<泛> C++3D數學庫設計詳解 簡單光學幾何 && 隨機向量生成
// 注:本內容為作者原創,禁止在其他網站複述內容以及用於商業盈利,如需引用,請標明出處:http://www.cnblogs.com/lv_anchoret/
Preface
當初寫這個庫,是為了支援光線追蹤的學習,所以,學完第一本書,這時候,我們整合一些物理光學方面的運算,封裝到我們的泛型庫裡面
新庫增加的目錄:
--lvgm
----opticsfunc.hpp
----randfunc.cpp
Ready
需要大家擁有之前的向量庫做支援
我們這一篇涉及到的庫檔案比較少
我們這一篇涉及到的基本是函式
據說,寫庫一般用hpp比較好,所以我們開始用hpp寫C++泛型庫
theory
1.反射
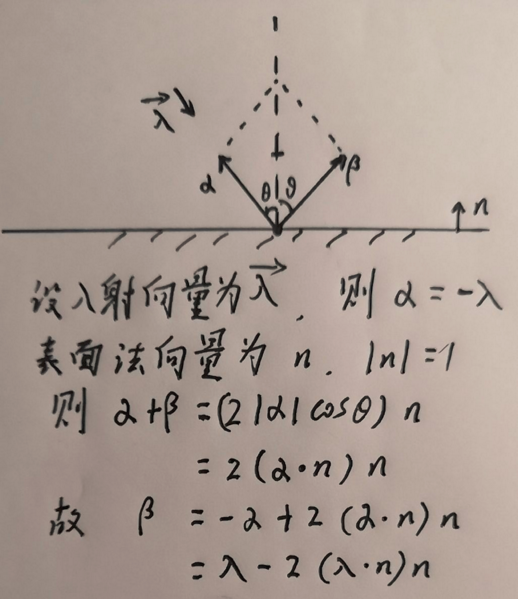
2.折射
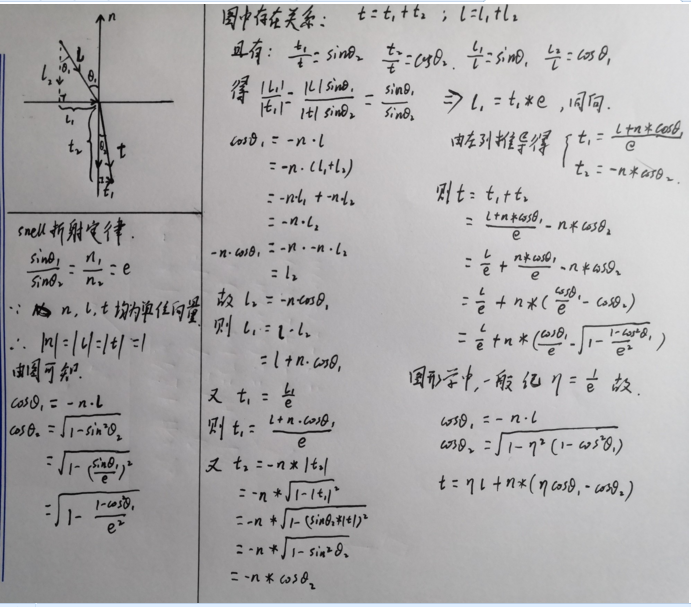
公式中的η為相對摺射率:n2/n1
而由於入射光線方向的隨機性和eta的不同,可能導致 1-η*η*(1-cosθ1 * cosθ1)小於0,此時取根號毫無意義
而事實上,這也就是全反射現象。即:當光線從光密介質進入光疏介質中如果入射角大於某個臨界值的時候,就會發生全反射現象。
該臨界角即折射角為90°時對應的入射角,也就是cosθ2恰好等於0的時候
完整工程應用見https://www.cnblogs.com/lv-anchoret/p/10217719.html
3.單位球體內部隨機向量
根據一個完全隨機演算法,確保生成一個0~1的隨機數,用這樣的三個隨機數構建一個三維向量t
設 β = 2 * t - (1,1,1)
即保證了β的每一個分量均隨機分佈於0~1
這樣的話,我們的向量β就等於時一個單位正方體之內的存在,而我們需要的是單位球體
所以,我們篩出單位球體外的,通過x^2 + y^2 + z^2 >= 1.0 式(a) 篩掉球體之外的
如果β = (x,y,z),也就是式(a)也就等價於 β·β >= 1.0
4.單位圓盤內的隨機向量
和上面一樣,減少一維即可
/// opticsfunc.hpp // ----------------------------------------------------- // [author] lv // [ time ] 2019.1 // [brief ] optics functions // reflect // refract // ----------------------------------------------------- #pragma once #include <lvgm\type_vec\type_vec.h> namespace lvgm { /* @in: the Incident light @n: the Surface normal @ret: the reflected light */ template<typename T> const T reflect(const T& in, const T& n) { return in - 2 * dot(in, n)*n; } /* @in: the Incident light @n: the Surface normal @eta: the Refractive indices @ret: if it has a refracted light or not */ template<typename T> const bool refract(const T& in, const T& n, lvgm::precision eta, T& refracted) { if (typeid(T) == typeid(lvgm::vec2<int>)) { cerr < "the refract is adapted to float and percision-upper\n"; return false; } T unitIn = in.ret_unitization(); //將入射光線單位化 lvgm::precision cos1 = dot(-unitIn, n); lvgm::precision cos2 = 1. - eta*eta*(1. - cos1*cos1); if (cos2 > 0) { refracted = eta * unitIn + n * (eta * cos1 - std::sqrt(cos2)); return true; } return false; } }
/// randfunc.hpp // ----------------------------------------------------- // [author] lv // [ time ] 2019.1 // [brief ] random functions // rand01 // random_unit_sphere // random_unit_plane // ----------------------------------------------------- #pragma once #include <lvgm\type_vec\type_vec.h> #include <random> namespace lvgm { //@brief: create a random number that from 0 to 1 completely template<typename T = lvgm::precision> const T rand01() { if (typeid(T) == typeid(int)) { std::cerr << "integer doesn't have a random number from 0 to 1\n"; throw "integer doesn't have a random number from 0 to 1\n"; } std::mt19937 mt; std::uniform_real_distribution<T> r; return r(mt); } //@brief: find a random point in unit_ball template<typename T = lvgm::precision> const lvgm::vec3<T> random_unit_sphere() { if (typeid(T) == typeid(int)) { std::cerr << "integer doesn't have a random number from 0 to 1\n"; throw "integer doesn't have a random number from 0 to 1\n"; } lvgm::vec3<T> p; do { p = 2.0*lvgm::vec3<T>(rand01(), rand01(), rand01()) - lvgm::vec3<T>(1, 1, 1); } while (dot(p, p) >= 1.0); return p; } //@brief: find a random point in unit_plane template<typename T = lvgm::precision> const lvgm::vec2<T> random_unit_plane() { if (typeid(T) == typeid(int)) { std::cerr << "integer doesn't have a random number from 0 to 1\n"; throw "integer doesn't have a random number from 0 to 1\n"; } lvgm::vec2<T> p; do { p = 2.0*lvgm::vec2<T>(rand01(), rand01()) - lvgm::vec2<T>(1, 1); } while (dot(p, p) >= 1.0); return p; } }
感謝您的閱讀,生活愉快~
