二叉樹的常見筆試面試題
阿新 • • 發佈:2019-01-07
在二叉樹的基本操作裡已經說明如何用遞迴的方法進行二叉樹的遍歷,那麼如何用非遞迴的方法來進行二叉樹的遍歷呢,請看下文
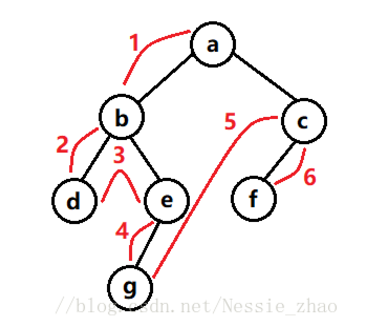
1.使用非遞迴方式進行二叉樹的先序遍歷
思想:先將根節點入棧然後出棧,繼續將右子樹先入棧,然後將左子樹入棧,因為棧是先進後出的原則,所以左子樹後進是先出來的
實現程式碼:
void TreePreOrderByLoop(TreeNode* root) { if(root == NULL) { return; } //先把根結點入棧 SeqStack stack; SeqStackInit(&stack); SeqStackPush(&stack,root); //迴圈開始,棧為空時迴圈結束 TreeNode* cur = NULL; while(SeqStackTop(&stack,&cur)) { //取棧頂元素為當前元素。出棧 SeqStackPop(&stack); //列印當前元素 printf("%c ",cur->data); //把當前元素的左子樹入棧 if(cur->rchild != NULL) { SeqStackPush(&stack,cur->rchild); } //把當前的右子樹入棧 if(cur->lchild != NULL) { SeqStackPush(&stack,cur->lchild); } } printf("\n"); return; }
測試程式碼:
void TestPreOrderByLoop()
{
TEST_HEADER;
TreeNodeType data[] = "abd##eg###c#f##";
TreeNode* root = TreeCreate(data,sizeof(data)/sizeof(data[0])-1,'#');
TreePreOrderByLoop(root);
}執行結果:
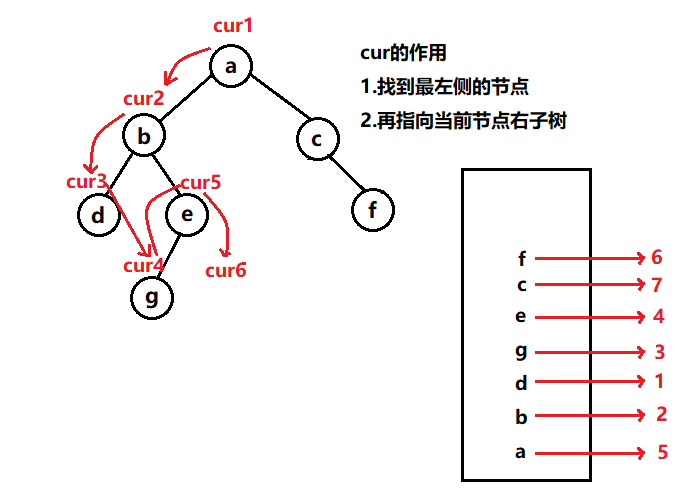
2.使用非遞迴方式進行二叉樹的中序遍歷
實現程式碼:
void TreeInOrderByLoop(TreeNode* root) { if(root == NULL) { return; } SeqStack stack; SeqStackInit(&stack); //定義cur指向根節點 TreeNode* cur = root; while(1) { //迴圈的判定cur是否為空,如果不為空,就將cur入棧 //並將cur指向cur->lchild while(cur != NULL) { SeqStackPush(&stack,cur); cur = cur->lchild; } //如果cur為空,取棧頂元素,訪問出棧 TreeNode* top; int ret = SeqStackTop(&stack,&top); if(ret == 0) { //說明棧中已經沒有元素了 return; } printf("%c ",top->data); SeqStackPop(&stack); //讓cur指向棧頂元素的右子樹,重複剛才迴圈判空的過程 cur = top->rchild; } printf("\n"); return; }
測試程式碼:
void TestInOrderByLoop()
{
TEST_HEADER;
TreeNodeType data[] = "abd##eg###c#f##";
TreeNode* root = TreeCreate(data,sizeof(data)/sizeof(data[0])-1,'#');
TreeInOrderByLoop(root);
}執行結果:
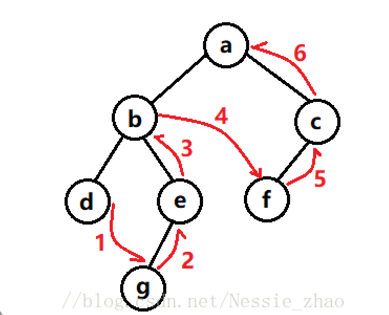
3.使用非遞迴方式進行二叉樹的後序遍歷
實現程式碼:
void TreePostOrderByLoop(TreeNode* root) { if(root == NULL) { return; } SeqStack stack; SeqStackInit(&stack); //定義一個cur指向root TreeNode* cur = root; //pre儲存上一個訪問過的元素 TreeNode* pre = NULL; while(1) { //迴圈判斷cur是否為空,如果不為空就將cur入棧 //並且將cur指向cur->lchild while(cur != NULL) { SeqStackPush(&stack,cur); cur = cur->lchild; } TreeNode* top; int ret = SeqStackTop(&stack,&top); if(ret == 0) { printf("\n"); return; } //如果cur為空,迴圈取棧頂元素 //對棧頂元素進行判定 //a)如果棧頂元素的右子樹和訪問的上一個元素是同一個元素 //b)棧頂元素的右子樹為空 // 此時才能夠訪問棧頂元素,同時進行出棧 //如果不滿足剛才的條件,就讓cur指向棧頂元素的右子樹,重複迴圈 if(top->rchild == NULL || top->rchild == pre) { printf("%c ",top->data); SeqStackPop(&stack); pre = top; } else { cur = top->rchild; } } return; }
測試程式碼:
void TestPostOrderByLoop()
{
TEST_HEADER;
TreeNodeType data[] = "abd##eg###c#f##";
TreeNode* root = TreeCreate(data,sizeof(data)/sizeof(data[0])-1,'#');
TreePostOrderByLoop(root);
}執行結果:
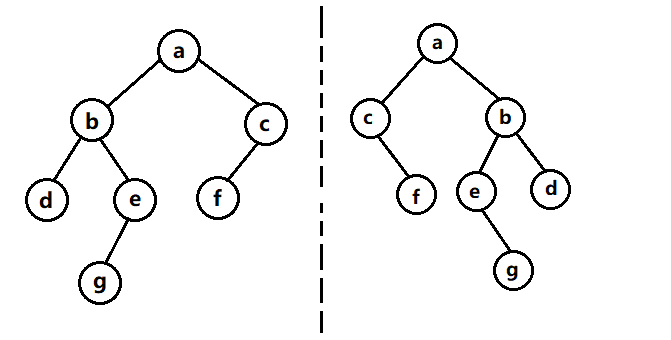
4.二叉樹的映象(就像人照鏡子一樣,原來的左子樹變為右子樹,原來的右子樹變為左子樹)
(1)遞迴方法
實現程式碼:
void Swap(TreeNode** a,TreeNode** b)
{
TreeNode* tmp = *a;
*a = *b;
*b = tmp;
return;
}
void TreeMirror(TreeNode* root)
{
if(root == NULL)
{
return;
}
Swap(&root->lchild,&root->rchild);
TreeMirror(root->lchild);
TreeMirror(root->rchild);
}測試程式碼:
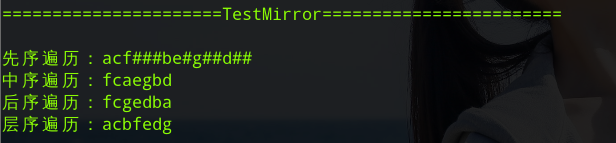
void TestMirror()
{
TEST_HEADER;
TreeNodeType data[] = "abd##eg###c#f##";
TreeNode* root = TreeCreate(data,sizeof(data)/sizeof(data[0])-1,'#');
TreeMirror(root);
printf("\n先序遍歷:");
TreePreOrder(root);
printf("\n中序遍歷:");
TreeInOrder(root);
printf("\n後序遍歷:");
TreePostOrder(root);
printf("\n層序遍歷:");
TreeLevelOrder(root);
}執行結果:
(2)非遞迴方法:
實現程式碼:
void TreeMirrorByLoop(TreeNode* root)
{
if(root == NULL)
{
return;
}
SeqQueue queue;
SeqQueueInit(&queue);
SeqQueuePush(&queue,root);
TreeNode* cur = NULL;
while(SeqQueueFront(&queue,&cur))
{
//此處的訪問相當於交換左右子樹
Swap(&cur->lchild,&cur->rchild);
SeqQueuePop(&queue);
if(cur->lchild != NULL)
{
SeqQueuePush(&queue,cur->lchild);
}
if(cur->rchild != NULL)
{
SeqQueuePush(&queue,cur->rchild);
}
}
return;
}測試程式碼:
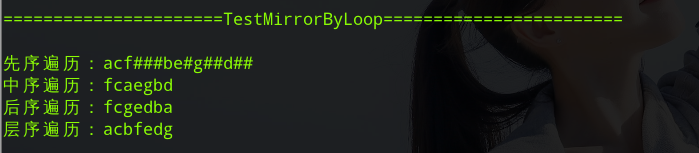
void TestMirrorByLoop()
{
TEST_HEADER;
TreeNodeType data[] = "abd##eg###c#f##";
TreeNode* root = TreeCreate(data,sizeof(data)/sizeof(data[0])-1,'#');
TreeMirrorByLoop(root);
printf("\n先序遍歷:");
TreePreOrder(root);
printf("\n中序遍歷:");
TreeInOrder(root);
printf("\n後序遍歷:");
TreePostOrder(root);
printf("\n層序遍歷:");
TreeLevelOrder(root);
}執行結果:
5.判斷一個數是不是完全二叉樹
首先介紹一下什麼是完全二叉樹
完全二叉樹是由滿二叉樹而引出來的。對於深度為K的,有n個節點的二叉樹,當且僅當其每個節點都與深度為K的滿二叉樹中的編號從1至n的節點一一對應時稱之為完全二叉樹。
完全二叉樹具有以下的特點:
1)只允許最後一層有空缺節點且空缺在右邊,即葉子節點只能在層次最大的兩層上出現;
2)對任一節點,如果其右子樹的深度為j,則其左子樹的深度必為j或j+1,即度為1
的點只有1個或0個
實現程式碼:
int IsCompleteTree(TreeNode* root)
{
if(root == NULL)
{
return 0;
}
SeqQueue queue;
SeqQueueInit(&queue);
SeqQueuePush(&queue,root);
//是否要進入第二階段
int is_step_tow_flag = 0;
TreeNode* cur = NULL;
while(SeqQueueFront(&queue,&cur))
{
SeqQueuePop(&queue);
//階段一走這個分支
if(is_step_tow_flag == 0)
{
if(cur->lchild != NULL && cur->rchild != NULL)
{
//同時具備左右子樹
SeqQueuePush(&queue,cur->lchild);
SeqQueuePush(&queue,cur->rchild);
}
else if(cur->rchild != NULL && cur->lchild == NULL)
{
//只有右子樹,沒有左子樹,一定不是完全二叉樹
return 0;
}
else if(cur->rchild == NULL && cur->lchild != NULL)
{
//只有左子樹沒有右子樹,需要進入第二階段
is_step_tow_flag = 1;
SeqQueuePush(&queue,cur->lchild);
}
else
{
//沒有左右子樹
is_step_tow_flag = 1;
}
}
else
{
//階段二分支
if(cur->lchild == NULL && cur->rchild == NULL)
{
break;
}
else
{
return 0;
}
}//結束階段一和階段二的判定
}//迴圈結束
//所有節點都遍歷完了,此時是完全二叉樹
return 1;
}測試程式碼:
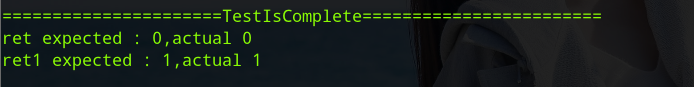
void TestIsComplete()
{
TEST_HEADER;
TreeNodeType data[] = "abd##eg###c#f##";
TreeNode* root = TreeCreate(data,sizeof(data)/sizeof(data[0])-1,'#');
int ret = IsCompleteTree(root);
printf("ret expected : 0,actual %d\n",ret);
TreeNodeType data1[] = "ab##c##";
TreeNode* root1 = TreeCreate(data1,sizeof(data1)/sizeof(data1[0])-1,'#');
int ret1 = IsCompleteTree(root1);
printf("ret1 expected : 1,actual %d\n",ret1);
}執行結果:
6.知道二叉樹的先序和中序的遍歷結果建立一個樹
實現程式碼:
size_t Find(TreeNodeType array[],size_t left,size_t right,TreeNodeType to_find)
{
size_t i = left;
for(;i < right ;++i)
{
if(array[i] == to_find)
{
return i;
}
}
return 0;
}
TreeNode* _TreeRebuild(TreeNodeType pre_order[],size_t pre_order_size,size_t* pre_order_index,\
TreeNodeType in_order[],size_t in_order_left,size_t in_order_right)
{
if(in_order_right >= in_order_left)
{
//無效區間內,當前子樹的中序遍歷結果就是空的,此時說明這棵子樹就是空樹
return NULL;
}
if(pre_order_index == NULL )
{
//非法輸入
return NULL;
}
if(*pre_order_index >= pre_order_size)
{
//遍歷完了
return NULL;
}
//根據先序遍歷結果取出當前值,基於這個值構建一個節點
//new_node相當於前子樹的根節點
TreeNode* new_node = CreateTreeNode(pre_order[*pre_order_index]);
//查詢一下當前節點在中序序列的位置
size_t cur_root_in_order_index = Find(in_order,in_order_left,in_order_right,new_node->data);
assert(cur_root_in_order_index != (size_t)-1);
++(*pre_order_index);
//左子樹區間[in_order_left,cur_root_in_order_index)
new_node->lchild = _TreeRebuild(pre_order,pre_order_size,pre_order_index,\
in_order,in_order_left,cur_root_in_order_index);
//右子樹區間[cur_root_in_order_index+1,in_order_right)
new_node->rchild = _TreeRebuild(pre_order,pre_order_size,pre_order_index,\
in_order,cur_root_in_order_index+1,in_order_right);
return new_node;
}
TreeNode* TreeRebuild(TreeNodeType pre_order[],TreeNodeType in_order[],size_t size)
{
size_t pre_order_index = 0;
//[in_order_left,in_order_right)
size_t in_order_left = 0;
size_t in_order_right = size;
return _TreeRebuild(pre_order,size,&pre_order_index,in_order,in_order_left,in_order_right);
}測試程式碼:
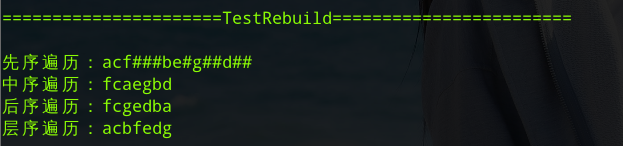
void TestRebuild()
{
TEST_HEADER;
TreeNodeType pre_order[] = "acfbegd";
TreeNodeType in_order[] = "fcaegbd";
TreeNode* root = TreeRebuild(pre_order,in_order,sizeof(pre_order)/sizeof(pre_order[0])-1);
printf("\n先序遍歷:");
TreePreOrder(root);
printf("\n中序遍歷:");
TreeInOrder(root);
printf("\n後序遍歷:");
TreePostOrder(root);
printf("\n層序遍歷:");
TreeLevelOrder(root);
printf("\n");
}執行結果: