海量資料處理的 Top K演算法(問題) 小頂堆實現
問題描述:有N(N>>10000)個整數,求出其中的前K個最大的數。(稱作Top k或者Top 10)
問題分析:由於(1)輸入的大量資料;(2)只要前K個,對整個輸入資料的儲存和排序是相當的不可取的。
可以利用資料結構的最小堆(小頂堆)來處理該問題。
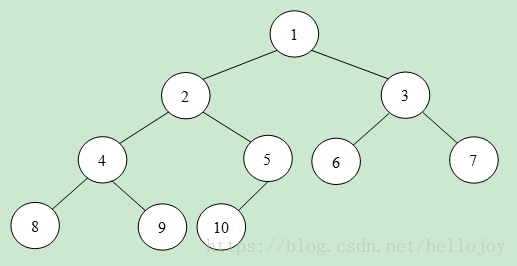
最小堆如圖所示,對於每個非葉子節點的數值,一定不大於孩子節點的數值。這樣可用含有K個節點的最小堆來儲存K個目前的最大值(當然根節點是其中的最小數值)。
每次有資料輸入的時候可以先與根節點比較。若不大於根節點,則捨棄;否則用新數值替換根節點數值。並進行最小堆的調整。
在系統中,我們經常會遇到這樣的需求:將大量(比如幾十萬、甚至上百萬)的物件進行排序,然後只需要取出最Top的前N名作為排行榜的資料,這即是一個TopN演算法。常見的解決方案有三種:
(1)直接使用List的Sort方法進行處理。
(2)使用排序二叉樹進行排序,然後取出前N名。
(3)使用最大堆排序,然後取出前N名。
第一種方案的效能是最差的,後兩種方案效能會好一些,但是還是不能滿足我們的需求。最主要的原因在於使用二叉樹和最大堆排序時,都是對所有的物件進行排序,而不是將代價花費在我們需要的少數的TopN上。
對於堆結構來說,並不需要你獲取所有的資料,只需要對前N個數據進行處理。因此可以通過堆疊的進入排出,用小頂堆實現,調整最小堆的時間複雜度為lnN,總時間複雜度為nlnN
myheap:
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
# 最小堆化heap
def siftdown(heap, start, end):
while True:
left_child = start * 2 + 1
if left_child > end:
break
if left_child + 1 <= end:
if heap[left_child] > heap[left_child+1]:
left_child += 1
if heap[left_child] < heap[start]:
heap[left_child], heap[start] = heap[start], heap[left_child]
start = left_child
else:
break
def minheapstyle(heap):
first = len(heap) // 2 - 1
for x in xrange(first, -1, -1):
siftdown(heap, x, len(heap)-1)
def push(heap, item):
heap.append(item)
minheapstyle(heap)
def pushpop(heap, item):
if heap[0] < item:
heap[0] = item
minheapstyle(heap)
if __name__ == '__main__':
heap = [10,4,5,3,5,6,2]
minheapstyle(heap)
print heap
TOPN:
import myheap
def findminn(list, n):
heap = []
for x in list:
if len(heap) < n:
myheap.push(heap, x)
else :
myheap.pushpop(heap, x)
return heap
if __name__ == '__main__':
l = [5,6,7,8,9,10,5646]
#n=5
heap = findminn(l,5)
print heap
雖然python有類似的最小堆結構,但是當我們需要處理更復雜的問題時,可能依然需要自己定製。