資料結構和演算法——Huffman樹和Huffman編碼
Huffman樹是一種特殊結構的二叉樹,由Huffman樹設計的二進位制字首編碼,也稱為Huffman編碼在通訊領域有著廣泛的應用。在word2vec模型中,在構建層次Softmax的過程中,也使用到了Huffman樹的知識。
在通訊中,需要將傳輸的文字轉換成二進位制的字串,假設傳輸的報文為:“AFTERDATAEARAREARTAREA”,現在需要對該報文進行編碼。
一、Huffman樹的基本概念
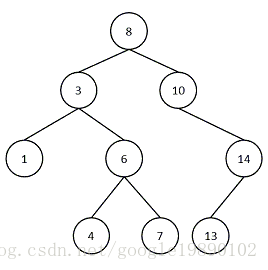
在二叉樹中有一些基本的概念,對於如下所示的二叉樹:
- 路徑
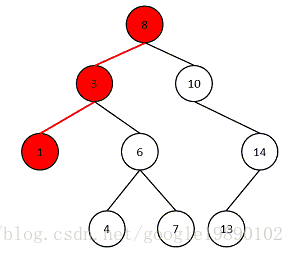
路徑是指在一棵樹中,從一個節點到另一個節點之間的分支構成的通路,如從節點8到節點1的路徑如下圖所示:
- 路徑長度
路徑長度指的是路徑上分支的數目,在上圖中,路徑長度為2。
- 節點的權
節點的權指的是為樹中的每一個節點賦予的一個非負的值,如上圖中每一個節點中的值。
- 節點的帶權路徑長度
節點的帶權路徑長度指的是從根節點到該節點之間的路徑長度與該節點權的乘積:如對於1節點的帶權路徑長度為:2。
- 樹的帶權路徑長度
樹的帶權路徑長度指的是所有葉子節點的帶權路徑長度之和。
有了如上的概念,對於Huffman樹,其定義為:
給定
n 權值作為n 個葉子節點,構造一棵二叉樹,若這棵二叉樹的帶權路徑長度達到最小,則稱這樣的二叉樹為最優二叉樹,也稱為Huffman樹。
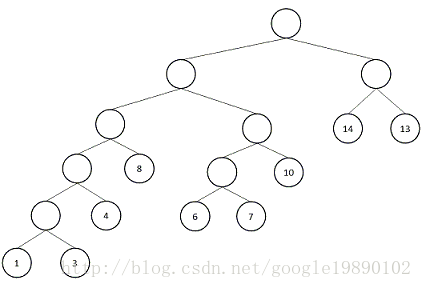
由以上的定義可以知道,Huffman樹是帶權路徑長度最小的二叉樹,對於上面的二叉樹,其構造完成的Huffman樹為:
二、Huffman樹的構建
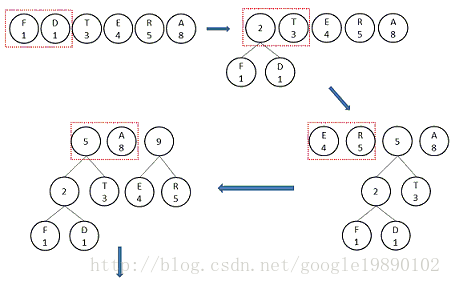
由上述的Huffman樹可知:節點的權越小,其離樹的根節點越遠。那麼應該如何構建Huffman樹呢?以上述報文為例,首先需要統計出每個字元出現的次數作為節點的權:
接下來構建Huffman樹:
- 重複以下的步驟:
- 按照權值對每一個節點排序:D-F-T-E-R-A
- 選擇權值最小的兩個節點,此處為D和F生成新的節點,節點的權重為這兩個節點的權重之和,為2
- 直到只剩最後的根節點
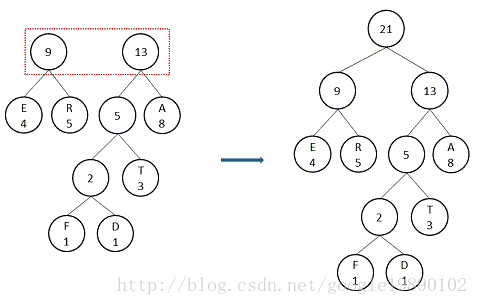
按照上述的步驟,該報文的Huffman樹的生成過程為:
對於樹中節點的結構為:
#define LEN 512
struct huffman_node{
char 對於Huffman樹的構建過程為:
int huffman_tree_create(huffman_node *&root, map<char, int> &word){
char line[MAX_LINE];
vector<huffman_node *> huffman_tree_node;
map<char, int>::iterator it_t;
for (it_t = word.begin(); it_t != word.end(); it_t++){
// 為每一個節點申請空間
huffman_node *node = (huffman_node *)malloc(sizeof(huffman_node));
node->c = it_t->first;
node->weight = it_t->second;
node->left = NULL;
node->right = NULL;
huffman_tree_node.push_back(node);
}
// 開始從葉節點開始構建Huffman樹
while (huffman_tree_node.size() > 0){
// 按照weight升序排序
sort(huffman_tree_node.begin(), huffman_tree_node.end(), sort_by_weight);
// 取出前兩個節點
if (huffman_tree_node.size() == 1){// 只有一個根結點
root = huffman_tree_node[0];
huffman_tree_node.erase(huffman_tree_node.begin());
}else{
// 取出前兩個
huffman_node *node_1 = huffman_tree_node[0];
huffman_node *node_2 = huffman_tree_node[1];
// 刪除
huffman_tree_node.erase(huffman_tree_node.begin());
huffman_tree_node.erase(huffman_tree_node.begin());
// 生成新的節點
huffman_node *node = (huffman_node *)malloc(sizeof(huffman_node));
node->weight = node_1->weight + node_2->weight;
(node_1->weight < node_2->weight)?(node->left=node_1,node->right=node_2):(node->left=node_2,node->right=node_1);
huffman_tree_node.push_back(node);
}
}
return 0;
}其中,map結構的word為每一個字元出現的頻率,是從檔案中解析出來的,解析的程式碼為:
int read_file(FILE *fn, map<char, int> &word){
if (fn == NULL) return 1;
char line[MAX_LINE];
while (fgets(line, 1024, fn)){
fprintf(stderr, "%s\n", line);
//解析,統計詞頻
char *p = line;
while (*p != '\0' && *p != '\n'){
map<char, int>::iterator it = word.find(*p);
if (it == word.end()){// 不存在,插入
word.insert(make_pair(*p, 1));
}else{
it->second ++;
}
p ++;
}
}
return 0;
}當構建好Huffman樹後,我們分別利用先序遍歷和中序遍歷去遍歷Huffman樹,先序遍歷的程式碼為:
void print_huffman_pre(huffman_node *node){
if (node != NULL){
fprintf(stderr, "%c\t%d\n", node->c, node->weight);
print_huffman_pre(node->left);
print_huffman_pre(node->right);
}
}中序遍歷的程式碼為:
void print_huffman_in(huffman_node *node){
if (node != NULL){
print_huffman_in(node->left);
fprintf(stderr, "%c\t%d\n", node->c, node->weight);
print_huffman_in(node->right);
}
}得到的結構與上圖中的結構一致。
三、由Huffman樹生成Huffman編碼
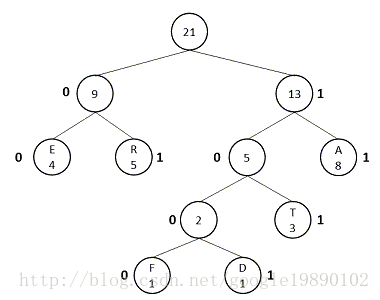
有了上述的Huffman樹的結構,現在我們需要利用Huffman樹對每一個字元編碼,該編碼又稱為Huffman編碼,Huffman編碼是一種字首編碼,即一個字元的編碼不是另一個字元編碼的字首。在這裡約定:
- 將權值小的最為左節點,權值大的作為右節點
- 左孩子編碼為0,右孩子編碼為1
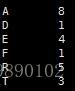
因此,上述的編碼形式如下圖所示:
從上圖中,E節點的編碼為:00,同理,D節點的編碼為1001
Huffman編碼的實現過程為:
int get_huffman_code(huffman_node *&node){
if (node == NULL) return 1;
// 利用層次遍歷,構造每一個節點
huffman_node *p = node;
queue<huffman_node *> q;
q.push(p);
while(q.size() > 0){
p = q.front();
q.pop();
if (p->left != NULL){
q.push(p->left);
strcpy((p->left)->huffman_code, p->huffman_code);
char *ptr = (p->left)->huffman_code;
while (*ptr != '\0'){
ptr ++;
}
*ptr = '0';
}
if (p->right != NULL){
q.push(p->right);
strcpy((p->right)->huffman_code, p->huffman_code);
char *ptr = (p->right)->huffman_code;
while (*ptr != '\0'){
ptr ++;
}
*ptr = '1';
}
}
return 0;
}利用上述的程式碼,測試的主函式為:
int main(){
// 讀檔案
FILE *fn = fopen("huffman", "r");
huffman_node *root = NULL;
map<char, int> word;
read_file(fn, word);
huffman_tree_create(root, word);
fclose(fn);
fprintf(stderr, "pre-order:\n");
print_huffman_pre(root);
fprintf(stderr, "in-order:\n");
print_huffman_in(root);
get_huffman_code(root);
fprintf(stderr, "the final result:\n");
print_leaf(root);
destory_huffman_tree(root);
return 0;
}print_leaf函式用於打印出每個葉節點的Huffman編碼,其具體實現為:
void print_leaf(huffman_node *node){
if (node != NULL){
print_leaf(node->left);
if (node->left == NULL && node->right == NULL) fprintf(stderr, "%c\t%s\n", node->c, node->huffman_code);
print_leaf(node->right);
}
}destory_huffman_tree函式用於銷燬Huffman樹,其具體實現為:
void destory_huffman_tree(huffman_node *node){
if (node != NULL){
destory_huffman_tree(node->left);
destory_huffman_tree(node->right);
free(node);
node = NULL;
}
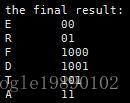
}其最終的結果為:
參考文獻
- 《大話資料結構》
- 《資料結構》(C語言版)