MySQL初步學習4:處理大資料物件
阿新 • • 發佈:2019-01-09
大資料物件這裡主要指CLOB和BLOB兩種型別的欄位。
CLOB可以儲存文字資料,而BLOB中可以儲存二進位制資料,如圖片,電影等。而程式中處理這些大物件資料,必須呼叫PreparedStatement完成,所有的內容以IO流的方式從大文字欄位中儲存和讀取。
PreparedStatement類中提供了兩種方法寫入資料
setAsciiStream():文字輸入
setBinaryStream():二進位制輸入
另外,有幾種讀取資料方式:
getAsciiStream() 獲取文字輸出流
getBinaryStream() 獲取二進位制輸出流
getClob()
getBlob() 獲取BLOB資料
1、處理CLOB資料
Clob表示大文字資料,在MySQL中有longtext表示大文字型別,最大儲存4G資料。
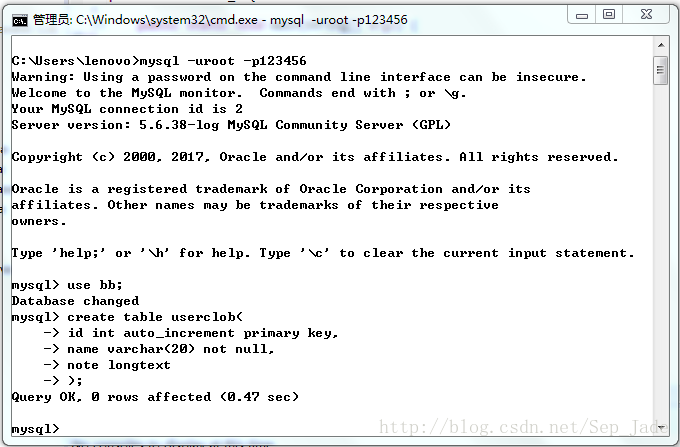
首先在資料庫bb中建表如下:
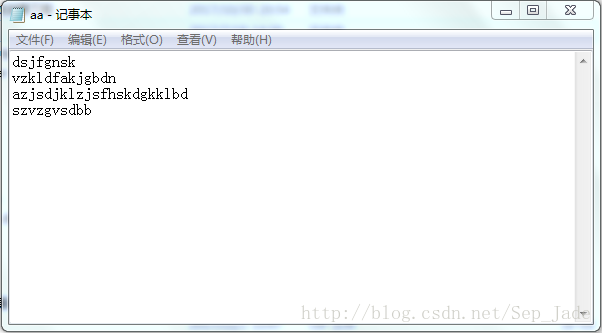
文字文件aa存放路徑在”d:\aa.txt”,文字內容:
在eclipse中寫入大文字資料
package fileOperation;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.sql.*;
public 讀取大文字資料
package fileOperation;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.sql.*;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class CLOB_2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
Connection con=null;
PreparedStatement ps=null;
ResultSet rs=null;
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
con=DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/bb","root","123456");
ps=con.prepareStatement(" select name,note from userclob where id=? ");
ps.setInt(1,1);
rs=ps.executeQuery();
while (rs.next()) {
String name=rs.getString(1);
StringBuffer note=new StringBuffer();
InputStream input = rs.getAsciiStream(2);//接收全部大文字資料
Scanner scan=new Scanner(input);
scan.useDelimiter("\r\n"); //將檔案換行作為分隔符
while(scan.hasNext()) {
note.append(scan.next()).append("\n"); //不斷讀取資料
}
System.out.println("內容為"+note);
System.out.println("*****************************************************************");
Clob c=rs.getClob(2);
String note1=c.getSubString(1, (int) c.length());
System.out.println("內容為"+note);
c.truncate(10); //讀取10個長度的內容
System.out.println("讀取部分內容: "+c.getSubString(1, (int)c.length()) );
//可以看到,兩種方法均可以讀取檔案中的內容,而下面的這種方法更為簡單
}
rs.close();
ps.close();
con.close();
}
}結果如下:
內容為dsjfgnsk
vzkldfakjgbdn
azjsdjklzjsfhskdgkklbd
szvzgvsdbb
*****************************************************************
內容為dsjfgnsk
vzkldfakjgbdn
azjsdjklzjsfhskdgkklbd
szvzgvsdbb
讀取部分內容: dsjfgnsk可以看到,用CLOB讀取資料更加簡潔。
2、處理BLOB物件
BLOB操作與CLOB相似,專門用於存放二進位制資料,如電影、圖片等。在MySQL中定義了longblob型別變數,最高可以存放4G資料。
在資料庫建表userblob,方法和上面一樣。
將圖片寫入到資料表中
用到的圖片存放到d盤:

在eclipse中程式設計:
package fileOperation;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.sql.Clob;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class BLOB_1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
Connection con=null;
PreparedStatement ps=null; //必須用預處理語句讀取資料
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
con=DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/bb","root","123456");
ps=con.prepareStatement(" insert into userblob (name,photo) values (?,?) ");
File f=new File("d:"+File.separator+"11.gif"); //File.separator表示分隔符
InputStream input=new FileInputStream(f);
ps.setString(1, "bb");
ps.setBinaryStream(2,input,(int)f.length());
ps.executeUpdate();
ps.close();
con.close();
}
}
新建一個圖片,內容為空,儲存在d盤,用於接收資料(也可以程式建立,如下一個例子)。讀取內容,將圖片資訊儲存。
package fileOperation;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.sql.*;
public class BLOB_2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
Connection con=null;
PreparedStatement ps=null;
ResultSet rs=null;
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
con=DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/bb","root","123456");
ps=con.prepareStatement(" select name,photo from userblob where id = ? ");
ps.setInt(1, 1);
rs=ps.executeQuery();
while(rs.next()) {
String name = rs.getString(1);
InputStream input =rs.getBinaryStream(2);
FileOutputStream output = new FileOutputStream(new File("d:"+File.separator+"12.gif"));
int temp=0;
while((temp=input.read())!=-1) {
output.write(temp);
}
input.close();
output.close();
}
rs.close();
ps.close();
con.close();
}
}
使用BLOB讀取內容,更加簡單:
package fileOperation;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.sql.*;
public class BLOB_3 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
Connection con=null;
PreparedStatement ps=null;
ResultSet rs=null;
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
con=DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/bb","root","123456");
ps=con.prepareStatement(" select name,photo from userblob where id = ? ");
ps.setInt(1, 1);
rs=ps.executeQuery();
while(rs.next()) {
String name = rs.getString(1);
Blob b=rs.getBlob(2);
File f=new File("d:"+File.separator+"13.gif");
if(f.exists()) {
f.delete();
}
else
{
f.createNewFile();
}
FileOutputStream output = new FileOutputStream(new File("d:"+File.separator+"13.gif"));
output.write(b.getBytes(1, (int) b.length()));
output.close();
}
rs.close();
ps.close();
con.close();
}
}