kubernetes1.13.1部署ingress-nginx並配置https轉發dashboard
https://github.com/kubernetes/ingress-nginx https://www.jianshu.com/p/e30b06906b77 https://github.com/kubernetes/ingress-nginx/issues/2474 https://www.cnblogs.com/zhangeamon/p/7007076.html https://github.com/kubernetes/kubernetes/issues/45324 https://kubernetes.io/docs/reference/access-authn-authz/admission-controllers/ https://kubernetes.io/docs/reference/access-authn-authz/admission-controllers/#securitycontextdeny https://jimmysong.io/kubernetes-handbook/concepts/admission-controller.html https://github.com/kubernetes/ingress-nginx/issues/3608 https://blog.csdn.net/ygqygq2/article/details/82791101
簡介
Ingress
An API object that manages external access to the services in a cluster, typically HTTP.
Ingress can provide load balancing, SSL termination and name-based virtual hosting.
Terminology
- Node: A single virtual or physical machine in a Kubernetes cluster.
- Cluster: A group of nodes firewalled from the internet, that are the primary compute resources managed by Kubernetes.
- Edge router: A router that enforces the firewall policy for your cluster. This could be a gateway managed by a cloud provider or a physical piece of hardware.
- Cluster network: A set of links, logical or physical, that facilitate communication within a cluster according to the Kubernetes networking model.
- Service: A Kubernetes Service that identifies a set of pods using label selectors. Unless mentioned otherwise, Services are assumed to have virtual IPs only routable within the cluster network.
What is Ingress?
Ingress, added in Kubernetes v1.1, exposes HTTP and HTTPS routes from outside the cluster to services within the cluster. Traffic routing is controlled by rules defined on the ingress resource.
internet
|
[ Ingress ]
--|-----|--
[ Services ]An ingress can be configured to give services externally-reachable URLs, load balance traffic, terminate SSL, and offer name based virtual hosting. An ingress controller is responsible for fulfilling the ingress, usually with a loadbalancer, though it may also configure your edge router or additional frontends to help handle the traffic.
An ingress does not expose arbitrary ports or protocols. Exposing services other than HTTP and HTTPS to the internet typically uses a service of type Service.Type=NodePort or Service.Type=LoadBalancer.
Prerequisites
FEATURE STATE: Kubernetes v1.1 beta
Before you start using an ingress, there are a few things you should understand. The ingress is a beta resource. You will need an ingress controller to satisfy an ingress, simply creating the resource will have no effect.
GCE/Google Kubernetes Engine deploys an ingress controller on the master. Review the beta limitations of this controller if you are using GCE/GKE.
In environments other than GCE/Google Kubernetes Engine, you may need to deploy an ingress controller. There are a number of ingress controller you may choose from.
Ingress controllers
In order for the ingress resource to work, the cluster must have an ingress controller running. This is unlike other types of controllers, which run as part of the kube-controller-manager binary, and are typically started automatically with a cluster. Choose the ingress controller implementation that best fits your cluster.
Kubernetes as a project currently supports and maintains GCE and nginx controllers.
Additional controllers include:
Contour is an Envoy based ingress controller provided and supported by Heptio.
F5 Networks provides support and maintenance for the F5 BIG-IP Controller for Kubernetes.
HAProxy based ingress controller jcmoraisjr/haproxy-ingress which is mentioned on the blog post HAProxy Ingress Controller for Kubernetes. HAProxy Technologies offers support and maintenance for HAProxy Enterprise and the ingress controller jcmoraisjr/haproxy-ingress.
Istio based ingress controller Control Ingress Traffic.
Kong offers community or commercial support and maintenance for the Kong Ingress Controllerfor Kubernetes.
NGINX, Inc. offers support and maintenance for the NGINX Ingress Controller for Kubernetes.
Traefik is a fully featured ingress controller (Let’s Encrypt, secrets, http2, websocket), and it also comes with commercial support by Containous.
You may deploy any number of ingress controllers within a cluster. When you create an ingress, you should annotate each ingress with the appropriate ingress-class to indicate which ingress controller should be used if more than one exists within your cluster. If you do not define a class, your cloud provider may use a default ingress provider.
官網部署方法
https://github.com/kubernetes/ingress-nginx/blob/master/docs/deploy/index.md
kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kubernetes/ingress-nginx/master/deploy/mandatory.yaml
kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kubernetes/ingress-nginx/master/deploy/provider/cloud-generic.yaml部署ingress-controller
[root@elasticsearch01 ingree-nginx]# kubectl create -f mandatory.yaml
namespace/ingress-nginx created
configmap/nginx-configuration created
configmap/tcp-services created
configmap/udp-services created
serviceaccount/nginx-ingress-serviceaccount created
clusterrole.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/nginx-ingress-clusterrole created
role.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/nginx-ingress-role created
rolebinding.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/nginx-ingress-role-nisa-binding created
clusterrolebinding.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/nginx-ingress-clusterrole-nisa-binding created
deployment.extensions/nginx-ingress-controller created報錯
Error creating: pods "nginx-ingress-controller-565dfd6dff-g977n" is forbidden: SecurityContext.RunAsUser is forbidden
排錯
需要對準入控制器進行修改,然後重啟apiserver
--enable-admission-plugins=NamespaceLifecycle,LimitRanger,ServiceAccount,ResourceQuota,NodeRestriction \
SecurityContextDeny 不enable就行
[root@elasticsearch01 ingree-nginx]# vim /k8s/kubernetes/cfg/kube-apiserver
[root@elasticsearch01 ingree-nginx]# systemctl restart kube-apiserver.service
[root@elasticsearch01 ingree-nginx]# systemctl status kube-apiserver.service
● kube-apiserver.service - Kubernetes API Server
Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/kube-apiserver.service; enabled; vendor preset: disabled)
Active: active (running) since Mon 2019-01-07 11:30:07 CST; 7s ago
Docs: https://github.com/kubernetes/kubernetes
Main PID: 12796 (kube-apiserver)
CGroup: /system.slice/kube-apiserver.service
└─12796 /k8s/kubernetes/bin/kube-apiserver --logtostderr=true --v=4 --etcd-servers=https://10.2.8.44:2379,https://10.2....檢查狀態
[root@elasticsearch01 ingree-nginx]# kubectl get pods -n ingress-nginx
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
pod/nginx-ingress-controller-565dfd6dff-vj52t 1/1 Running 0 2m36s部署svc
[root@elasticsearch01 ingree-nginx]# kubectl create -f cloud-generic.yaml
service/ingress-nginx created
[root@elasticsearch01 ingree-nginx]# kubectl get svc -n ingress-nginx
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
ingress-nginx LoadBalancer 10.254.156.80 <pending> 80:40133/TCP,443:36517/TCP 12s
測試功能
之前dashboard是通過nodeport暴露,現在使用ingress方式,註意ingress後端是https,需要添加如下配置
宣告annotations
apiVersion: extensions/v1beta1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
annotations:
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/ingress.class: nginx
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/secure-backends: "true"
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/ssl-passthrough: "true"生成ingress-secret證書
[root@elasticsearch01 ingress-nginx]# kubectl -n kube-system create secret tls ingress-secret --key /certs/dashboard.key --cert /certs/dashboard.crt
secret/ingress-secret created創建ingress服務
[root@elasticsearch01 ~]# cat /k8s/yaml/ingress-nginx/k8s.yaml
apiVersion: extensions/v1beta1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: dashboard-ingress
namespace: kube-system
annotations:
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/ingress.class: nginx
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/secure-backends: "true"
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/ssl-passthrough: "true"
spec:
tls:
- hosts:
- dashboard.minminmsn.com
secretName: ingress-secret
rules:
- host: dashboard.minminmsn.com
http:
paths:
- path: /
backend:
serviceName: kubernetes-dashboard
servicePort: 443
[root@elasticsearch01 ingree-nginx]# kubectl create -f k8s.yaml
ingress.extensions/dashboard-ingress created[root@elasticsearch01 ingree-nginx]# kubectl get ingress -n ingress-nginx
NAME HOSTS ADDRESS PORTS AGE
dashboard-ingress dashboard.zhidaoauto.com 80 2m51s
[root@elasticsearch01 ingree-nginx]# kubectl describe ingress dashboard-ingress -n ingress-nginx
Name: dashboard-ingress
Namespace: ingress-nginx
Address:
Default backend: default-http-backend:80 (<none>)
Rules:
Host Path Backends
---- ---- --------
dashboard.zhidaoauto.com
kubernetes-dashboard:443 (10.254.73.2:8443)
Annotations:
ingress.kubernetes.io/ssl-passthrough: true
Events:
Type Reason Age From Message
---- ------ ---- ---- -------
Normal CREATE 3m3s nginx-ingress-controller Ingress ingress-nginx/dashboard-ingress
Normal CREATE 3m3s nginx-ingress-controller Ingress ingress-nginx/dashboard-ingress網頁瀏覽
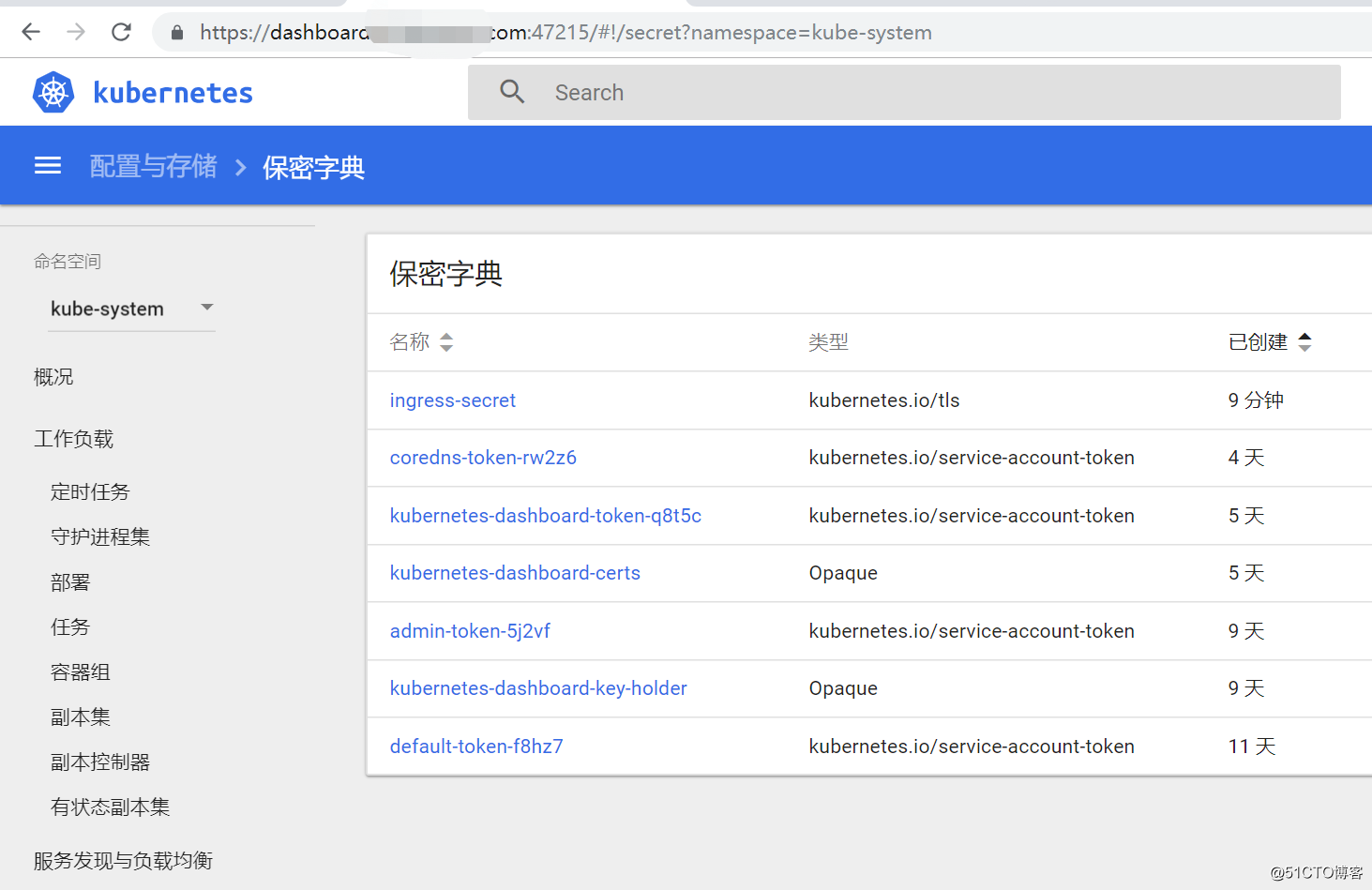
集群內部訪問直接https://dashboard.minminmsn.com 即可;集群外部訪問需要獲取對外端口47215,另外需要設置dns解析,訪問時同樣需要輸入token
[root@elasticsearch01 ~]# kubectl get svc -n ingress-nginx
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
ingress-nginx LoadBalancer 10.254.125.151 <pending> 80:33003/TCP,443:47215/TCP 16m
訪問效果如下
補充
準入控制器
To see which admission plugins are enabled:
kube-apiserver -h | grep enable-admission-plugins
In 1.13, they are:
NamespaceLifecycle,LimitRanger,ServiceAccount,PersistentVolumeClaimResize,DefaultStorageClass,DefaultTolerationSeconds,MutatingAdmissionWebhook,ValidatingAdmissionWebhook,ResourceQuota,Priority
LimitRanger:此準入控制器將確保所有資源請求不會超過 namespace 的 LimitRange。
SecurityContextDeny:此準入控制器將拒絕任何試圖設置某些升級的SecurityContext字段的pod 。
ServiceAccount:此準入控制器實現serviceAccounts的自動化。
ResourceQuota:此準入控制器將觀察傳入請求並確保它不違反命名空間的ResourceQuota對象中列舉的任何約束。
NodeRestriction:該準入控制器限制了 kubelet 可以修改的Node和Pod對象。
NamespaceExists:此許可控制器檢查除 Namespace 其自身之外的命名空間資源上的所有請求。如果請求引用的命名空間不存在,則拒絕該請求。
NamespaceLifecycle:此準入控制器強制執行正在終止的命令空間中不能創建新對象,並確保Namespace拒絕不存在的請求。此準入控制器還防止缺失三個系統保留的命名空間default、kube-system、kube-public。
kubernetes1.13.1部署ingress-nginx並配置https轉發dashboard