTION = 0.25 控制fast rcnn中rois的正負樣本比例為1:3
num_images = 1
rois_per_image = cfg.TRAIN.BATCH_SIZE / num_images # 預設為128
fg_rois_per_image = int(round(cfg.TRAIN.FG_FRACTION * rois_per_image)) # 0.25*128- 計算每個roi(proposal)與15個gt box做iou,得到overlaps(2000, 15) ,然後選擇最大的iou作為這個roi的gt label(坑點: gt box的順序不一定和label對應,一定要取gt box的第4個維度作為label,因為可能包含15個gt box,但是全庫是有20中label的)
- 然後記roi與其target label的ovlap>TRAIN.FG_THRESH(0.5)的為fg,0.1
if fg_inds.numel() > 0 and bg_inds.numel() > 0:
fg_rois_per_image = min(fg_rois_per_image, fg_inds.numel())
fg_inds = fg_inds[torch.from_numpy(npr.choice(np.arange(0, fg_inds.numel()), size=int(fg_rois_per_image), replace=False)).long().cuda()]
# ......
# 主要解讀npr.choice(np.arange(0, fg_inds.numel()), size=int(fg_rois_per_image), replace=False)
# 在np.arange(0, fg_inds.numel())隨機取int(fg_rois_per_image)個數,replace=False不允許重複roi pooling
上一步得到了很多大小不一的roi,對應到feature map上也是大小不一的,但是fc是需要fixed size的,於是根據SPPNet論文筆記和caffe實現說明,出來了roi pooling(spp poolingfroze 前面的卷積只更新後面的fc,why見fast rcnn的2.3段解釋的)
我主要參考了這篇部落格Region of interest pooling explained,但是我感覺它的示意圖是有問題的,應該有overlap的
1. 我們首先根據feature map和原圖的比例,把roi在原圖上的座標對映到feature map上, 然後扣出roi對應部分的feature(藍色框為實際位置,浮點座標(1.2,0.8)(7.2,9.7),四捨五入量化到紅色框(1,1)(7,10))
int roi_start_w = round(rois_flat[index_roi + 1] * spatial_scale); // spatial_scale 1/16
int roi_start_h = round(rois_flat[index_roi + 2] * spatial_scale);
int roi_end_w = round(rois_flat[index_roi + 3] * spatial_scale);
int roi_end_h = round(rois_flat[index_roi + 4] * spatial_scale);2. 對紅色紅色框進行roipooling
float bin_size_h = (float)(roi_height) / (float)(pooled_height); // 9/7
float bin_size_w = (float)(roi_width) / (float)(pooled_width); // 7/7=1
for (ph = 0; ph < pooled_height; ++ph){
for (pw = 0; pw < pooled_width; ++pw){
int hstart = (floor((float)(ph) * bin_size_h));
int wstart = (floor((float)(pw) * bin_size_w));
int hend = (ceil((float)(ph + 1) * bin_size_h));
int wend = (ceil((float)(pw + 1) * bin_size_w));
hstart = fminf(fmaxf(hstart + roi_start_h, 0), data_height);
hend = fminf(fmaxf(hend + roi_start_h, 0), data_height);
wstart = fminf(fmaxf(wstart + roi_start_w, 0), data_width);
wend = fminf(fmaxf(wend + roi_start_w, 0), data_width);
// ......
// 經過計算後w步長為1,視窗為1,沒有overlap,h視窗步長不定都有overlap,注意在ph=3時視窗為3了
// 注意邊界 pw=pooled_width-1時 wend=(ceil((float)(pw + 1) * bin_size_w))
// =(ceil((float)pooled_width * (float)(roi_width) / (float)
// =(pooled_width)))=ceil(roi_width)=roi_width
// 剛好把所有roi對應的feature map覆蓋完,hend同理
// roi_height roi_width小於pooled_height pooled_width時overlap就多一點唄3. 對每個劃分的pool bin進行max或者average pooling最後得到7*7的feature map
分類和迴歸
roi pooling後就得到fixed size的feature map(7*7),然後送入cls_score_net得到分類,送入bbox_pred_net粗暴的座標迴歸和rpn時一樣
self.cls_score_net = nn.Linear(self._fc7_channels, self._num_classes)
self.bbox_pred_net = nn.Linear(self._fc7_channels, self._num_classes * 4)Loss採用smooth L1 Loss(和fast rcnn一致,rcnn採用的是L2 Loss)。
prior_centers = center_size(prior_boxes) #(cx, cy, w, h)
gt_centers = center_size(gt_boxes) #(cx, cy, w, h)
# tx=(gx-px)/pw gx是gt的中心座標x,px是proposal的中心座標x,pw是預測的寬。ty同理
center_targets = (gt_centers[:, :2] - prior_centers[:, :2]) / prior_centers[:, 2:]
# 參照tw,th的公式
# 加了log, 降低w,h產生的loss的數量級, 讓它在loss裡佔的比重小些, 不至於因為w,h的loss太大而讓x,y產生的loss無用
# 因為若是x,y沒預測準確, w,h再準確也沒有用.
size_targets = torch.log(gt_centers[:, 2:]) - torch.log(prior_centers[:, 2:])
all_targets = torch.cat((center_targets, size_targets), 1)
loss = F.smooth_l1_loss(deltas, all_targets, size_average=False)/(eps + prior_centers.size(0))smoothed L1 Loss is a robust L1 loss that is less sensitive to outliers than the L2 loss used in R-CNN and SPPnet.
上述是Fast RCNN解釋為什麼採用smoothed L1, 因為它對噪音點不那麼敏感,即對離目標太遠的點不敏感。因為L2loss求導後 0.5*(t-v)^2 求導-> (t-v) 會有一個(t-v) 的係數在,如果v離t太遠梯度很容易爆炸(需要精緻地調節學習率),而smoothed L1中當|t-v|>1, |t-v|-0.5 求導-> 係數是±1, 這樣就避免了梯度爆炸, 也就是它更加魯棒。(t是target,v是需要預測出來的中心xy和尺寸wh)
測試
繼續假設全部類別數是20種
1. 圖片送入網路後前傳,沒有給anchor proposal指定gt的部分(忽略_anchor_target_layer _proposal_target_layer)
2. 經過proposal得到300個roi,經過cls_score_net bbox_pred_net得到每個roi在20個類別的置信度和4個座標迴歸值(可在測試時把這個迴歸值用上,也可以不用)
3. 測試時300個roi類別未知,所以可以對應20個類別,即有300*20個box,300*20個置信度
3. 對每一類,取300個roi>thresh(預設為0.),然後進行nms獲得留下的box
4. 然後對20類留下的所有box,按概率排序,留下設定的max_per_image個box
有個不解就是為什麼對於每個roi,不是選擇其置信度最大的類別,而可以對應到20種類別,可能是map演算法,同等置信度下,多一些box得分會高一些
for j in range(1, imdb.num_classes):
inds = np.where(scores[:, j] > thresh)[0]
cls_scores = scores[inds, j]
cls_boxes = boxes[inds, j*4:(j+1)*4]
cls_dets = np.hstack((cls_boxes, cls_scores[:, np.newaxis])) \
.astype(np.float32, copy=False)
keep = nms(torch.from_numpy(cls_dets), cfg.TEST.NMS).numpy() if cls_dets.size > 0 else []
cls_dets = cls_dets[keep, :]
all_boxes[j][i] = cls_dets延伸
• First, take the top K regions according to RPN score.
• Then, non-maximal suppression (NMS) with overlapping ratio of 0.7 is applied to perform de-duplication.
• Third, top k regions are selected as RoIs.
Intuitively, it is more likely for large regions to overlap than small regions, so large regions have a higher chance to be suppressed對這句話保留意見,nms算的是iou,沒有偏向抑制大的region吧
ALL是top12000 proposal都送入後面的網路,不進行nms PRE是利用第一行已經訓練好的faster rcnn直接得到最終的正負樣本比例 POW: 比例和scale成反比,詳細見文章。TOP是test是選擇top 5000不進行nms(faster rcnn本身是選擇top 6000然後nms,最後再取top300)
In fact, we find this advantage of TOP over NMS consistently exists when K is sufficiently large.