核心模組遍歷程序和任務佇列儲存到proc檔案中
阿新 • • 發佈:2019-01-07
實現一個模組用它遍歷當前程序的父程序和任務佇列,並將遍歷的結果輸出到一個proc 檔案中(遍歷可以從 current 當前程序開始,父程序遍歷到初始化程序,遍歷任務佇列可以利用 for_each_process 巨集)。
下面是我的核心模組的實現部分:
/************************************************************
* 使用核心模組從當前程序開始先前遍歷,知道找到第一個程序為止 *
* 並將遍歷的結果儲存到proc檔案中 *
***********************************************************/ 其中的Makefile檔案為:
obj-m := process.o
all:
make -C /lib/modules/$(shell uname -r)/build M=$(shell pwd) modules
clean:
make -C /lib/modules/$(shell uname -r)/build M=$(shell pwd) clean 現在我們使用make命令編譯,編譯完成時候,我們動態載入核心模組
sudo insmod process.ko
然後我們檢視proc文件下我們建立的檔案:
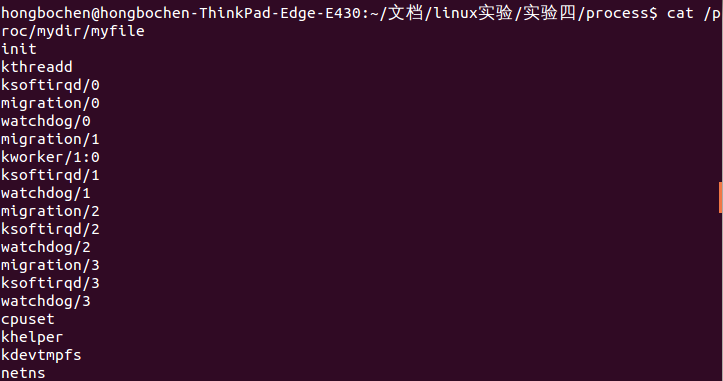
cat /proc/mydir/myfile執行後的效果為:
下面我們檢視一下所有的父程序的檔案:
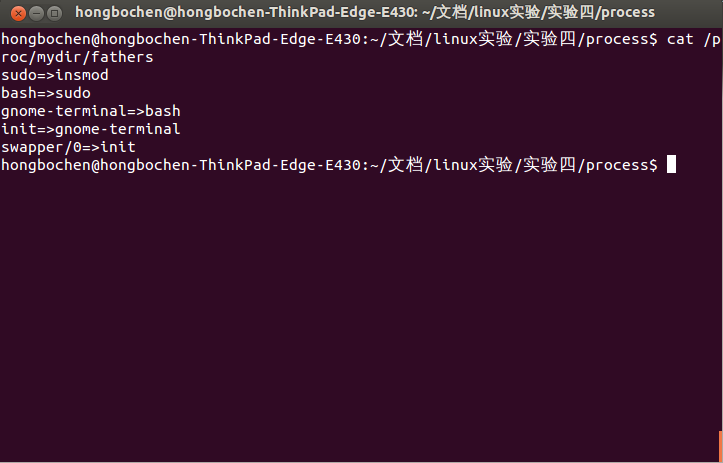
cat /proc/mydir/fathers執行效果為: